La estomatitis es un término general que se refiere a la inflamación de las membranas mucosas de la boca, que puede incluir a las llagas. La estomatitis puede estar causada por infecciones, trastornos autoinmunes, reacciones alérgicas o exposición a sustancias irritantes. La presentación típica puede ser solitaria o con un grupo de lesiones orales dolorosas. La etiología de la lesión se diagnostica basándose en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la apariencia y los LOS Neisseria síntomas asociados. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el alivio sintomático, pero las causas infecciosas pueden requerir antivirales/antibióticos y las etiologías autoinmunes pueden requerir terapia con esteroides.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La estomatitis, a veces llamada mucositis Mucositis Stomatitis is a general term referring to inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth, which may include sores. Stomatitis can be caused by infections, autoimmune disorders, allergic reactions, or exposure to irritants. The typical presentation may be either solitary or a group of painful oral lesions. Stomatitis, es un término amplio que hace HACE Altitude Sickness referencia a las lesiones inflamatorias de la mucosa oral de diversas etiologías.
Dada la variedad de las etiologías, una historia clínica y un examen físico cuidadosos son esenciales para afinar el diagnóstico. Las pruebas de laboratorio pueden confirmar los LOS Neisseria hallazgos y la sospecha clínica.
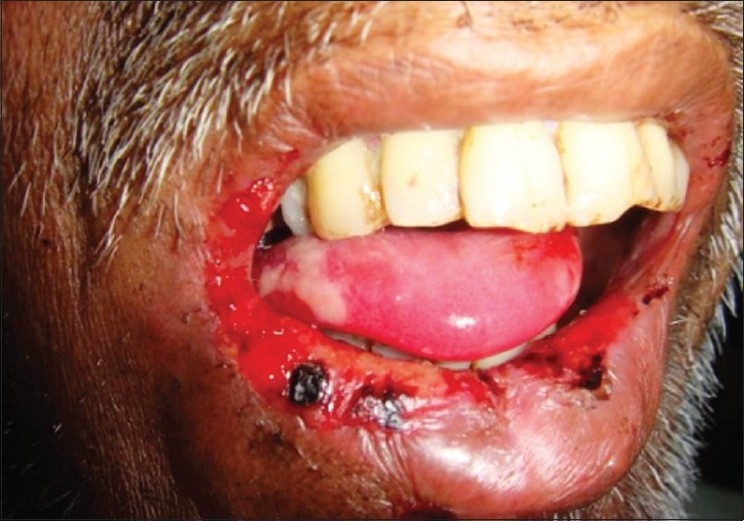
Mucositis oral en un paciente sometido a radioterapia
Imagen: “Radiation induced oral mucositis” por Ps SK, Balan A, Sankar A, Bose T. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El tratamiento se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum medidas de soporte, la reducción del dolor Dolor Inflammation y la prevención de la infección secundaria de la mucosa oral expuesta mientras se trata la causa subyacente.