La enfermedad hepática alcohólica es un espectro de trastornos que van desde el hígado graso hasta la cirrosis secundaria al AL Amyloidosis abuso crónico de alcohol. El consumo excesivo y prolongado de alcohol da como resultado el deterioro de la vía de la lipólisis, lo que provoca cambios inflamatorios dentro de los LOS Neisseria hepatocitos. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes típicamente se presentan durante la etapa de hepatitis con ictericia, fiebre y dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum antecedentes de abuso de alcohol y se confirma mediante un trastorno de laboratorio con una relación aspartato aminotransferasa/alanina aminotransferasa ( AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests/ ALT ALT An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of l-alanine and 2-oxoglutarate to pyruvate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests) > 2. La enfermedad hepática alcohólica conlleva una alta tasa de mortalidad si los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan hepatitis grave. El tratamiento requiere la abstinencia de alcohol para revertirla ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ciertas etapas) y abordar los LOS Neisseria factores contribuyentes (como infecciones virales o medicamentos) para minimizar el daño a los LOS Neisseria hepatocitos. Aproximadamente el 10% de los LOS Neisseria casos revierten con la abstinencia de alcohol durante la etapa de hepatitis. La cirrosis es frecuentemente irreversible.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad hepática alcohólica abarca la esteatosis alcohólica (hígado graso, reversible), la esteatohepatitis (puede ser reversible) y la cirrosis (irreversible). Todas secundarias al AL Amyloidosis abuso de alcohol.
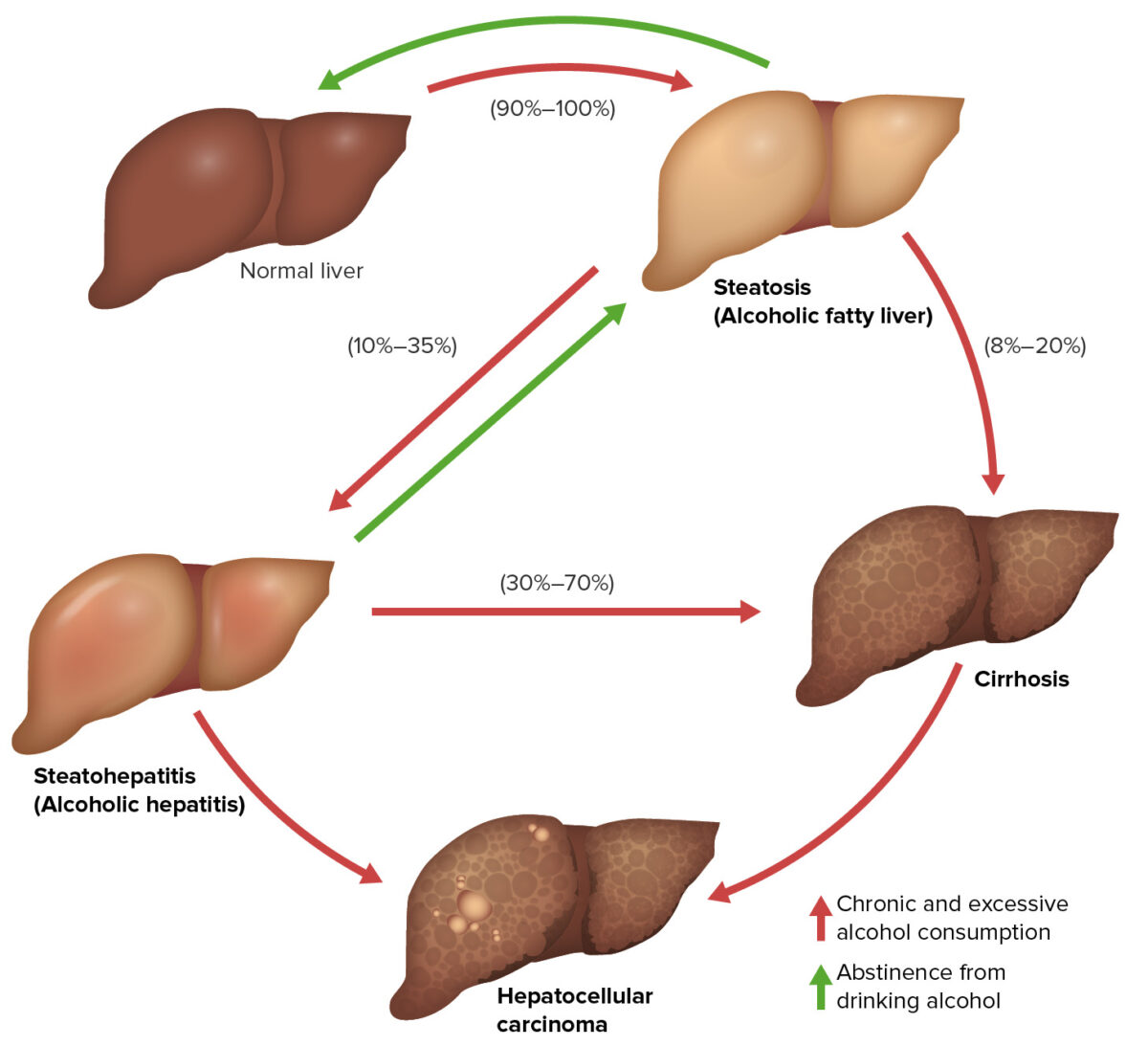
Las 3 etapas de la enfermedad hepática alcohólica:
Estas 3 etapas de la enfermedad hepática alcohólica pueden superponerse y no necesariamente ocurren en secuencia: hígado graso alcohólico (reversible), hepatitis alcohólica (reversible si se suspende el alcohol) y cirrosis relacionada con el alcohol (irreversible). También son factores de riesgo para desarrollar carcinoma hepatocelular.
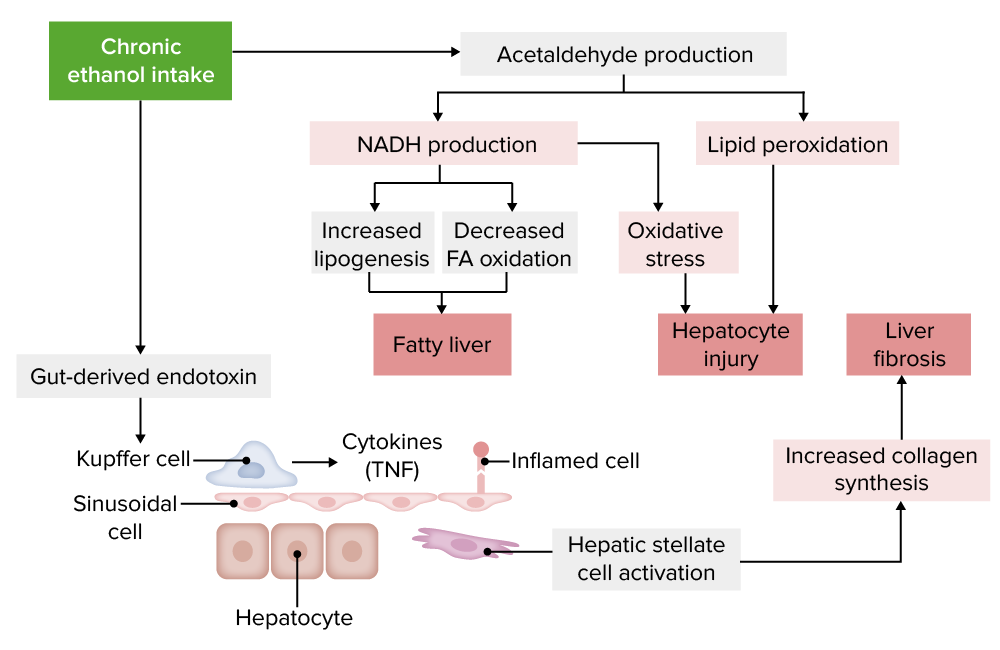
Fisiopatología de la enfermedad hepática alcohólica:
AF: ácido graso; TNF: factor de necrosis tumoral
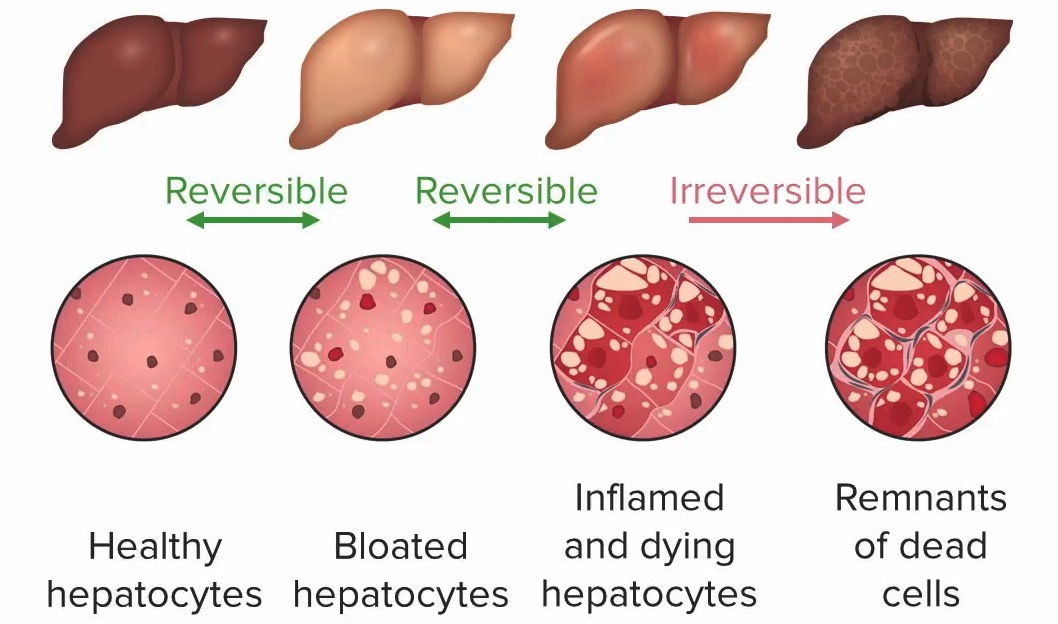
Progresión del daño hepático en la enfermedad hepática alcohólica (de izquierda a derecha):
1. Hepatocitos sanos (sin daño hepático)
2. Hepatocitos abultados con esteatosis (distendidos por gotas de grasa), sin inflamación: esteatosis (daño hepático aún reversible)
3. Hepatocitos inflamados y moribundos, posible fibrosis: hepatitis (daño hepático aún reversible)
4. Células muertas: cirrosis (daño hepático irreversible)
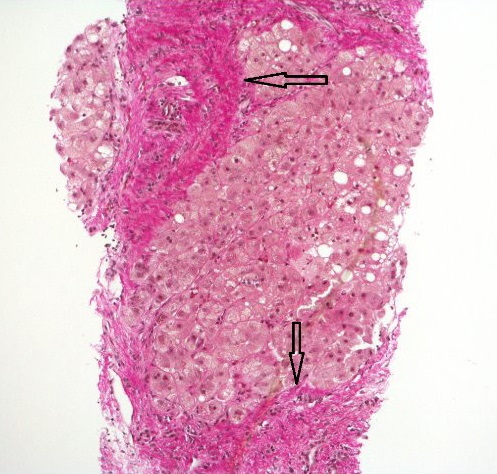
Esteatohepatitis con cirrosis establecida; bandas gruesas de fibrosis (flechas) que rodean un nódulo de hepatocitos
Imagen: “Hematoxylin and Van Gieson’s stain” por Alexander Boyd et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0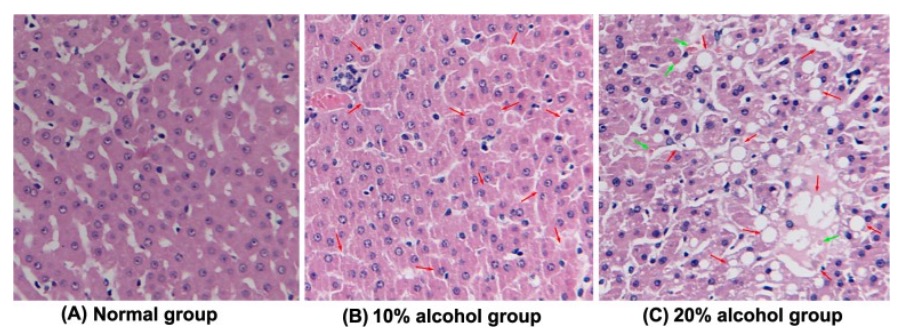
Esteatosis inducida por alcohol (características histológicas en secciones de hígado):
(A): grupo control normal
(B): hígado graso inducido por alcohol al 10% con macrovesículas (indicadas por una punta de flecha) de hepatocitos
(C): hígado graso inducido por alcohol al 20% con macrovesículas (indicadas por una flecha roja) de hepatocitos clasificados como altos en el grupo de enfermedad de hígado graso alcohólico. La flecha verde representa la formación de cuerpos de Mallory.
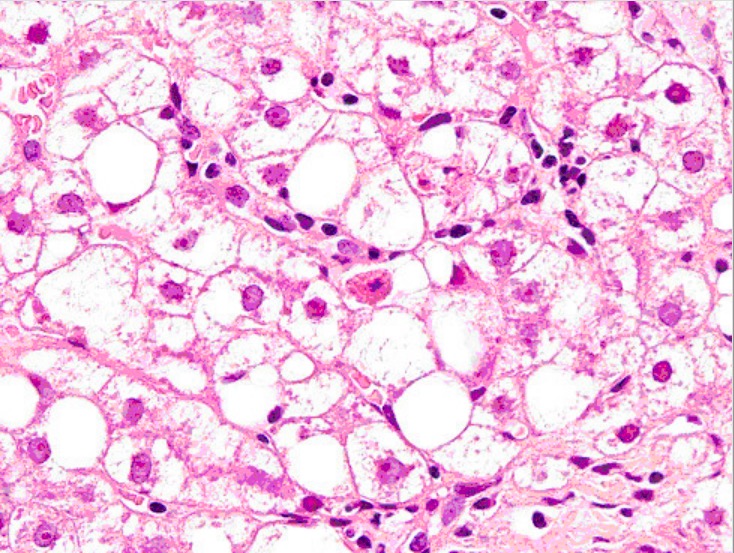
Biopsia hepática que muestra cuerpos de Mallory, esteatosis de gotas grandes y neutrófilos
Imagen: “Liver biopsy” por Institute of Infectious and Tropical Diseases, University of Brescia, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0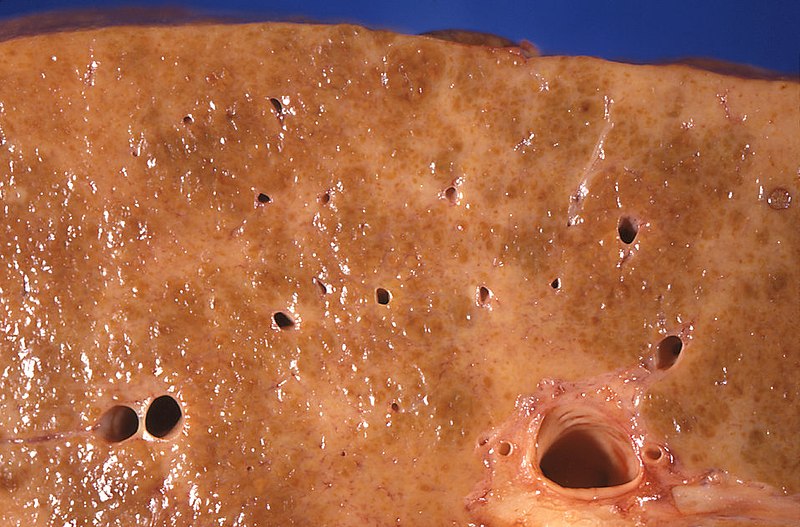
Patología macroscópica de la cirrosis hepática alcohólica: la superficie de corte muestra áreas con palidez difusa debido a una densa red de tejido cicatricial.
Imagen: “Gross pathology of alcoholic liver cirrhosis” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Dr. Edwin P. Ewing, Jr. Licencia: CC0 1.0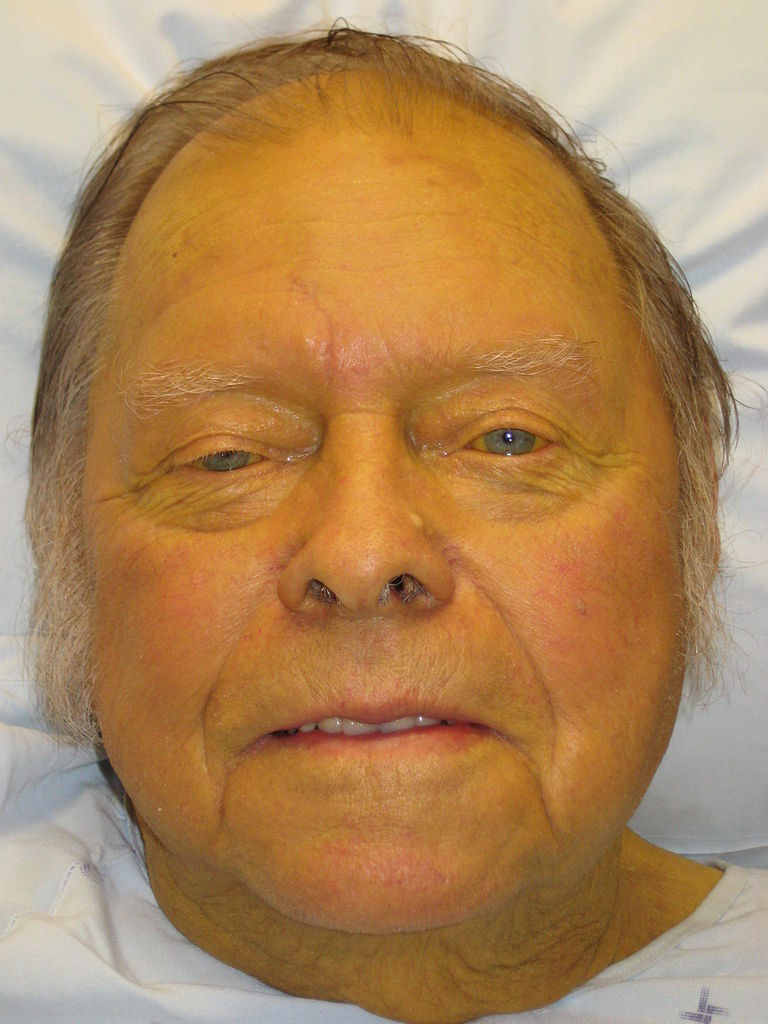
Ictericia: coloración amarilla de la piel debido a la deposición de bilirrubina
Imagen: “Jaundice08” por James Heilman, MD. Licencia: CC BY 3.0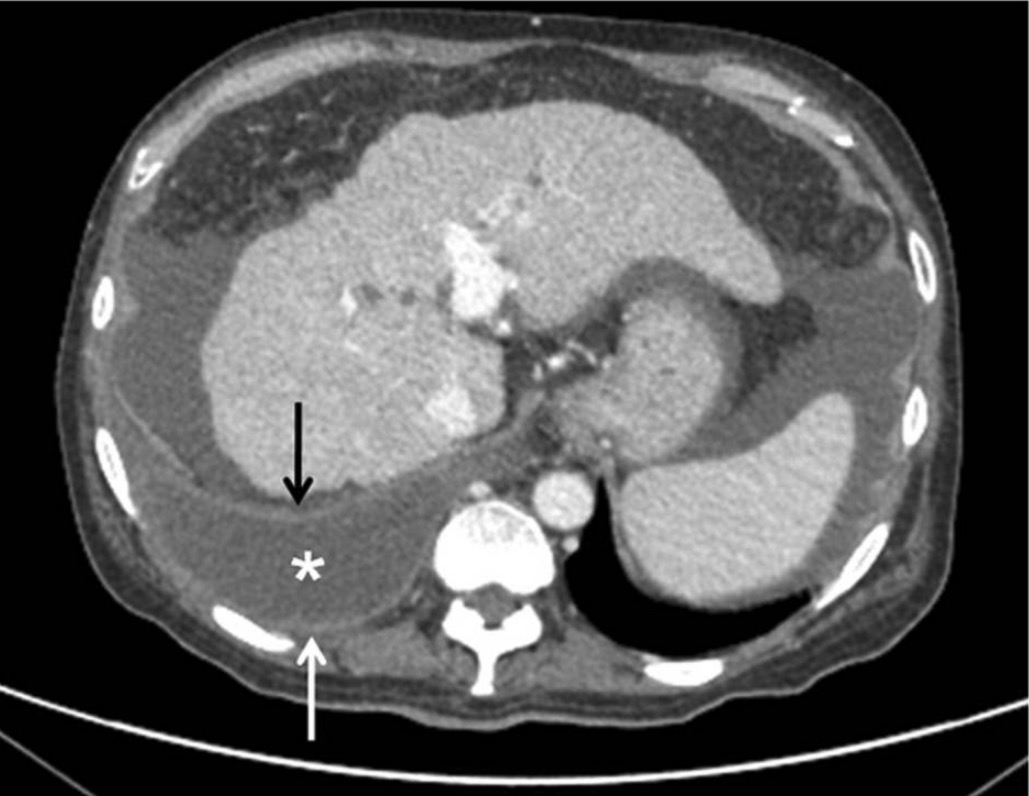
Cirrosis hepática con empiema concomitante (asterisco y flechas):
El hígado parece nodular, irregular y encogido (observe la ascitis abdominal).
Función discriminante de Maddrey:
Puntuación para hepatitis alcohólica de Glasgow:
Modelo para la puntuación de enfermedad hepática en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum etapa terminal:
Hepatitis leve a moderada:
Hepatitis severa:
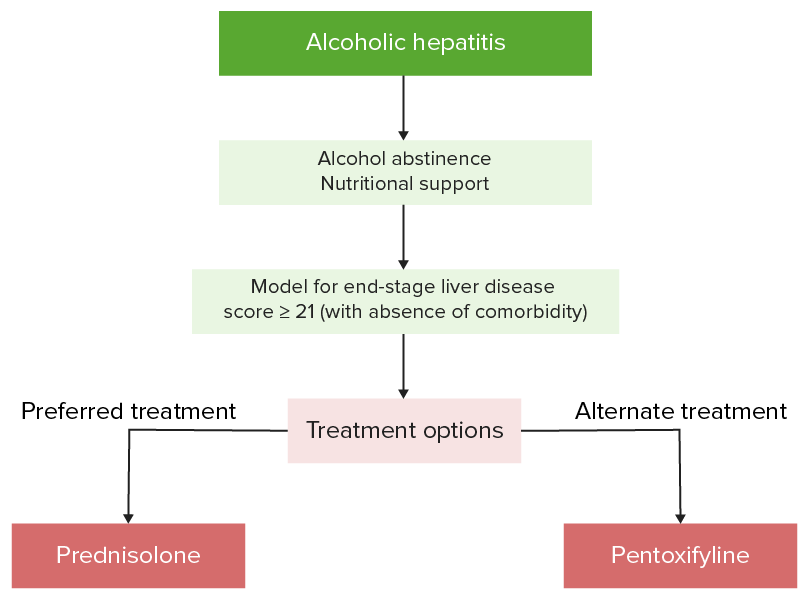
Algoritmo de manejo o hepatitis alcohólica
Imagen por Lecturio.