El carcinoma hepatocelular (CHC) surge típicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un hígado con enfermedad crónica o cirrótico y es el cáncer de hígado primario más común. El diagnóstico puede incluir ecografía, tomografía computarizada, resonancia magnética, biopsia (si la imagen no es concluyente) y/o biomarcadores. Las opciones de tratamiento incluyen resección y quimioterapia/radioterapia, y trasplante de hígado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos seleccionados. Las metástasis hepáticas son mucho más comunes que los LOS Neisseria cánceres hepáticos primarios y generalmente se originan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sitios primarios colorrectales, pulmonares, mamarios y pancreáticos. Las metástasis se diagnostican con mayor frecuencia mediante tomografías computarizadas o tomografías por emisión de positrones ( PET PET An imaging technique that combines a positron-emission tomography (PET) scanner and a ct X ray scanner. This establishes a precise anatomic localization in the same session. Nuclear Imaging). El manejo depende del tipo y estadio del cáncer primario.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Cirrosis:
Un tercio de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con cirrosis desarrollarán carcinoma hepatocelular durante su vida, incluidos los LOS Neisseria causados por:
Otros:
Los hepatocitos muestran “cambio de células grandes” y “cambio de células pequeñas” con una arquitectura anormal (trabéculas gruesas) al AL Amyloidosis microscopio.
Apariencia macroscópica:
Aspecto microscópico:
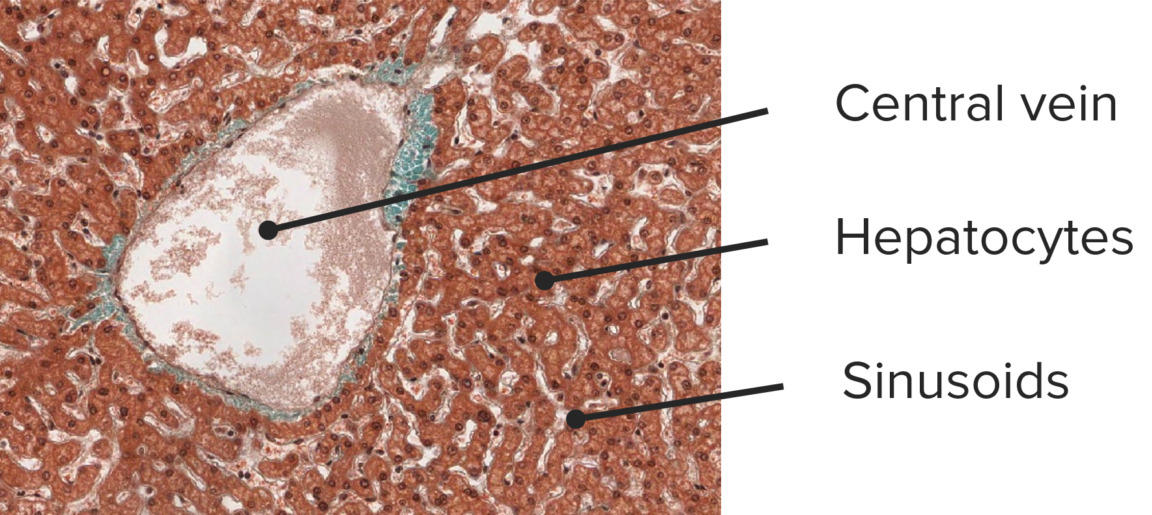
Histología de un hígado normal:
microfotografía de un hígado normal con una vena central dilatada pero arquitectura normal que muestra trabéculas delgadas (capa de una sola célula) (tinción tricrómica, 100x)
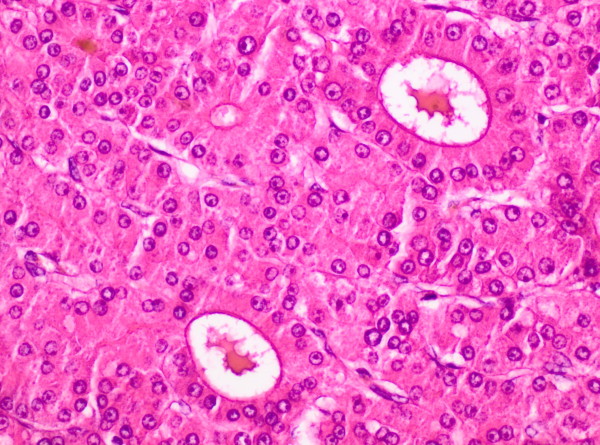
Histología del carcinoma hepatocelular:
microfotografía de un carcinoma hepatocelular moderadamente diferenciado que muestra un patrón de trabéculas engrosadas (2 a 6 capas de células) rodeadas de células endoteliales aplanadas. Obsérvese el pigmento biliar marrón en la parte superior izquierda y los 2 grandes espacios seudoglandulares que contienen material proteínico rosado. Los hepatocitos muestran atipia moderada. Compare las trabéculas engrosadas con las trabéculas unicelulares de un hígado normal.
Cuatro posibles presentaciones clínicas para carcinoma hepatocelular:
Se recomienda realizar un tamizaje de vigilancia mediante ultrasonido cada 6 meses a los LOS Neisseria pacientes de los LOS Neisseria siguientes grupos de alto riesgo:
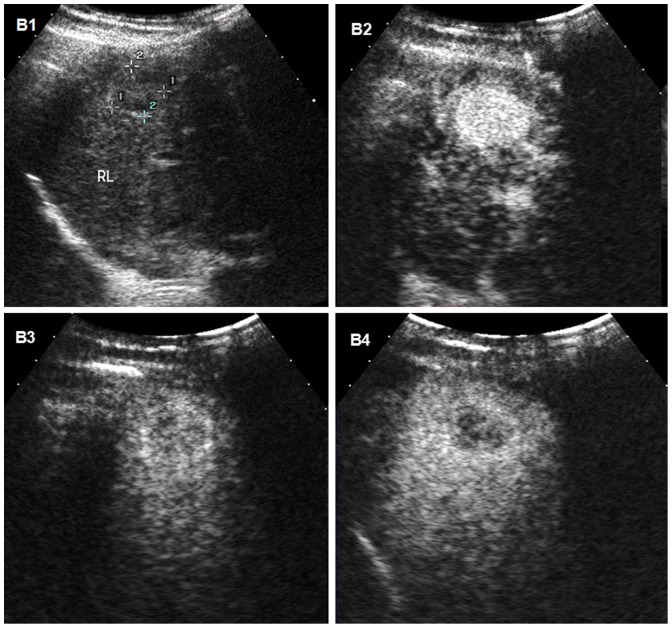
Carcinoma hepatocelular en ultrasonido: imágenes de ultrasonido de carcinoma hepatocelular en el hígado de un hombre de 31 años con cirrosis
B1: ultrasonido convencional que muestra la masa como un nódulo hipoecoico mal delimitado
B2, B3, B4: imágenes de ultrasonido mejorado con contraste secuenciadas en el tiempo (CEUS) después de la inyección de un agente de contraste de microburbujas
B2: hipervascularización típica (realce) de carcinoma hepatocelular durante la fase arterial a los 95 segundos después de la inyección del agente de contraste
B3, B4: masa que se vuelve hipoecogénica en fase portal y tardía
B4: imagen de fase tardía que muestra un ligero lavado del medio de contraste a los 179 s, lo que ayuda a diferenciar el carcinoma hepatocelular de un colangiocarcinoma o un tumor metastásico (tiempos de lavado más rápidos)
Si el ultrasonido muestra una lesión > 1 cm, se realiza una imagen de contraste dinámico por TC o RM.
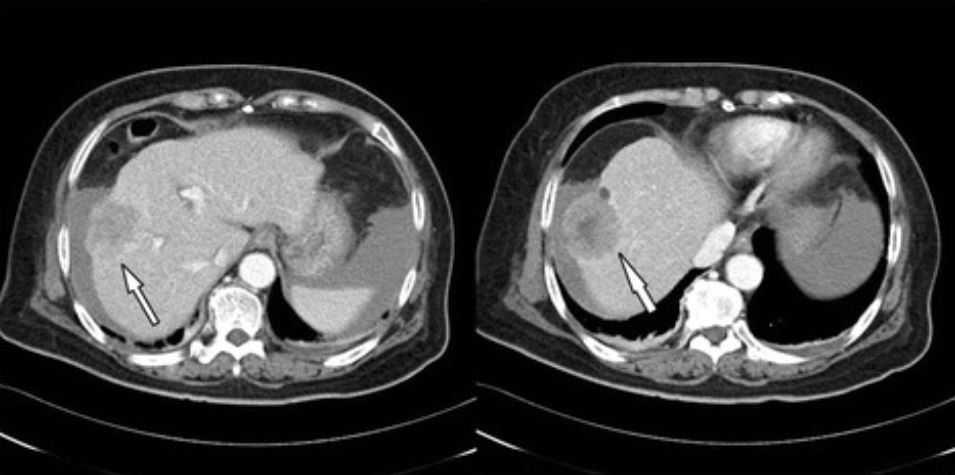
Carcinoma hepatocelular en tomografía computarizada (TC):
TC abdominal trifásico que revela tumor de gran tamaño (4,8 cm de diámetro) en lóbulo derecho compatible con carcinoma hepatocelular (flecha)
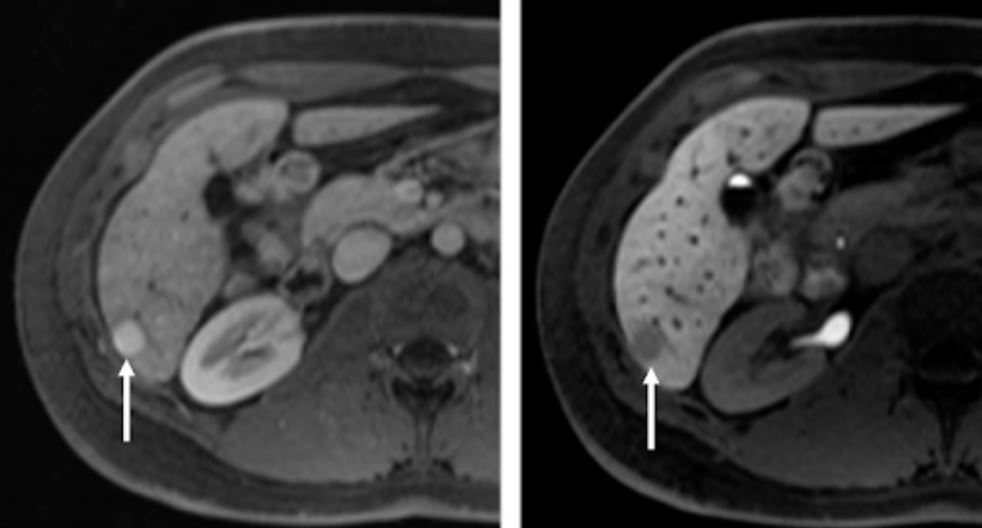
Características típicas de la resonancia magnética nuclear (RMN) del carcinoma hepatocelular:
RM axial del hígado después de la administración intravenosa (IV) de un agente de contraste específico para hepatocitos en las fases arterial (izquierda) y hepatobiliar (derecha) 20 min después de la aplicación de contraste IV
En el segmento 6 se observa una lesión hipervascular (imagen izquierda, flecha apuntando a la lesión).
En la fase hepatobiliar, la lesión (imagen de la derecha, flecha apuntando a la lesión) es hipointensa en relación con el hígado circundante debido a la reducción de la captación de agente de contraste debido a la pérdida de hepatocitos funcionantes en la lesión de carcinoma hepatocelular pobremente diferenciada.
Si los LOS Neisseria resultados de las imágenes son inequívocos, no siempre se necesita una biopsia.
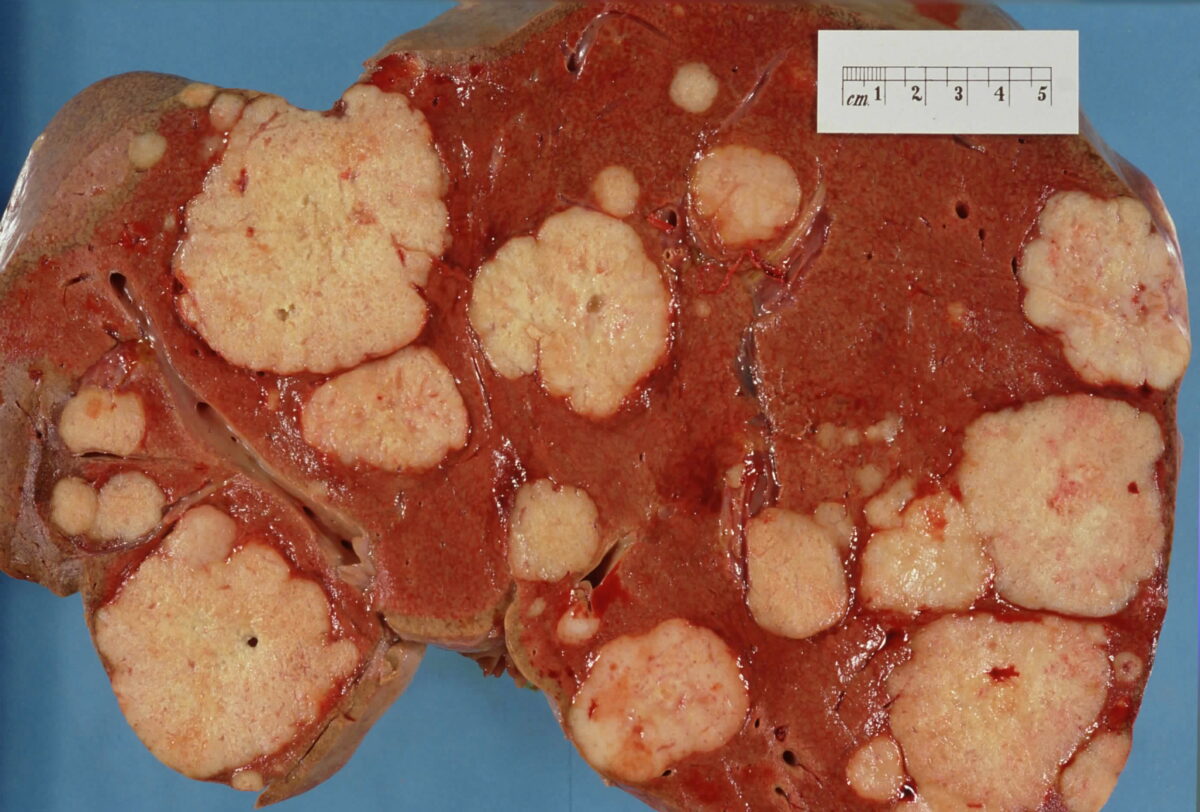
Muestra macroscópica del hígado que muestra múltiples tumores metastásicos
Imagen: “Secondary tumor deposits in the liver from a primary cancer of the pancreas” por John Hayman. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria siguientes son diagnósticos diferenciales importantes de una masa sólida en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hígado:
Lesiones benignas:
Lesiones malignas:
Colangiocarcinoma (cáncer de las vías biliares): surge de las células epiteliales de las vías biliares intrahepáticas y extrahepáticas. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria Estados Unidos incluyen colangitis esclerosante primaria y enfermedad hepática fibropoliquística (e.g., quistes de colédoco). La hepatolitiasis (colangitis piógena recurrente) es el mayor factor de riesgo de colangiocarcinoma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Asia ASIA Spinal Cord Injuries.