La endoftalmitis es un proceso inflamatorio de las capas internas del ojo, que puede ser infeccioso o estéril. La endoftalmitis infecciosa puede provocar una pérdida de visión irreversible si no se trata rápidamente. Según el modo de entrada de la fuente infecciosa, la endoftalmitis se divide en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum tipos endógena y exógena. La endoftalmitis exógena se produce a través de la inoculación directa de organismos infecciosos durante la cirugía de cataratas, el traumatismo ocular o la inyección intravítrea. La endoftalmitis endógena es el resultado de una propagación hematógena. La endoftalmitis estéril puede ser el resultado de toxinas o de material del cristalino retenido después de una operación ocular. Las características clínicas varían según el tipo y la evolución de la enfermedad. Las características pueden incluir disminución de la visión, inyección conjuntival, dolor Dolor Inflammation ocular, hipopión y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema corneal. El diagnóstico depende principalmente de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes y el examen oftalmológico, y el tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la causa subyacente. La endoftalmitis estéril suele resolverse espontáneamente, mientras que la infecciosa se trata con antimicrobianos (antibióticos o antifúngicos). La vitrectomía puede ser necesaria en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum caso de enfermedad grave.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La endoftalmitis es un proceso inflamatorio de las cavidades intraoculares (e.g., humor Humor Defense Mechanisms acuoso y/o vítreo) causado generalmente por bacterias u hongos.
Exógena:
Endógena:
Normalmente, la barrera hemato-ocular resiste de forma natural a los LOS Neisseria organismos invasores.
Fisiopatología:
Factores de riesgo:
Fisiopatología:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos unilaterales, el ojo derecho tiene el doble de probabilidades de infectarse que el izquierdo.
Factores de riesgo:
Aguda:
Crónica:
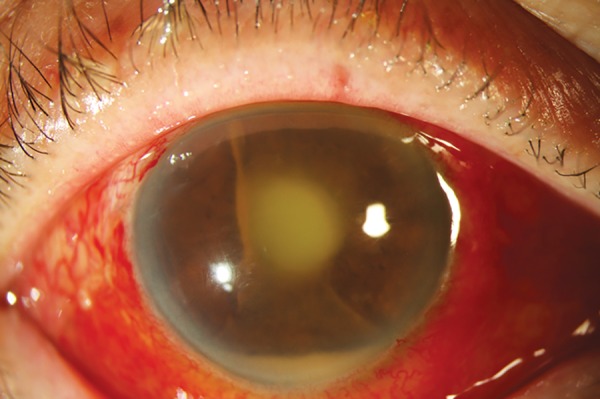
Hipopión y rastro de pus con endoftalmitis asociada a la exposición del stent intraluminal de la derivación de glaucoma
Imagen: “Hypopyon and track of pus from tube at presentation with endophthalmitis” por Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers (P) Ltd. Licencia: CC BY 3.0El diagnóstico de la endoftalmitis se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica con la confirmación mediante pruebas de laboratorio del humor Humor Defense Mechanisms acuoso y/o vítreo.
Fundoscopia:
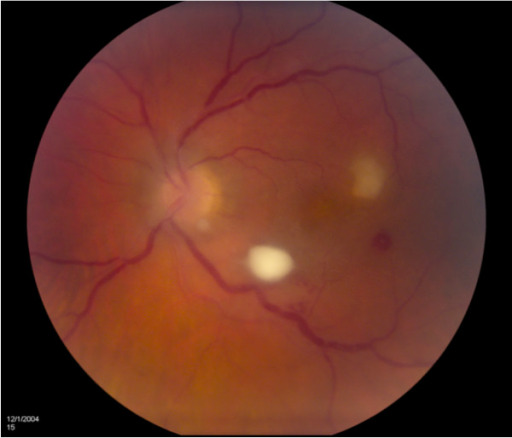
El examen fundoscópico de un paciente con endoftalmitis fúngica endógena demuestra una lesión retiniana amarilla medial al nervio óptico.
Imagen: “Endogenous fungal endophthalmitis: risk factors, clinical features, and treatment outcomes in mold and yeast infections.” por Sridhar J, Flynn HW, Kuriyan AE, Miller D, Albini T. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Examen con lámpara de hendidura:
Las pruebas diagnósticas soportan el estudio para buscar el origen de la endoftalmitis endógena:
El tratamiento depende de la causa subyacente y el resultado depende en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum gran medida del diagnóstico y el tratamiento oportunos.
Hongos:
Bacteriana: