El citomegalovirus (CMV) es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) de doble cadena, ubicuo, que pertenece a la familia Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Las infecciones por CMV pueden transmitirse a través de fluidos corporales, como la sangre, saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy, orina, semen y leche materna. La infección inicial suele ser asintomática en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el huésped inmunocompetente, o puede presentarse con síntomas de mononucleosis Mononucleosis Infectious mononucleosis (IM), also known as "the kissing disease," is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Its common name is derived from its main method of transmission: the spread of infected saliva via kissing. Clinical manifestations of IM include fever, tonsillar pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy. Mononucleosis. Después de la infección primaria, el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology se vuelve latente. La reactivación puede producirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos inmunocomprometidos, dando lugar a afecciones como esofagitis, colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis, hepatitis, retinitis, encefalitis y neumonía por CMV.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
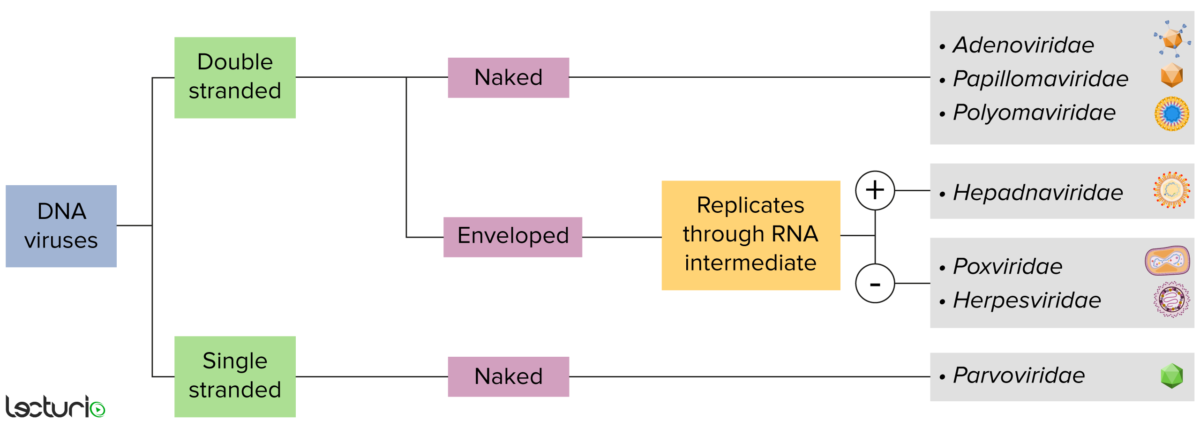
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ácido ribonucleico (ARN). Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que suele tomarse de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
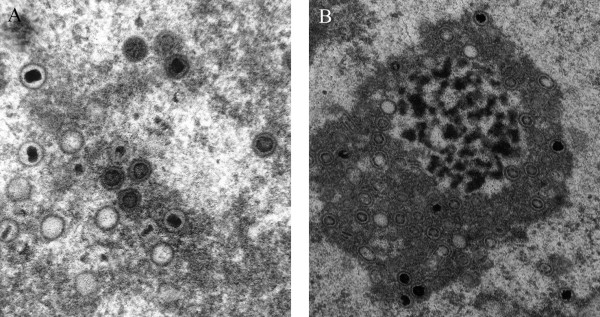
Imágenes de micrografía electrónica de transmisión del CMV:
A: Partículas de CMV humano claramente definidas y no deformadas.
B: Diversos tipos de textura de fondo y partículas deformadas en el núcleo celular
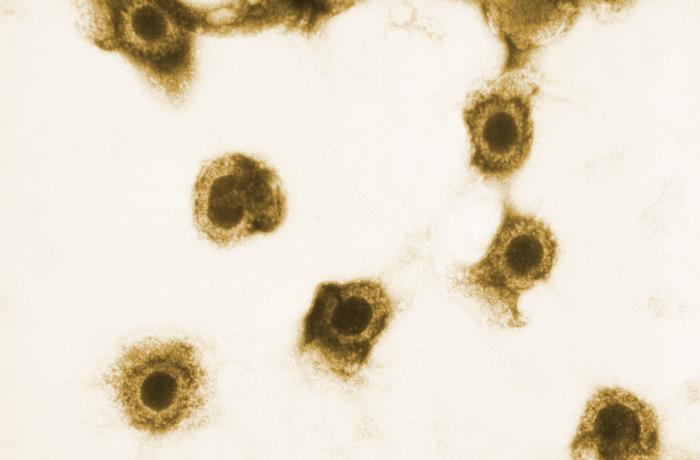
Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión que muestra varios viriones de CMV
Imagen: “Transmission electron microscopic image showing a number of cytomegalovirus (CMV) virions” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa cepa de CMV asociada a la infección humana sólo se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos.
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocomprometidos tienen un mayor riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad por CMV.
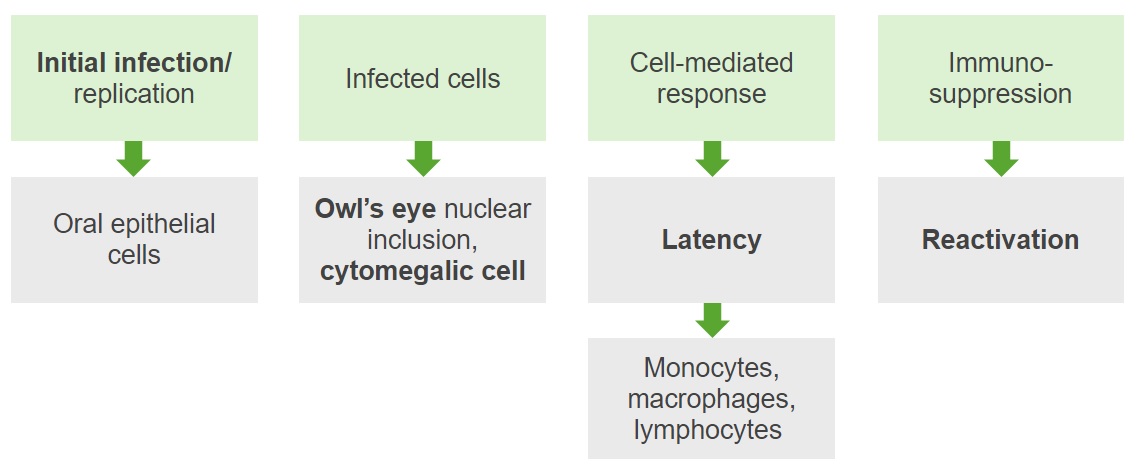
Patogénesis del CMV
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Las células infectadas por CMV:
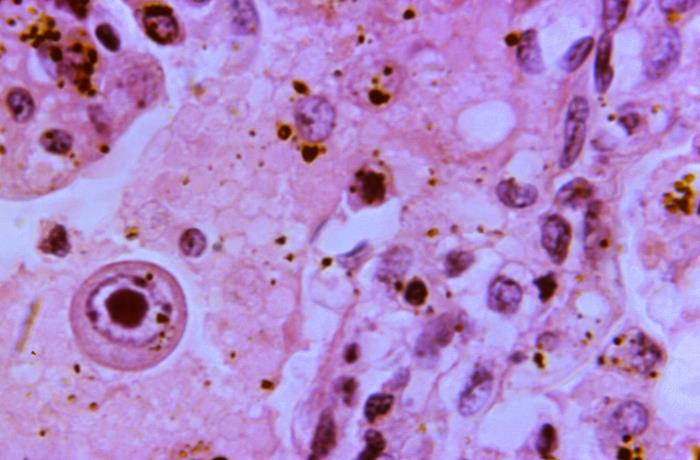
Microfotografía de una sección de tejido pulmonar que revela la presencia de una gran célula de inclusión citomegálica, también denominada célula de inclusión en ojo de búho, en un caso de CMV.
Imagen: “This photomicrograph of a section of lung tissue, harvested from an infant, revealed the presence of a large cytomegalic inclusion cell” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público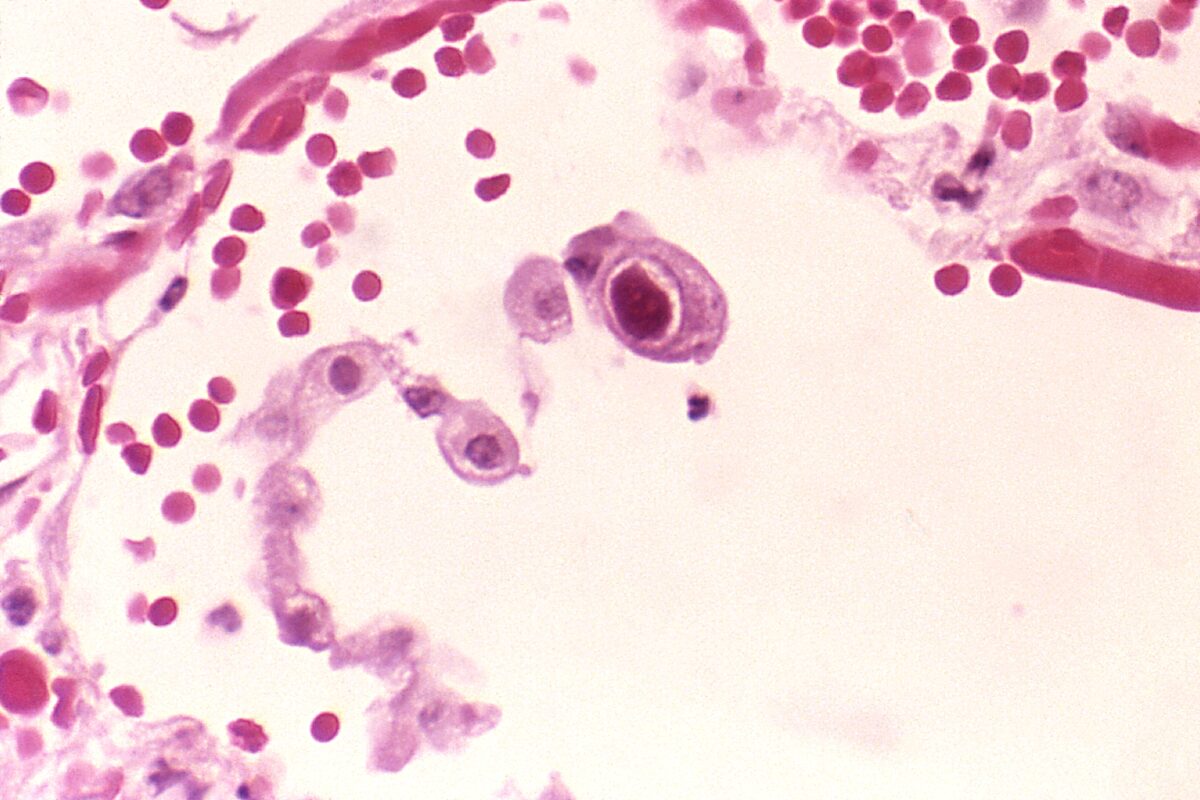
Fotomicrografía de una muestra de tejido pulmonar de un paciente con síndrome de inmunodeficiencia adquirida (SIDA) con una infección activa por citomegalovirus:
La histopatología reveló la presencia de una célula agrandada, que contenía la característica inclusión intranuclear en “ojo de búho” consistente con la infección por citomegalovirus.
El espectro de presentaciones clínicas del CMV es diverso y depende del estado inmunitario del huésped.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes inmunocompetentes serán asintomáticos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la minoría que son sintomáticos, la presentación más común es un síndrome similar a la mononucleosis Mononucleosis Infectious mononucleosis (IM), also known as “the kissing disease,” is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Its common name is derived from its main method of transmission: the spread of infected saliva via kissing. Clinical manifestations of IM include fever, tonsillar pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy. Mononucleosis infecciosa por el virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Epstein-Barr ( EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés).
El CMV congénito es una de las infecciones perinatales TORCH (toxoplasmosis, otros agentes, rubéola, citomegalovirus y herpes simple).
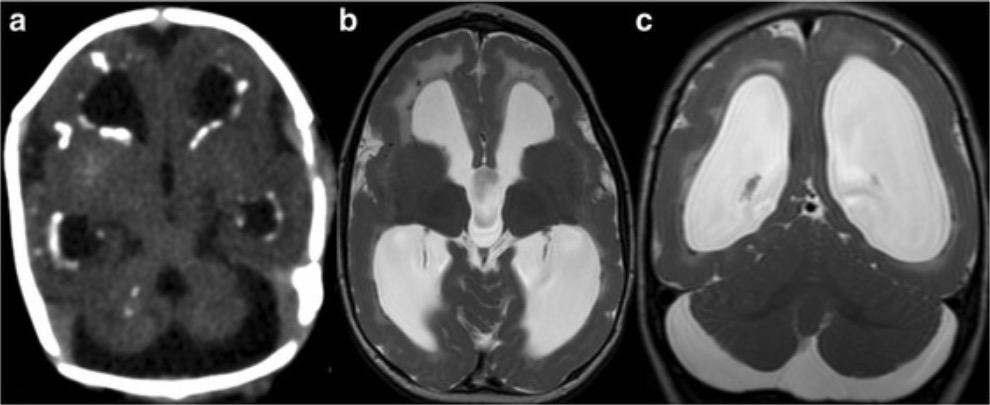
Resonancia magnética (RM) de un lactante con citomegalovirus congénito que demuestra calcificaciones periventriculares, ventriculomegalia e hipoplasia cerebelosa
Imagen: “Axial computed tomography (CT) image” por Department of Neurology, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Las siguientes manifestaciones son raras en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum huéspedes inmunocompetentes y suelen ser el resultado de la reactivación de una infección latente. Nota: Las infecciones fuera de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos, bazo e hígado se consideran afecciones definitorias de SIDA.
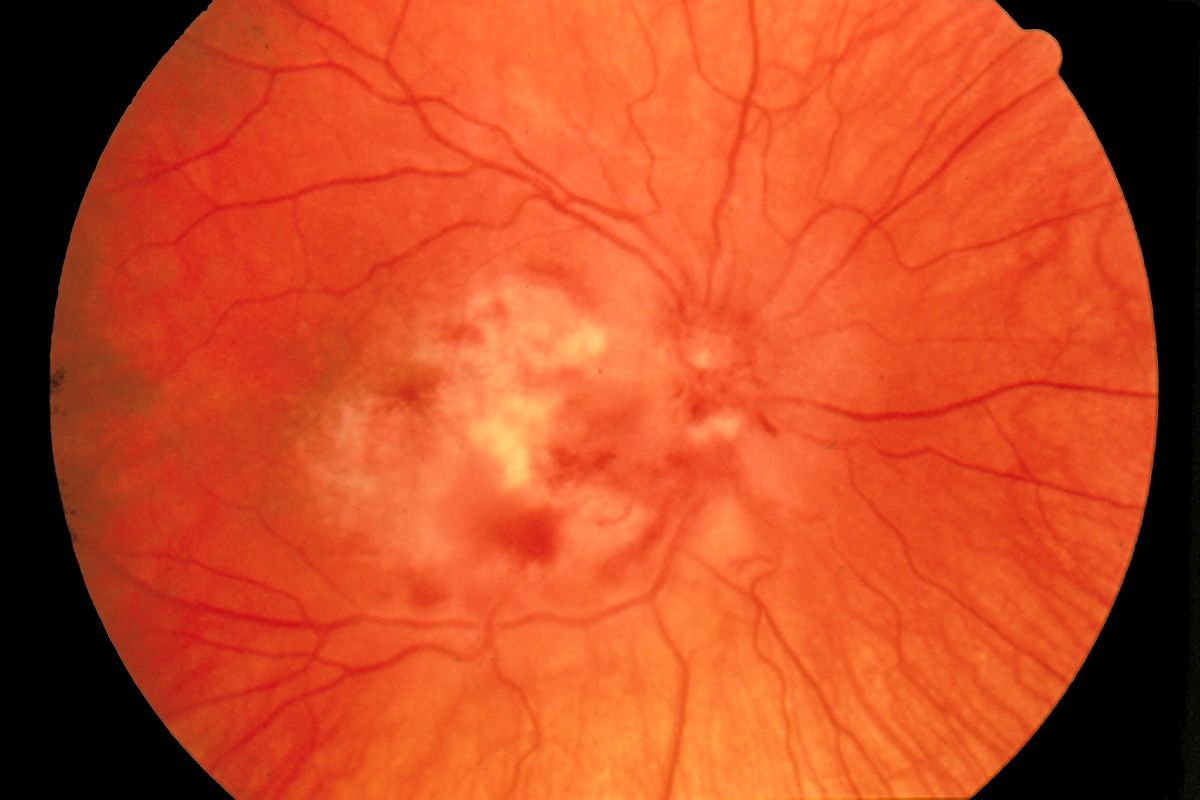
Imagen fundoscópica de la retinitis por CMV
Imagen: “Fundus photograph-CMV retinitis” por National Eye Institute. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa siguiente tabla compara los LOS Neisseria 9 herpesvirus considerados endémicos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ser humano; se conocen 115 especies de herpesvirus, agrupadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 familias:
| Herpesvirus humano | Nombre común | Células diana primarias | Sitio de latencia | Presentación clínica* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (grupo alfa) |
VHS-1 | Células mucoepiteliales | Ganglios de la raíz dorsal |
|
|
2 (grupo alfa) |
VHS-2 |
|
||
|
3 (grupo alfa) |
VZV |
|
||
|
4 (grupo gamma) |
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus | Células epiteliales células B | Células B de memoria |
|
|
5 (grupo beta) |
CMV |
|
Células progenitoras hematopoyéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea |
|
|
6A, 6B (grupo beta) |
HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | Células T | Monocitos | Roséola |
|
7 (grupo beta) |
HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | Células T | ||
|
8 (grupo gamma) |
Herpesvirus asociado al AL Amyloidosis sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |
|
Células B | Sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |