El cáncer urológico es un término amplio que involucra el cáncer de las vías urinarias masculinas y femeninas y los LOS Neisseria órganos reproductores masculinos. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo para el cáncer urológico son el tabaquismo; exposición a sustancias químicas como la bencidina, la beta-naftilamina y el arsénico; predisposición genética; e irritación crónica del sistema urinario. La presentación clínica incluye hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma indolora, dolor Dolor Inflammation de costado y/o suprapúbico, disuria y pérdida de peso significativa e inexplicable. El estándar de oro para el diagnóstico es la endoscopia de las estructuras urológicas (cistoscopia, cistouretroscopia, ureteropieloscopia) con biopsia. Los LOS Neisseria estudios adicionales incluyen imagenología radiológica, que brinda información sobre la invasión del tumor Tumor Inflammation y la propagación de la enfermedad a otros sitios u órganos. El tratamiento incluye cirugía, quimioterapia, radioterapia y tratamiento de soporte, según la localización, extensión e histología.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Crecimiento de células anormales del revestimiento de los LOS Neisseria órganos de las vías urinarias masculinas y femeninas y de los LOS Neisseria órganos reproductores masculinos.
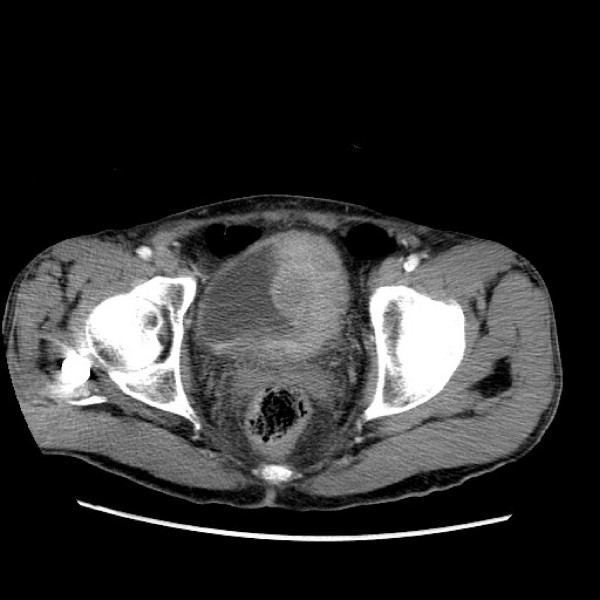
TC de cáncer de vejiga:
Masa de tejido blando lobulada en el lado derecho en la vejiga.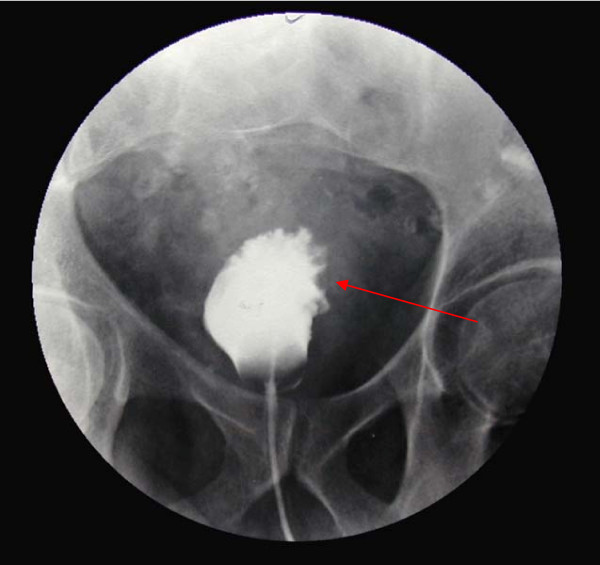
Cistograma (fase en pielografía intravenosa), que muestra marcado engrosamiento trabecular en un individuo con carcinoma de vejiga.
Imagen: “Cystogram that shows gross trabecular enlargement” por Gaurav K, Fitch J, Panda M. Licencia: CC BY 2.0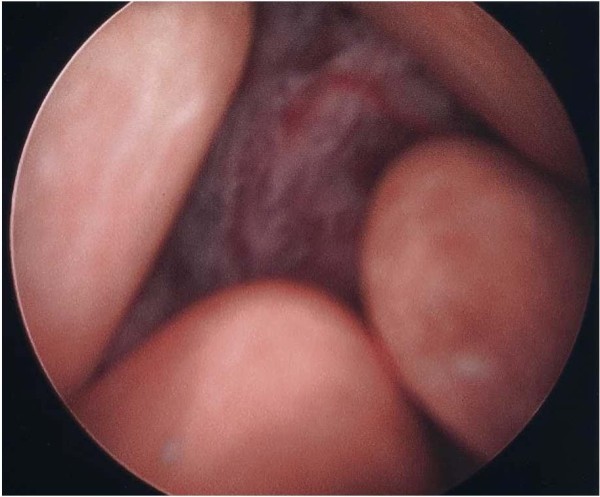
Cistoscopia que muestra una masa vesical y múltiples cálculos
Imagen: “Cystoscopy that shows a vesical mass and mutiple calculi”. por Cho JH, Holley JL. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Los LOS Neisseria estadios patológicos del cáncer de vejiga se basan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sistema de estadificación TNM.
| Categoría (T) tumor Tumor Inflammation |
Descripción |
|---|---|
| Tx | Tumor Tumor Inflammation primario que no puede ser evaluado. |
| T0 | Sin evidencia de tumor Tumor Inflammation primario |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Lesiones papilares o exofíticas no invasivas |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ (“ tumor Tumor Inflammation plano”) |
| T1 | El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade la lámina propia (o submucosa). |
| T2 | El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade la muscular propia. |
| T2a: El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade la capa muscular propia superficial (mitad interna). | |
| T2b: El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade la capa muscular propia profunda (mitad exterior). | |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade la grasa perivesical. |
| T3a: Invasión microscópica | |
| T3b: Invasión macroscópica (masa extravesical) | |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade 1 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes: estroma prostático, vesículas seminales, útero, vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy, pared pélvica, pared abdominal. |
| T4a: El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade el estroma prostático, útero, vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy (órganos adyacentes). | |
| T4b: El tumor Tumor Inflammation invade la pared pélvica, la pared abdominal u otros órganos. |
| Categoría (N) nódulos | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Nx | No se pueden evaluar los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos. |
| N0 | Ausencia de metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos |
| N1 | Metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un solo nódulo linfático regional en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy verdadera (nódulos linfáticos perivesicales, obturadores, ilíacos internos y externos o sacros) |
| N2 | Múltiples metástasis a los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos regionales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy verdadera (metástasis de nódulos linfáticos perivesicales, obturadores, ilíacos internos y externos o sacros) |
| N3 | Metástasis a los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos ilíacos comunes |
| Categoría (M) metástasis | Descripción |
|---|---|
| M0 | No existen metástasis a distancia |
| M1 | Metástasis a distancia |
| M1a: Metástasis a distancia limitada a los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos más allá de los LOS Neisseria nódulos ilíacos comunes | |
| M1b: Metástasis a distancia no linfática |
| Estadio | T | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0a | Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio 0is | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio II | T2a | N0 | M0 |
| T2b | N0 | M0 | |
| Estadio IIIA | T3a, T3b, T4a | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio IIIA | T1–T4a | N1 | M0 |
| Estadio IIIB | T1–T4a | N2, N3 | M0 |
| Estadio IVA | T4b | Cualquier N | M0 |
| Estadio IVA | Cualquier T | Cualquier N | M1a |
| Estadio IVB | Cualquier T | Cualquier N | M1b |
Crecimiento anormal de células en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el revestimiento interno del uréter/uréteres, de las cuales > 90% son carcinomas uroteliales.
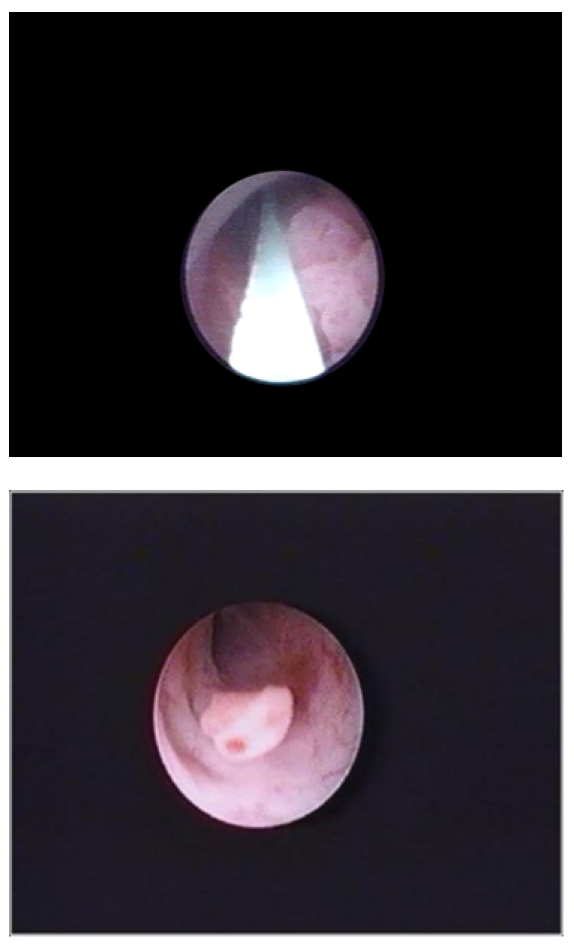
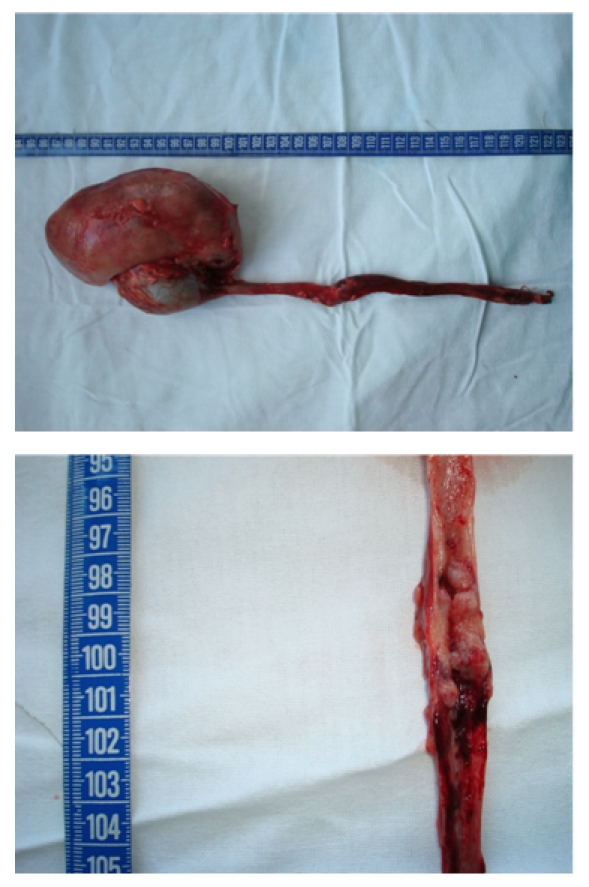
Tumor ureteral observado en el examen endoscópico del uréter.
Imagen: “Ureteral tumour with elective indication for endoscopic treatment” por Niţă G, Georgescu D, Mulţescu R, Draguţescu M, Mihai B, Geavlete B, Persu C, Geavlete P. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La estadificación se aplica al AL Amyloidosis cáncer que afecta la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy renal y el uréter.
| Categoría T | Descripción |
|---|---|
| TX | Tumor Tumor Inflammation primario que no se puede evaluar. |
| T0 | Sin evidencia de tumor Tumor Inflammation primario |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Lesiones papilares o exofíticas no invasivas |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ |
| T1 | Invasión tumoral del tejido conjuntivo subepitelial |
| T2 | Invasión tumoral de la capa muscular |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Solo para el uréter: Invasión más allá de la muscular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la grasa periureteral. Solo para pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy renal: Invasión más allá de la muscular en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la grasa peripélvica o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el parénquima renal |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invasión tumoral de órganos adyacentes o del riñón en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la grasa perirrenal |
| Categoría N | Descripción |
|---|---|
| NX | Los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos regionales no pueden ser evaluados. |
| N0 | Ausencia de metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum nódulos linfáticos |
| N1 | Metástasis ≤ 2 cm (nódulo linfático único) |
| N2 | Metástasis > 2 cm (nódulo linfático único o múltiples nódulos linfáticos) |
| Categoría M | Descripción |
|---|---|
| M0 | No existen metástasis a distancia |
| M1 | Metástasis a distancia |
| Estadio | T | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0a | Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio 0is | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio II | T2 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio III | T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio IV | T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | NX, N0 | M0 |
| Cualquier T | N1, N2 | M0 | |
| Cualquier T | Cualquier N | M1 |
El tratamiento del cáncer ureteral depende del sitio, el tamaño y la extensión del cáncer y la cirugía proporciona un tratamiento curativo.
Nefroureterectomía en el cáncer de ureteral
Imagen: “Nephroureterectomy (with endoscopic desinsertion) for ureteral tumours” por Niţă G, Georgescu D, Mulţescu R, Draguţescu M, Mihai B, Geavlete B, Persu C, Geavlete P. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El cáncer de uretra es una neoplasia maligna extremadamente rara (< 1% de todas las neoplasias genitourinarias) que implica el crecimiento anormal de células en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el revestimiento de la uretra.
El cáncer de uretra tiene un inicio insidioso y puede permanecer asintomático durante mucho tiempo. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas varían entre hombres y mujeres:
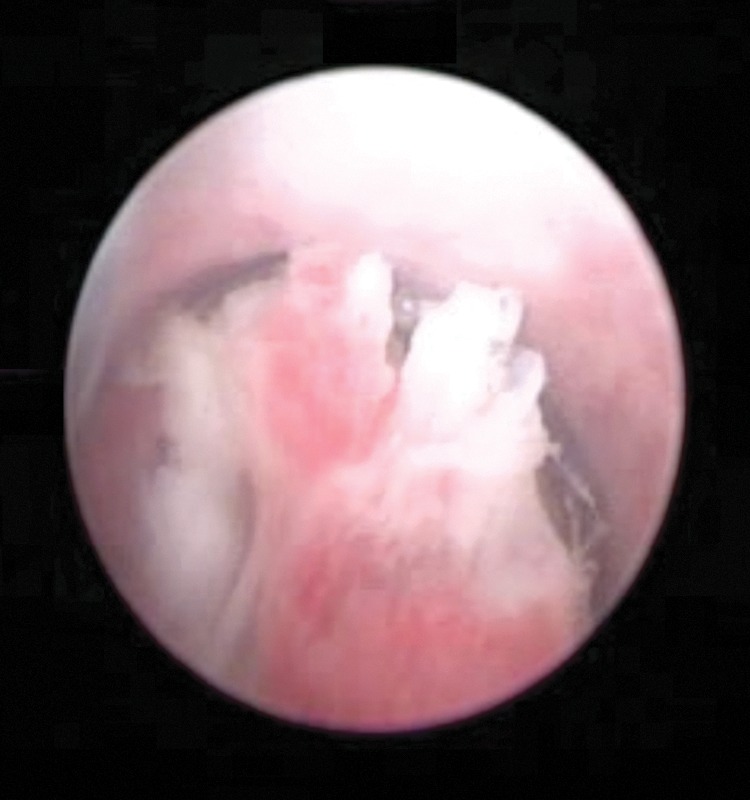
Videouretrocistoscopia que muestra un tumor papilar en la uretra bulbar
Imagen: “Video urethrocystoscopy showing papillary tumor at the level of bulbar urethra.” por Journal of Endourology Case Reports Licencia: CC BY 4.0El cáncer de uretra se estadifica según los LOS Neisseria criterios TNM.
| Categoría T | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Tx | Tumor Tumor Inflammation primario que no se puede evaluar. |
| T0 | Sin evidencia de tumor Tumor Inflammation primario |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Carcinoma papilar no invasivo |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ Carcinoma in situ A lesion with cytological characteristics associated with invasive carcinoma but the tumor cells are confined to the epithelium of origin, without invasion of the basement membrane. Leukoplakia |
| T1 | Invasión tumoral del tejido conjuntivo subepitelial |
| T2 | Invasión tumoral del cuerpo esponjoso o músculo periuretral |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Invasión tumoral del cuerpo cavernoso o vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy anterior |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invasión tumoral de otros órganos adyacentes |
| Categoría T | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Tx | Tumor Tumor Inflammation primario que no se puede evaluar. |
| T0 | Sin evidencia de tumor Tumor Inflammation primario |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Carcinoma papilar no invasivo |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ (compromete la uretra prostática o los LOS Neisseria conductos periuretrales o prostáticos sin invasión del estroma) |
| T1 | Invasión tumoral del tejido conjuntivo subepitelial inmediatamente subyacente al AL Amyloidosis urotelio |
| T2 | Invasión tumoral del estroma prostático que rodea los LOS Neisseria conductos ( al AL Amyloidosis extenderse directamente desde la superficie urotelial o al AL Amyloidosis invadir desde los LOS Neisseria conductos prostáticos) |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Invasión tumoral de la grasa periprostática |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invasión tumoral de los LOS Neisseria órganos adyacentes |
| Categoría N | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Nx | No pueden evaluarse los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos regionales. |
| N0 | No hay metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria nódulos linfáticos regionales. |
| N1 | Metástasis de nódulo linfático regional único en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la región inguinal o pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy verdadera o nódulo linfático presacro |
| N2 | Múltiples metástasis de nódulos linfáticos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la región inguinal o pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy verdadera o nódulos linfáticos presacros |
| Categoría M | Descripción |
|---|---|
| M0 | No existen metástasis a distancia |
| M1 | Metástasis a distancia |
| Estadio | T | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0a | Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio 0is | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio II | T2 | M0 | |
| Estadio III | T1, T2 | N1 | M0 |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | N0, N1 | M0 | |
| Estadio IV | T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | N0, N1 | M0 |
| Cualquier T | N2 | M0 | |
| Cualquier T | Cualquier N | M1 |
La enfermedad localizada (hasta T2) generalmente se trata con cirugía, mientras que las afecciones localmente avanzadas se tratan con terapia multimodal.
Los LOS Neisseria siguientes diagnósticos diferenciales son para un paciente que presenta hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma: