Las cefaleas de alto riesgo, a veces también denominadas cefaleas de alarma, abarcan causas secundarias de las cefaleas que pueden provocar daños irreversibles en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum órganos diana, déficits neurológicos, pérdida de la visión e incluso la muerte. Las entidades como la hemorragia subaracnoidea, la meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis/encefalitis y los LOS Neisseria tumores intracraneales conllevan un alto riesgo de morbilidad y mortalidad si no se reconocen y se tratan de inmediato. El diagnóstico de una cefalea de alto riesgo requiere un alto grado de sospecha clínica y se realiza mediante una evaluación clínica exhaustiva seguida de un estudio específico para la etiología más probable. El tratamiento depende de la etiología, pero consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento inmediato de la causa subyacente y la estabilización de la disfunción orgánica acompañante.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Una cefalea de alto riesgo es cualquier cefalea nueva y repentina, típicamente severa, con el potencial de causar daño a las estructuras o funciones cerebrales o precerebrales.
Existen muchas etiologías de las cefaleas de alto riesgo que el médico debe estar alerta y trabajar para descartar cuando se encuentra con una cefalea intensa. Aquí se presentan las etiologías más comunes, separadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum causas vasculares, infecciosas, neoplásicas y misceláneas.
| Entidad clínica | Antecedentes/factores de riesgo | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Hemorragia subaracnoidea (HSA) |
|
|
| Síndrome de vasoconstricción cerebral reversible (SVCR) |
|
|
| Disección de la arteria cervical/disección de la arteria vertebral |
|
|
| Trombosis de la vena cerebral/trombosis del seno dural |
|
|
| Hematoma Hematoma A collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematoma can be localized in an organ, space, or tissue. Intussusception subdural/ hematoma Hematoma A collection of blood outside the blood vessels. Hematoma can be localized in an organ, space, or tissue. Intussusception epidural |
|
|
| Hemorragia intraparenquimatosa |
|
Presentación variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables según el sitio de la hemorragia (muy parecida a un accidente cerebrovascular/ AIT AIT Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction) |
| Hipertensión intracraneal idiopática |
|
|
| Hipotensión intracraneal espontánea |
|
|
| Arteritis de células gigantes |
|
|
| Encefalopatía hipertensiva |
|
|
| Síndrome de encefalopatía posterior reversible |
|
|
| Entidad clínica | Antecedentes/factores de riesgo | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis y/o encefalitis |
|
|
| Absceso cerebral |
|
|
| Entidad clínica | Antecedentes/factores de riesgo | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Tumor Tumor Inflammation cerebral |
|
|
| Quiste coloide del 3er ventrículo |
|
|
| Infarto hipofisario |
|
|
| Entidad clínica | Antecedentes/factores de riesgo | Características clínicas |
|---|---|---|
| Glaucoma Glaucoma Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by typical visual field defects and optic nerve atrophy seen as optic disc cupping on examination. The acute form of glaucoma is a medical emergency. Glaucoma is often, but not always, caused by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). Glaucoma agudo de ángulo estrecho |
|
|
| Toxicidad por CO |
|
|
| Preeclampsia Preeclampsia A complication of pregnancy, characterized by a complex of symptoms including maternal hypertension and proteinuria with or without pathological edema. Symptoms may range between mild and severe. Pre-eclampsia usually occurs after the 20th week of gestation, but may develop before this time in the presence of trophoblastic disease. Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders/ eclampsia Eclampsia Onset of hyperreflexia; seizures; or coma in a previously diagnosed pre-eclamptic patient (pre-eclampsia). Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders |
|
|
Es importante realizar una evaluación enfocada y minuciosa de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes:
Es importante realizar un examen físico dirigido y completo:
Sospecha de etiología infecciosa:
Sospecha de etiología hematológica/vascular:
Sospecha de etiología neoplásica:
Cefalea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum trueno:
Meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis o encefalitis:
Aumento de la PIC:
Toxicidad por CO:
Cefalea con dolor Dolor Inflammation de cuello:
Cefalea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum adultos > 50 años de edad:
Cefalea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes inmunodeprimidos:
Cefalea en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con cáncer:
Cefalea durante el embarazo/postparto:
Cefalea con discapacidad visual, dolor Dolor Inflammation periorbitario, oftalmoplejía:
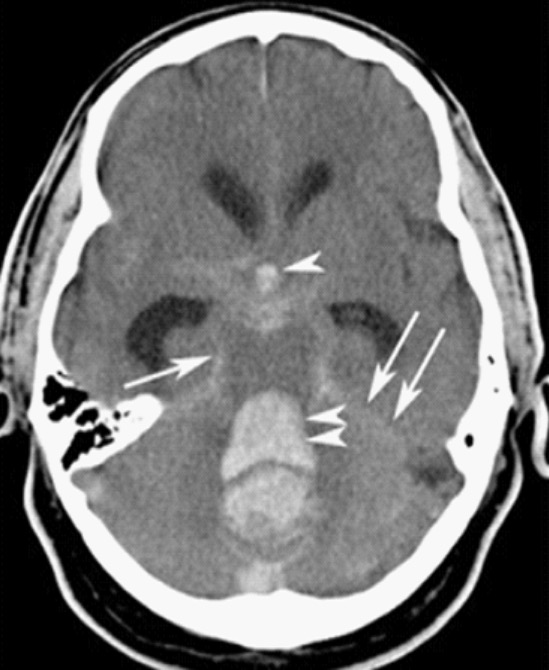
Hemorragia subaracnoidea:
TC que muestra una hemorragia intracraneal
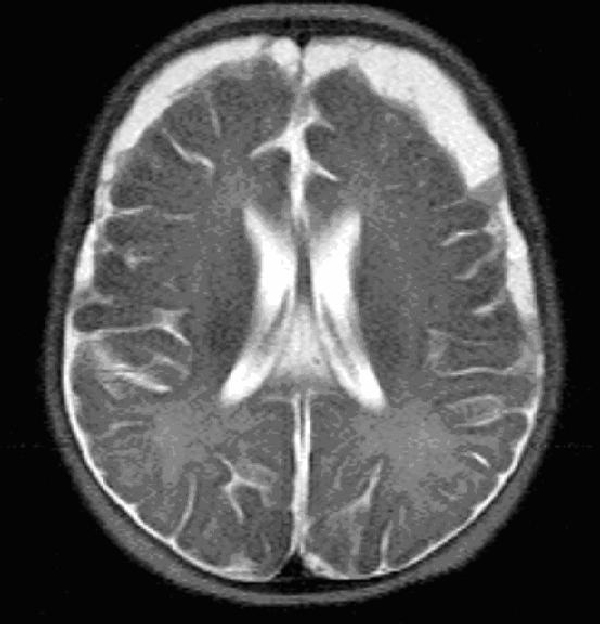
RM de meningitis:
Se observa el empiema subdural bifrontal/bitemporal Imagen : “MRI HEAD (axial) without contrast” por Yip K et al.Licencia: CC BY 3.0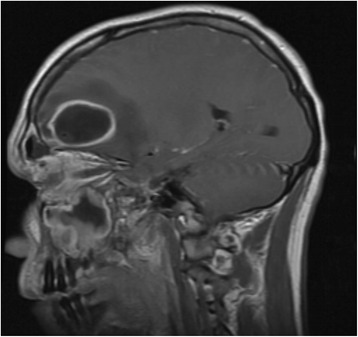
Resonancia magnética de la cabeza que muestra un absceso frontal:
Obsérvese la hiperintensidad que se extiende desde el seno frontal hasta la cavidad del absceso.