La colangitis aguda se refiere a la inflamación aguda del sistema de conductos biliares; es una afección potencialmente mortal caracterizada por fiebre, ictericia y dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal. Esta afección se desarrolla como resultado de la estasis y la infección del tracto biliar. Las posibles complicaciones graves son shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock séptico, absceso hepático y disfunción multiorgánica. El diagnóstico se confirma mediante ultrasonido (u otros estudios de imagen hepatobiliares) que muestran dilatación del conducto biliar común o cálculos biliares, pruebas de función hepática elevadas y leucocitosis. El tratamiento incluye estabilización hemodinámica, antibióticos de amplio espectro, drenaje biliar urgente y tratamiento de la etiología subyacente (e.g., colecistectomía por cálculos biliares).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Mnemotecnia: Bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology responsable de la colangitis—“KEEPS” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
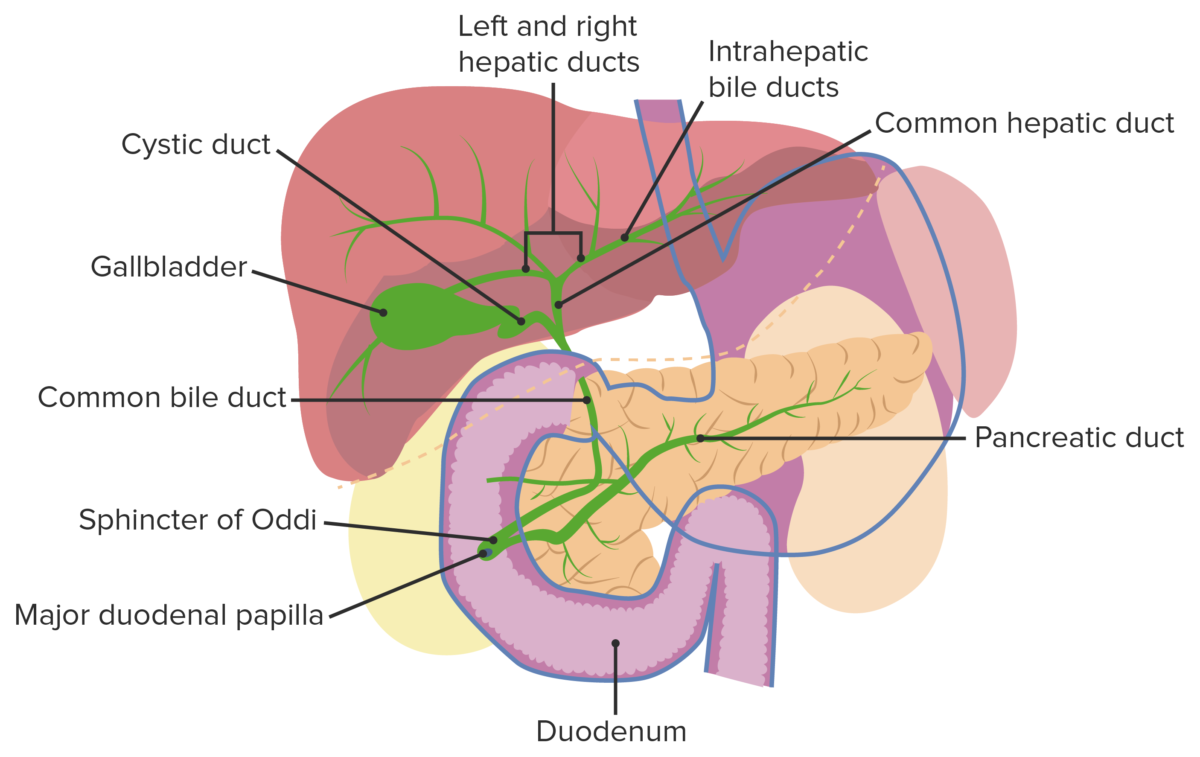
Vesícula biliar y tracto biliar: Las bacterias del duodeno pueden ascender al conducto biliar debido a una obstrucción o una interrupción en el esfínter de Oddi.
Imagen por Lecturio.
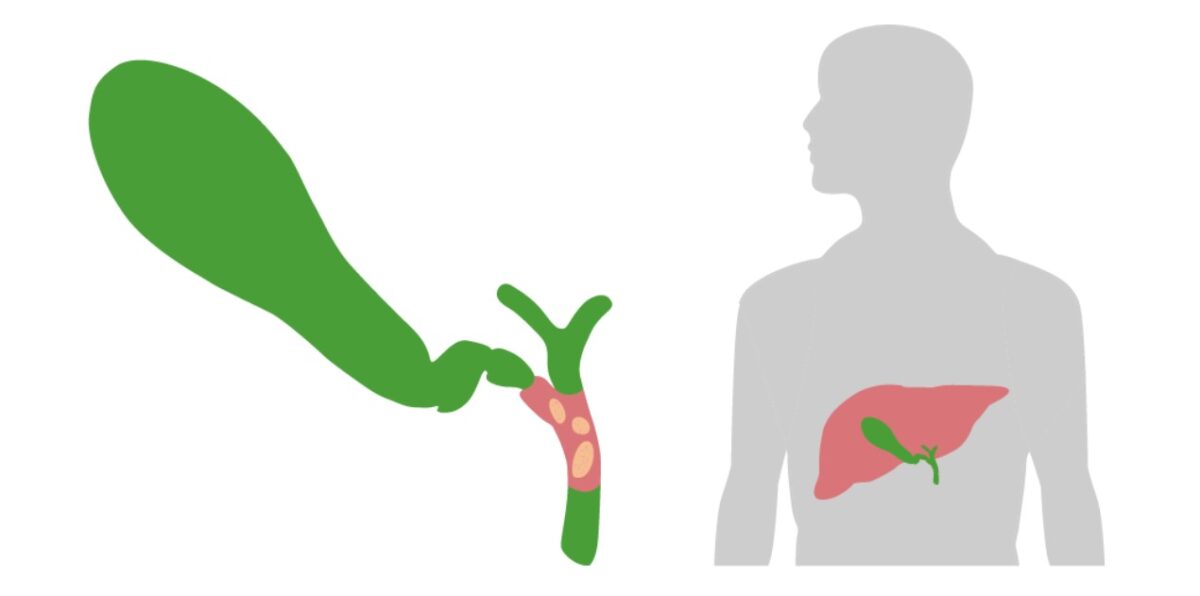
La obstrucción (generalmente debido a un cálculo) del colédoco es un paso crucial en el desarrollo de la colangitis aguda.
Imagen por Lecturio.Nota: si el paciente está hemodinámicamente inestable y tiene evidencia clínica de colangitis aguda, se omitirá este paso. El paciente debe proceder directamente a la descompresión biliar.
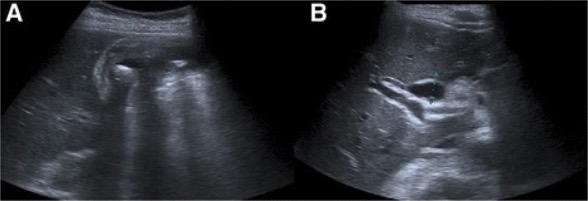
Colangitis aguda: Ultrasonido abdominal que muestra engrosamiento de la pared de la vesícula biliar, líquido pericolecístico y colelitiasis (a). El conducto biliar común está dilatado. (B).
Imagen: “Abdominal ultrasound” por Serviço de Gastrenterologia e Hepatologia, Hospital de Santa Maria, Centro Hospitalar Lisboa Norte, Avenida Professor Egas Moniz, Lisboa, 1649-035, Portugal. Licencia: CC BY 4.0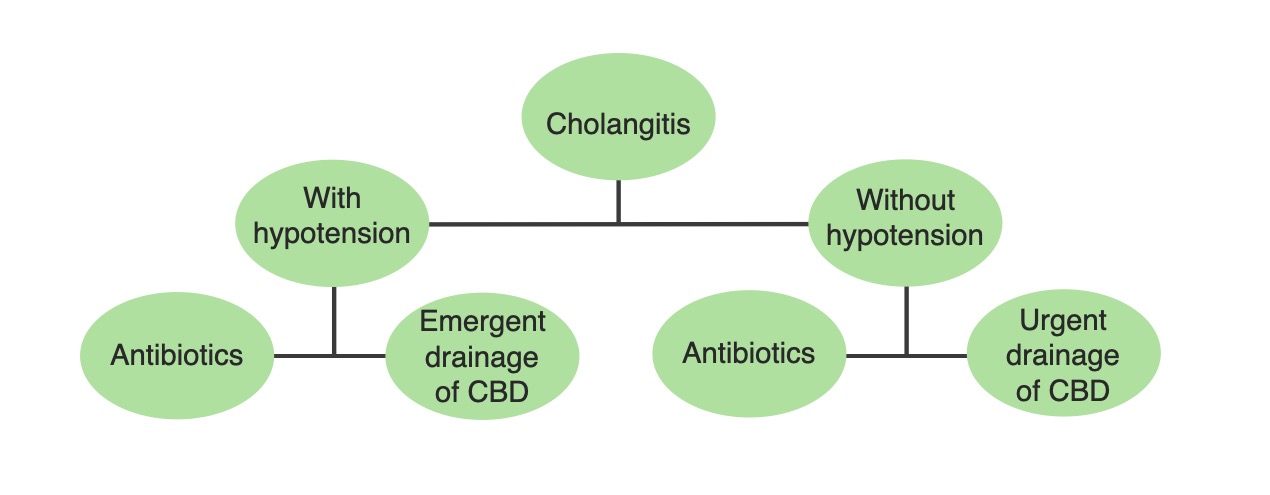
Un algoritmo de tratamiento simplificado para la colangitis aguda basado en la estabilidad hemodinámica del paciente: El tratamiento definitivo requiere control de la fuente con drenaje biliar. Por lo tanto, este tratamiento se realiza de forma urgente en pacientes hemodinámicamente inestables.
Imagen por Lecturio.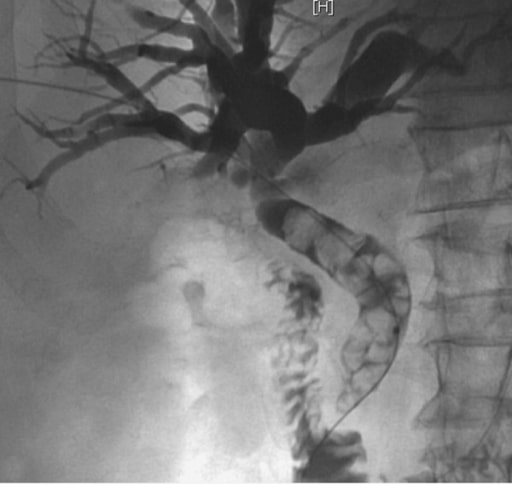
Un paciente acudió al servicio de urgencias con tríada de Charcot y se le diagnosticó colangitis aguda. La colangiografía transhepática percutánea muestra un colédoco dilatado que contiene múltiples cálculos calcificados afectados por encima de la papila de Vater. La extracción de cálculos y el drenaje biliar se realizarían durante este procedimiento.
Imagen: “Percutaneous cholangiography” por Service of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Geneva University Hospitals, Rue Gabrielle Perret Gentil 24, 1211 Geneva, Switzerland. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La siguiente tabla describe los LOS Neisseria diagnósticos biliares comunes y cómo se pueden diferenciar de la colangitis aguda:
| Condición | Patología | Presentación clínica | Diagnóstico | Tratamiento |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colelitiasis | Presencia de cálculos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vesícula biliar | Asintomático o cólico biliar ( dolor Dolor Inflammation constante, sordo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho que dura < 6 horas) |
|
|
| Colecistitis | Obstrucción del conducto cístico con inflamación de la vesícula biliar | Dolor Dolor Inflammation constante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho (> 6 horas), fiebre, náusea y vómito, signo de Murphy |
|
|
| Coledocolitiasis | Obstrucción del conducto biliar común debido a un cálculo | Cólico postpandrial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho > 6 h, ictericia |
|
CPRE y colecistectomía |
| Colangitis aguda | Infección del conducto biliar | Dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho, fiebre, ictericia, hipotensión, taquicardia |
|
|
Otros posibles diagnósticos a considerar: