Un absceso hepático piógeno es una infección polimicrobiana que surge de la diseminación contigua o hematógena. El absceso hepático piógeno es el tipo más común de absceso visceral. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden presentar la tríada de fiebre, malestar general y dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuadrante superior derecho. Los LOS Neisseria análisis de laboratorio pueden presentar leucocitosis y pruebas de función hepática anormales, y la imagenología puede revelar lesiones solitarias o múltiples en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ultrasonido o tomografía computarizada. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum imagenología con contraste, las lesiones generalmente aparecen bien definidas con realce del borde. El diagnóstico se establece principalmente mediante imágenes y aspiración para tinción de Gram y se recomienda el cultivo para identificar patógenos y guiar el tratamiento. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos casos, se puede colocar un catéter de drenaje. Para la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria abscesos >3-5 cm, el método principal de tratamiento es una combinación de drenaje y antibióticos intravenosos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos específicos, se utiliza el drenaje quirúrgico o la resección.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Tipos de abscesos hepáticos:
Factores de riesgo:
El lóbulo derecho es el sitio más común de infección debido a su mayor tamaño e irrigación. Existen múltiples vías para infectar el hígado con bacterias:
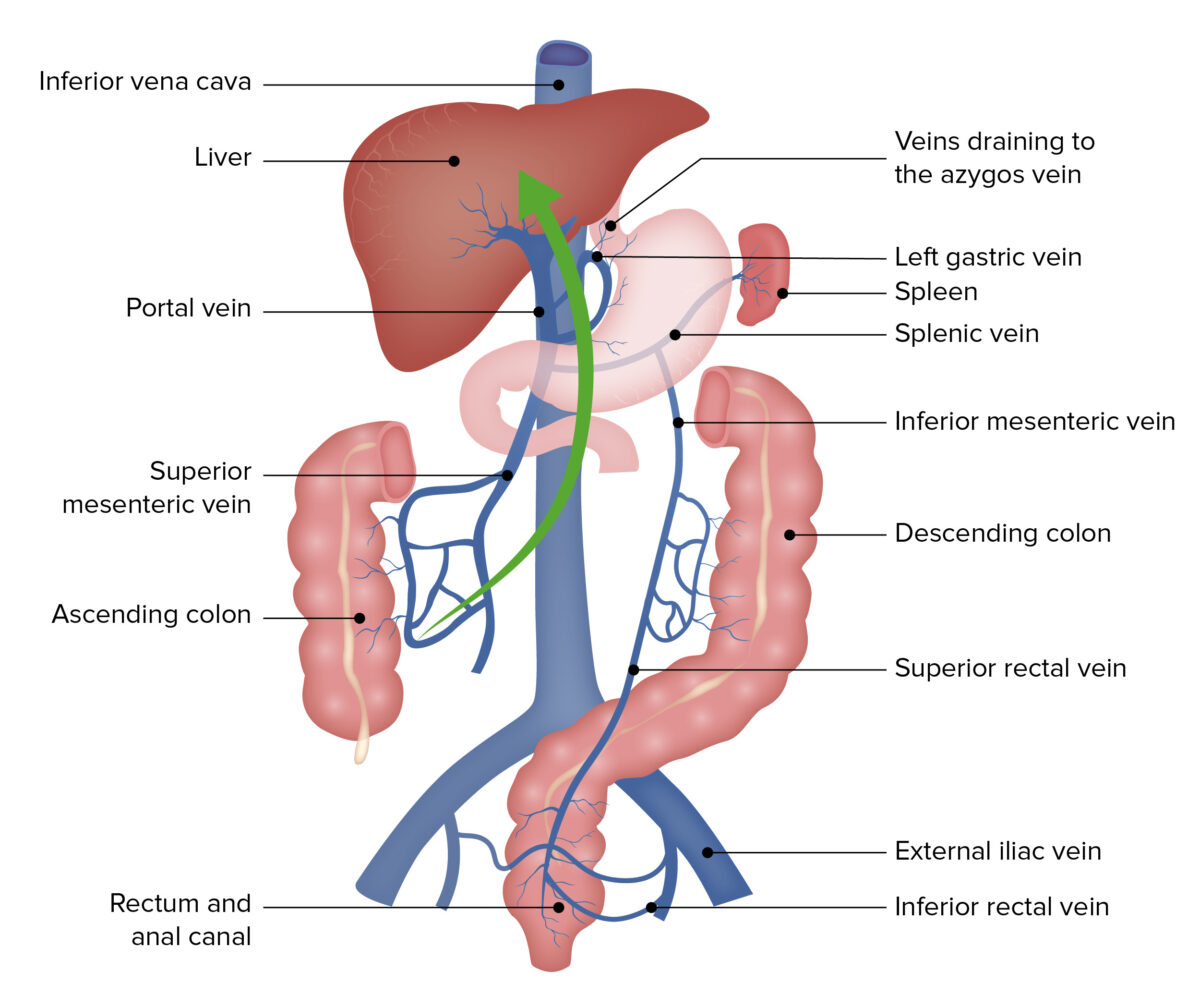
La circulación portal es la ruta principal de propagación bacteriana al hígado, lo que provoca un absceso hepático piógeno.
Imagen por Lecturio.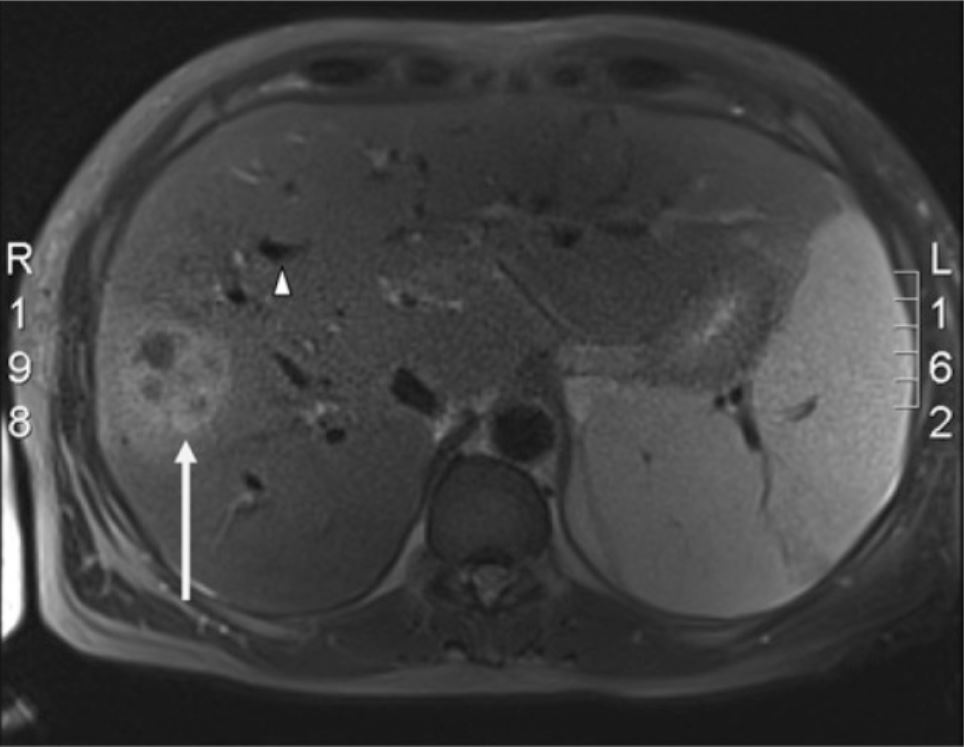
Colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética de hígado:
La lesión ocupante de espacio que se observa (flecha blanca) es compatible con un absceso hepático piógeno y se observa en el lóbulo derecho del hígado. También están presentes múltiples conductos biliares intrahepáticos dilatados (punta de flecha blanca).
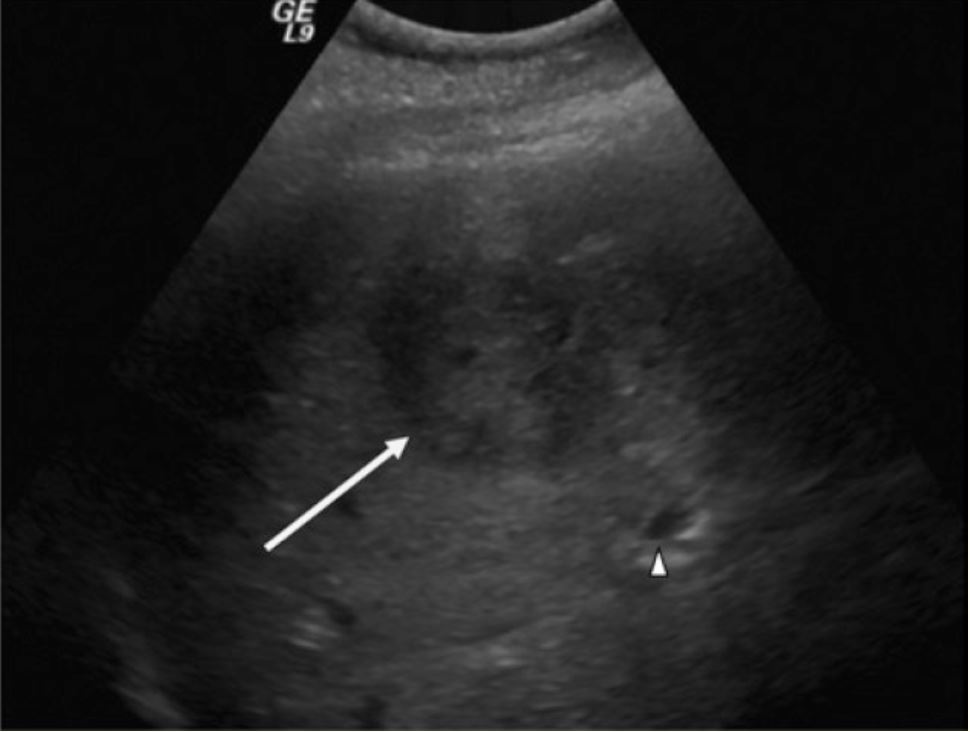
Ultrasonido de una masa hepática sospechosa:
Ultrasonido de cuadrante superior derecho que muestra un área hipodensa y bien delimitada (flecha) y un conducto biliar intrahepático adyacente dilatado (punta de flecha)
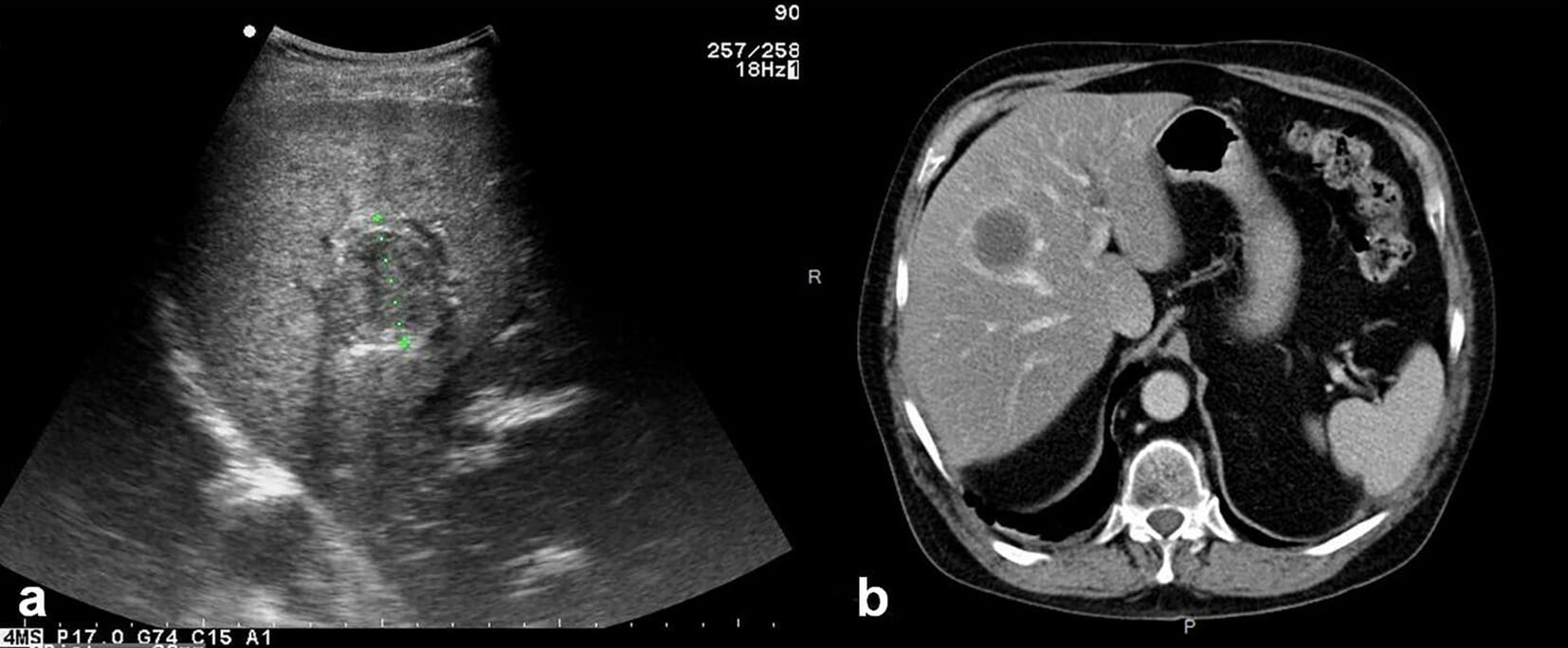
a: ultrasonido que muestra un absceso hepático
b: TC axial no contrastada que muestra un absceso hepático piógeno típicoAntibióticos intravenosos de amplio espectro inicialmente
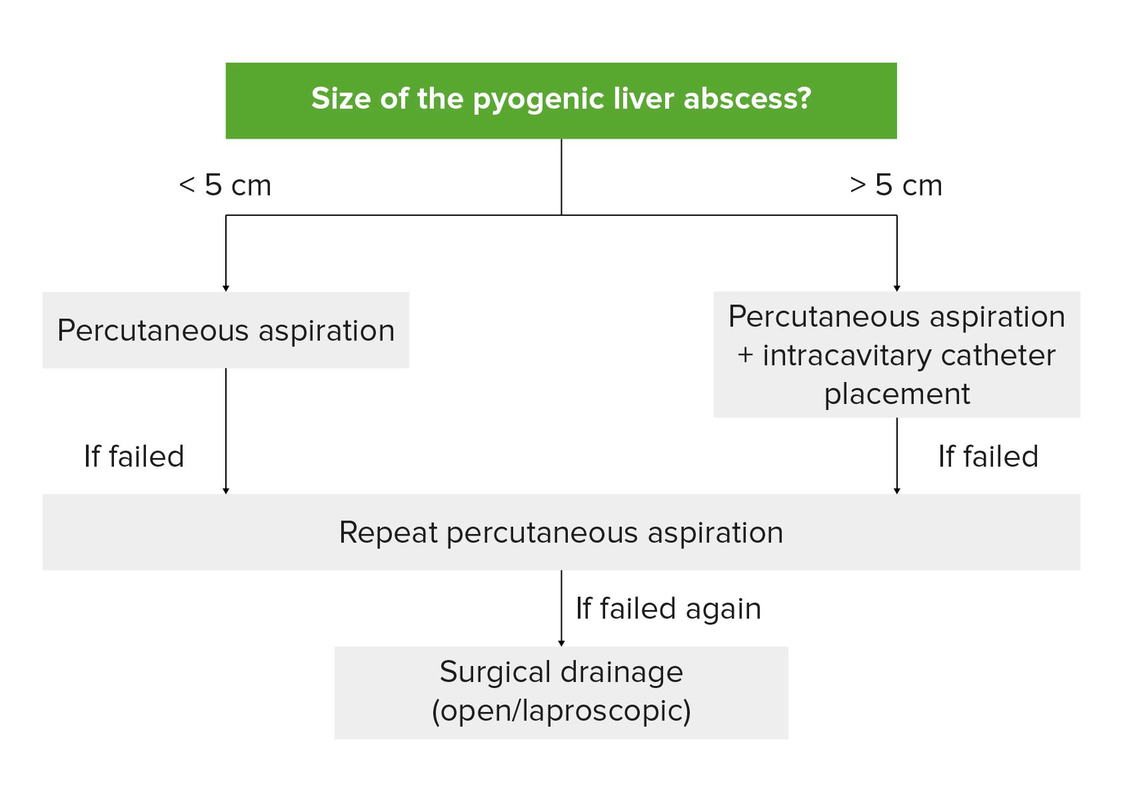
Drenaje de absceso piógeno unilocular:
Con absceso ≤ 5 cm se recomienda drenaje percutáneo (aspiración con aguja o colocación de catéter). Pueden ser necesarios intentos repetidos de aspiración con aguja. Los catéteres de drenaje permanecen colocados hasta que haya un drenaje mínimo. Para un absceso > 5 cm, se recomienda aspiración percutánea con colocación de catéter. El drenaje quirúrgico se realiza cuando falla el drenaje percutáneo en intentos repetidos.
| Absceso hepático amebiano | Absceso hepático piógeno | Quiste de equinococo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Número | Único | Único/múltiple | Único/múltiple |
| Síntomas asociados | Diarrea | Dolor Dolor Inflammation cuadrante superior derecho | Prurito perianal |
| Fiebre | +/- | + | – |
| Imagenología (TC) | Lesión solitaria en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el lóbulo derecho del hígado | Se observa realce del borde periférico con la administración de contraste intravenoso | Realce periférico incluso sin administración de contraste intravenoso (debido a la calcificación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cáscara de huevo) junto con con tabiques internos |
| Hemograma | ↑ Linfocitos | ↑ Neutrófilos | ↑ Eosinófilos |
| Diagnóstico | Serología amebiana | Imágenes + aspiración | Imágenes + serología |
| Tratamiento |
|
Antibióticos intravenosos y drenaje quirúrgico/percutáneo del absceso | Según clasificación (resección quirúrgica, albendazol, tratamiento percutáneo) |
| Hemangioma Hemangioma A vascular anomaly due to proliferation of blood vessels that forms a tumor-like mass. The common types involve capillaries and veins. It can occur anywhere in the body but is most frequently noticed in the skin and subcutaneous tissue. Imaging of the Liver and Biliary Tract hepático | Hiperplasia nodular focal | Adenoma hepatocelular | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Biopsia | Espacios vasculares cavernosos revestidos por células endoteliales planas | Nódulos de hepatocitos localizados con grandes ramas arteriales malformadas y tejido fibroso central | Hepatocitos agrandados con núcleos pequeños y regulares (sin anaplasia); arquitectura lobulillar hepática ausente |
| Hallazgos de la TC | Masa hipodensa bien delimitada con realce periférico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fase arterial y centrípeta relleno en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fases retardadas | Cicatriz estrellada central | Masa bien delimitada con realce heterogéneo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fase arterial e isodensa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum fase venosa (sin lavado de contraste) |
| Quiste simple | Enfermedad poliquística del hígado | Quiste de colédoco | Cistadenoma/cistadenocarcinoma | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descripción | Quiste hepático más común, contiene líquido claro, carece de comunicación con el árbol biliar intrahepático | Varios quistes reemplazan gran parte del hígado | Malformaciones congénitas del árbol pancreatobiliar, múltiples tipos según la ubicación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la sistema biliar |
|
| Presentación Clínica | Generalmente asintomático |
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
Ultrasonido: reemplazo del parénquima hepático por quistes de diferentes tamaños | Ultrasonido, TC, colangiografía transhepática, pruebas de función hepática |
|
| Tratamiento | Tratar con escisión (solo si es sintomático) | Resección hepática parcial o, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos raros, trasplante (solo si hay síntomas) | Todos los LOS Neisseria quistes multiloculados complejos (excepto el equinococo) deben extirparse debido al AL Amyloidosis riesgo de malignidad. |