El ántrax es una infección causada por la bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology Bacillus anthracis Bacillus anthracis A species of bacteria that causes anthrax in humans and animals. Anthrax, que suele afectar a la piel, los LOS Neisseria pulmones o los LOS Neisseria intestinos. El ántrax es una enfermedad zoonótica y suele transmitirse al AL Amyloidosis ser humano a partir de animales o a través de productos animales. Las esporas de Bacillus Bacillus Bacillus are aerobic, spore-forming, gram-positive bacilli. Two pathogenic species are Bacillus anthracis (B. anthracis) and B. cereus. Bacillus pueden persistir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el suelo durante mucho tiempo. Las esporas de Bacillus Bacillus Bacillus are aerobic, spore-forming, gram-positive bacilli. Two pathogenic species are Bacillus anthracis (B. anthracis) and B. cereus. Bacillus también se han utilizado como arma biológica. Los LOS Neisseria síntomas dependen del sistema orgánico afectado. La piel forma pequeñas ampollas con hinchazón alrededor que a menudo se convierten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una úlcera indolora con un centro negro. La exposición por inhalación provoca una neumonía fulminante grave. La exposición intestinal provoca úlceras en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mucosa, diarrea con sangre, dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, náuseas y vómitos. El diagnóstico se establece con cultivos, examen de tejidos y reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de la polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)). El tratamiento incluye antibióticos, antitoxinas y, con frecuencia, el ingreso en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el hospital/cuidados críticos. La mortalidad por enfermedad sistémica sigue siendo elevada.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El ántrax es una enfermedad infecciosa causada por el Bacillus anthracis Bacillus anthracis A species of bacteria that causes anthrax in humans and animals. Anthrax ( B. anthracis B. anthracis A species of bacteria that causes anthrax in humans and animals. Bacillus) y puede tener manifestaciones cutáneas, respiratorias y gastrointestinales.
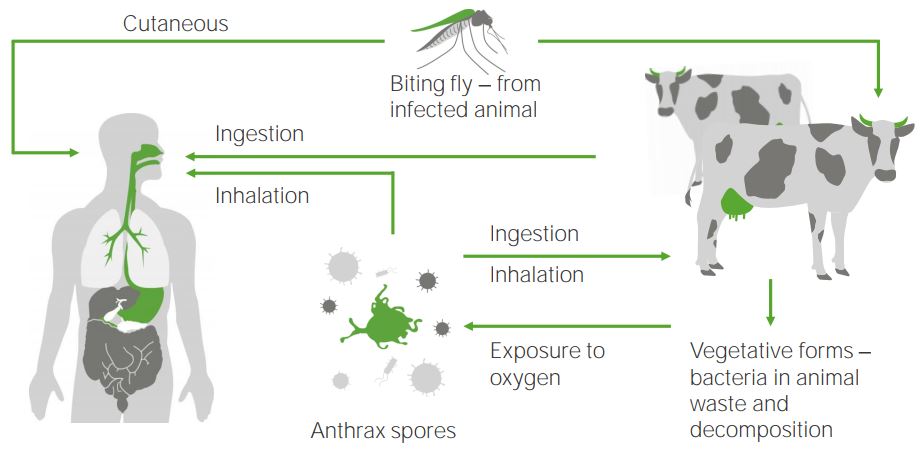
El ciclo del ántrax:
Las esporas del Bacillus anthracis (ántrax) infectan a los seres humanos o a los mamíferos a través de diferentes procesos: por ingestión, por inhalación o por vía cutánea a través de la picadura de un insecto infectado. Las esporas del ántrax se originan en la vegetación de los desechos excretados por el ganado que se expone al oxígeno.
Ántrax cutáneo:
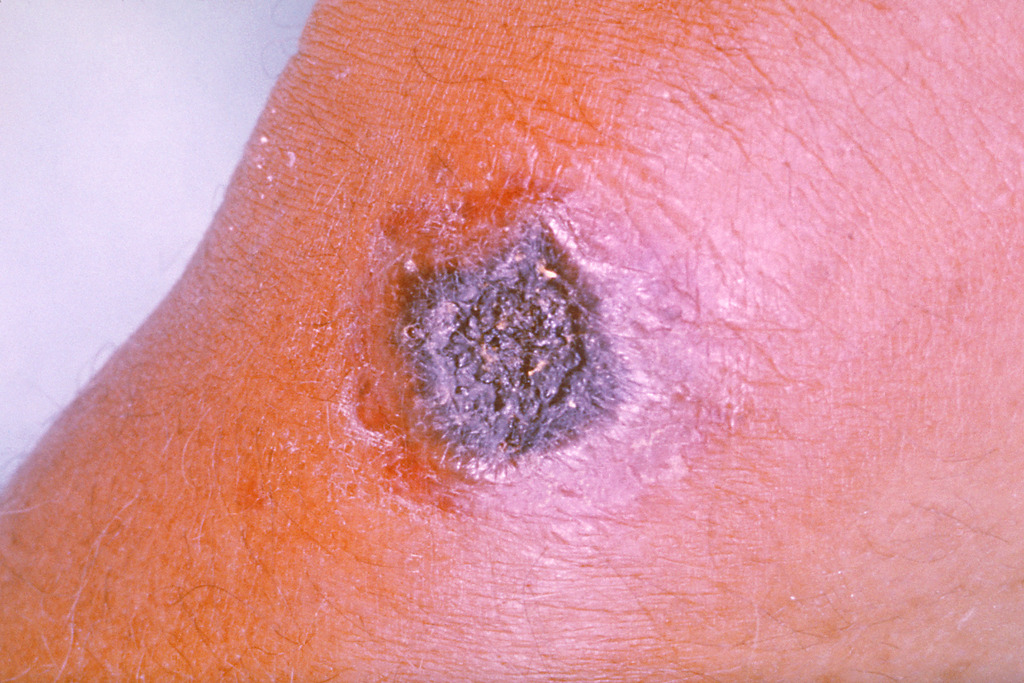
Infección cutánea por ántrax
Image: “Anthrax” por CDC/James H. Steele. Licencia: Dominio Público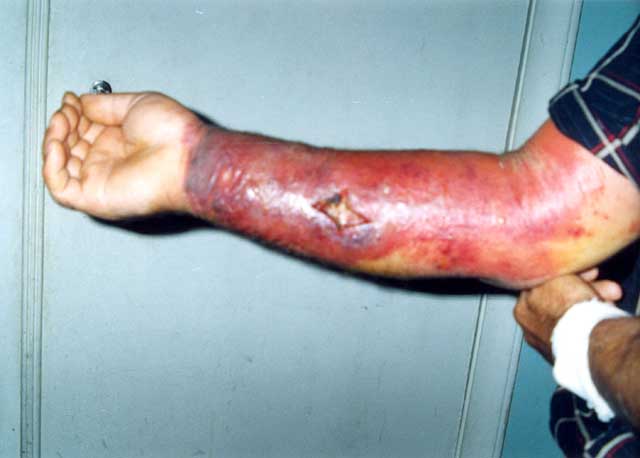
Ántrax cutáneo
Ántrax gastrointestinal:
Ántrax por inhalación (“enfermedad de Woolsorter”):
Ántrax inyectable:
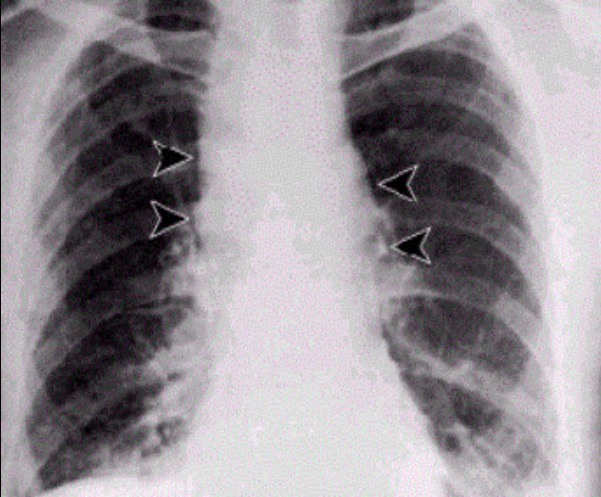
Ántrax pulmonar: La radiografía de tórax muestra un ensanchamiento del mediastino.
Image: “Inhalational anthrax” por JoJan. Licencia: Dominio Público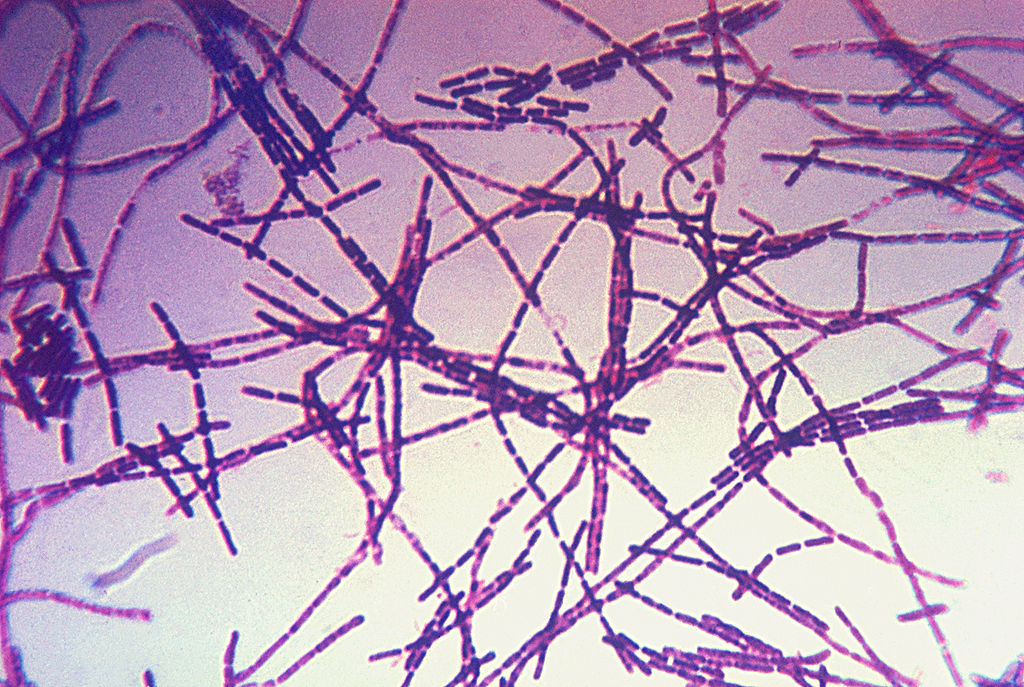
Tinción de Gram de B. anthracis
Image: “Photomicrograph of a Gram stain of the bacterium Bacillus anthracis” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoÁntrax cutáneo:
Ántrax por inhalación:
Ántrax gastrointestinal: