La apendicitis es la inflamación aguda del apéndice vermiforme y la urgencia quirúrgica abdominal más frecuente a nivel mundial. La enfermedad tiene un riesgo de por vida del 8%. Los LOS Neisseria rasgos característicos incluyen dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal periumbilical que migra al AL Amyloidosis cuadrante inferior derecho, fiebre, anorexia Anorexia The lack or loss of appetite accompanied by an aversion to food and the inability to eat. It is the defining characteristic of the disorder anorexia nervosa. Anorexia Nervosa, náuseas y vómitos. Con frecuencia, el diagnóstico puede establecerse clínicamente, pero el diagnóstico por imagenología se utiliza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos inciertos. La tomografía computarizada (TC) proporciona la mayor precisión diagnóstica. La perforación se produce en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 13%–20% de los LOS Neisseria casos y puede presentarse como localizada (absceso/flemón) o como perforación libre con peritonitis Peritonitis Inflammation of the peritoneum lining the abdominal cavity as the result of infectious, autoimmune, or chemical processes. Primary peritonitis is due to infection of the peritoneal cavity via hematogenous or lymphatic spread and without intra-abdominal source. Secondary peritonitis arises from the abdominal cavity itself through rupture or abscess of intra-abdominal organs. Penetrating Abdominal Injury generalizada. El tratamiento estándar es la apendicectomía, pero las perforaciones localizadas suelen tratarse de forma no quirúrgica con antibióticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La apendicitis es la inflamación del apéndice vermiforme.
Temprana:
Tardía:
Perforación:
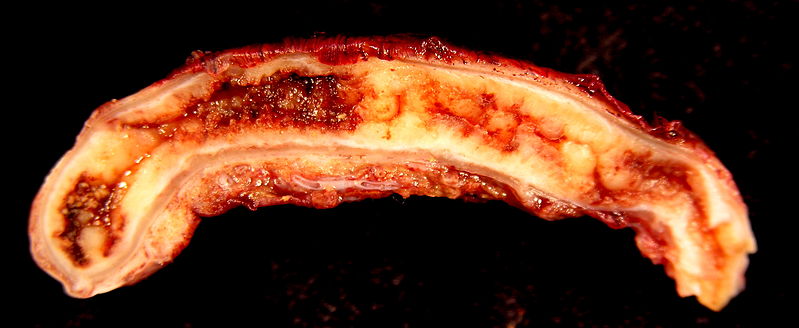
Apendicitis aguda
Imagen: “Acute Appendicitis” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Clásica:
Atípica:
Factores anatómicos:
Síntomas generales:
Examen abdominal:
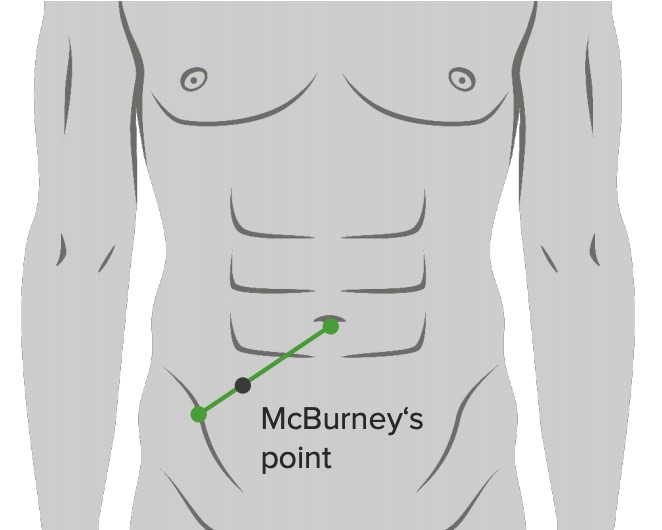
Localización del punto de McBurney: a 2/3 del ombligo en una línea recta desde el ombligo hasta la espina ilíaca anterosuperior
Imagen por Lecturio.
Localización del punto de McBurney: a 2/3 del ombligo en una línea recta desde el ombligo hasta la espina ilíaca anterosuperior
Imagen: “McBurney’s point” por Department of Basic Sciences, School of Medicine. Universidad de Caldas. Manizales, Colombia. Licencia: CC BY 2.5Tacto rectal:
Examen pélvico:
| Síntomas | M – Migratory pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways in the right iliac fossa ( dolor Dolor Inflammation migratorio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa ilíaca derecha) | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| A – Anorexia Anorexia The lack or loss of appetite accompanied by an aversion to food and the inability to eat. It is the defining characteristic of the disorder anorexia nervosa. Anorexia Nervosa ( anorexia Anorexia The lack or loss of appetite accompanied by an aversion to food and the inability to eat. It is the defining characteristic of the disorder anorexia nervosa. Anorexia Nervosa) | 1 | |
| N – Nausea Nausea An unpleasant sensation in the stomach usually accompanied by the urge to vomit. Common causes are early pregnancy, sea and motion sickness, emotional stress, intense pain, food poisoning, and various enteroviruses. Antiemetics and vomiting Vomiting The forcible expulsion of the contents of the stomach through the mouth. Hypokalemia (náuseas y vómitos) | 1 | |
| Signos | T – Tenderness in the right iliac fossa (sensibilidad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la fosa ilíaca derecha) | 2 |
| R – Rebound tenderness Rebound Tenderness Acute Abdomen (sensibilidad de rebote) | 1 | |
| E – Elevated temperature (temperatura elevada) | 1 | |
| Estudios del laboratorio | L – Leukocytosis Leukocytosis A transient increase in the number of leukocytes in a body fluid. West Nile Virus (leucocitosis) | 2 |
| S – Shift to left (desplazamiento a la izquierda) | 1 | |
| Total | 10 |
El diagnóstico por imagenología no es necesario si la puntuación de Alvarado es muy baja (< 3) o alta (> 7).
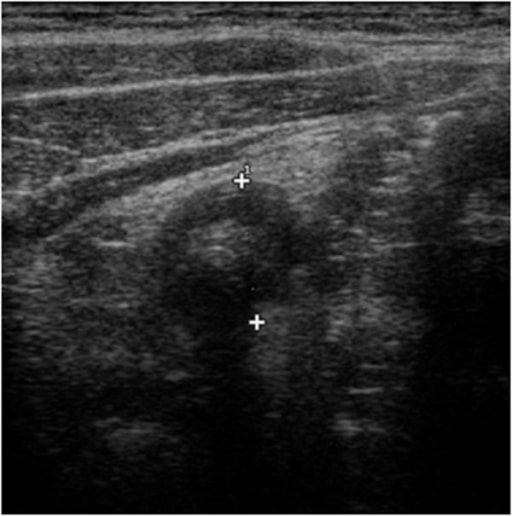
Características de ultrasonido en apendicitis: “signo de la diana” caracterizado por un centro lleno de líquido y rodeado por una mucosa y submucosa ecogénica y una muscularis hipoecoica
Imagen: “Ultrasound features of appendicitis” por Second University of Naples, Department of Clinical and Experimental Internistic F, Magrassi, Naples, Italy. Licencia: CC BY 2.0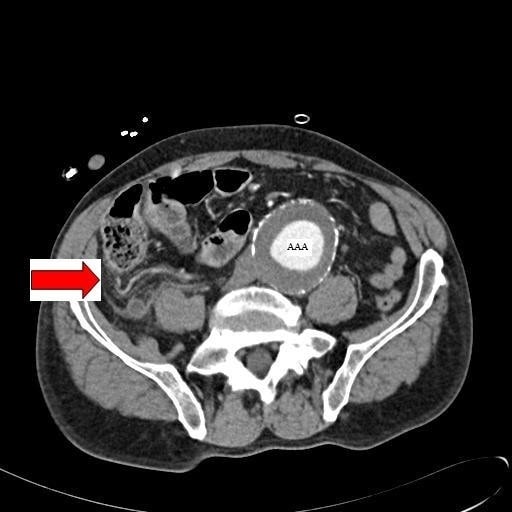
TC abdominal con contraste que muestra un apéndice inflamado (marcado por la flecha roja) en un paciente con un aneurisma aórtico abdominal concomitante (AAA).
Imagen: “Abdominal CT” por Department of General Surgery, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Queen Elizabeth Avenue, Sheriff Hill, Gateshead, Tyne & Wear, NE9 6SX, UK. Licencia: CC BY 2.0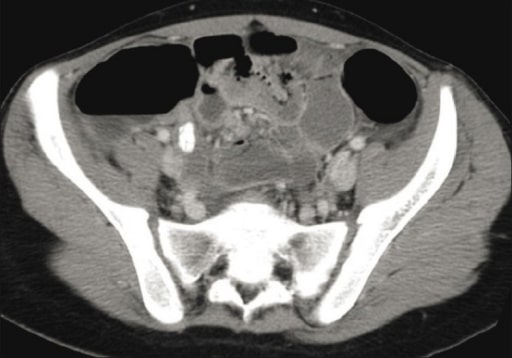
TC pélvica que muestra un apéndice inflamado con un apendicolito
Imagen: “CT scan” por Department of Radiology, King Khalid University Hospital, King Saud University, Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Tratamiento no quirúrgico:
Apendicectomía:
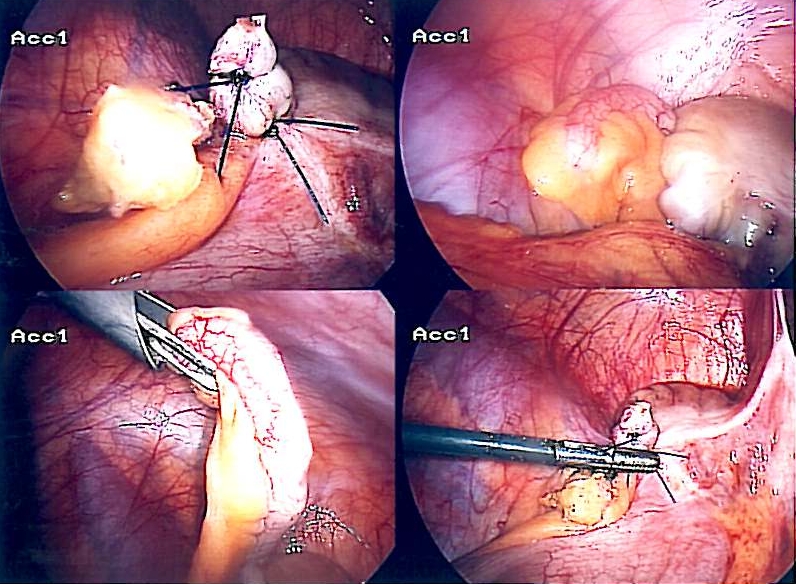
Apendicectomía laparoscópica
Imagen: “Appendix-Entfernung” por Life-of-hannes.de. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoDefinición: rotura apendicular con o sin flemón o formación de absceso.
Tratamiento inicial no quirúrgico:
Apendicectomía de intervalo:
Apendicectomía inmediata: