Las abrasiones, erosiones y úlceras corneales se clasifican como defectos epiteliales de la córnea. Estos defectos se diferencian en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de su profundidad: las abrasiones se producen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el epitelio de la superficie corneal, las erosiones afectan al AL Amyloidosis epitelio corneal y a la membrana basal epitelial, y las úlceras se extienden al AL Amyloidosis estroma subyacente. Los LOS Neisseria defectos de la córnea suelen estar causados por lesiones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ojo provocadas por cuerpos extraños, por causas espontáneas, como la distrofia epitelial corneal, o por infecciones. Estas lesiones se diagnostican con una buena toma de antecedentes y una exploración física adecuada. El examen con lámpara de hendidura se utiliza para la confirmación. El tratamiento incluye el uso de lubricantes tópicos, analgésicos y antibióticos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de las erosiones se utilizan procedimientos quirúrgicos menores. Las complicaciones incluyen infecciones, pérdida de visión, perforación y astigmatismo irregular.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La córnea es la parte transparente y avascular Avascular Corneal Abrasions, Erosion, and Ulcers del ojo que cubre el iris, la cámara anterior y la pupila. Las capas de la córnea incluyen:
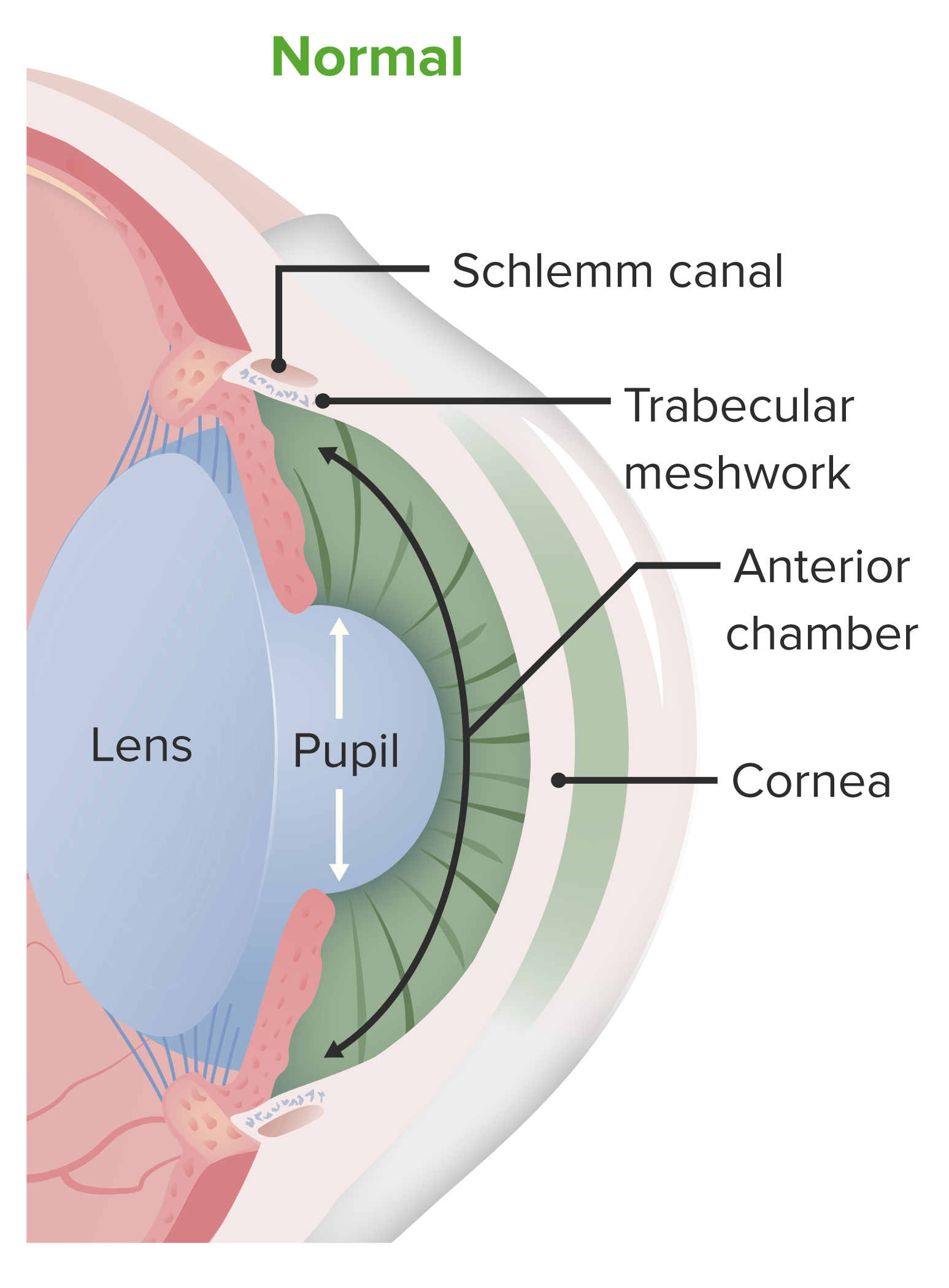
Anatomía de la cámara anterior del ojo:
La córnea contribuye a la refracción inicial de la luz que entra en el ojo y actúa como estructura protectora. La córnea forma parte de la capa fibrosa y recubre la cámara anterior.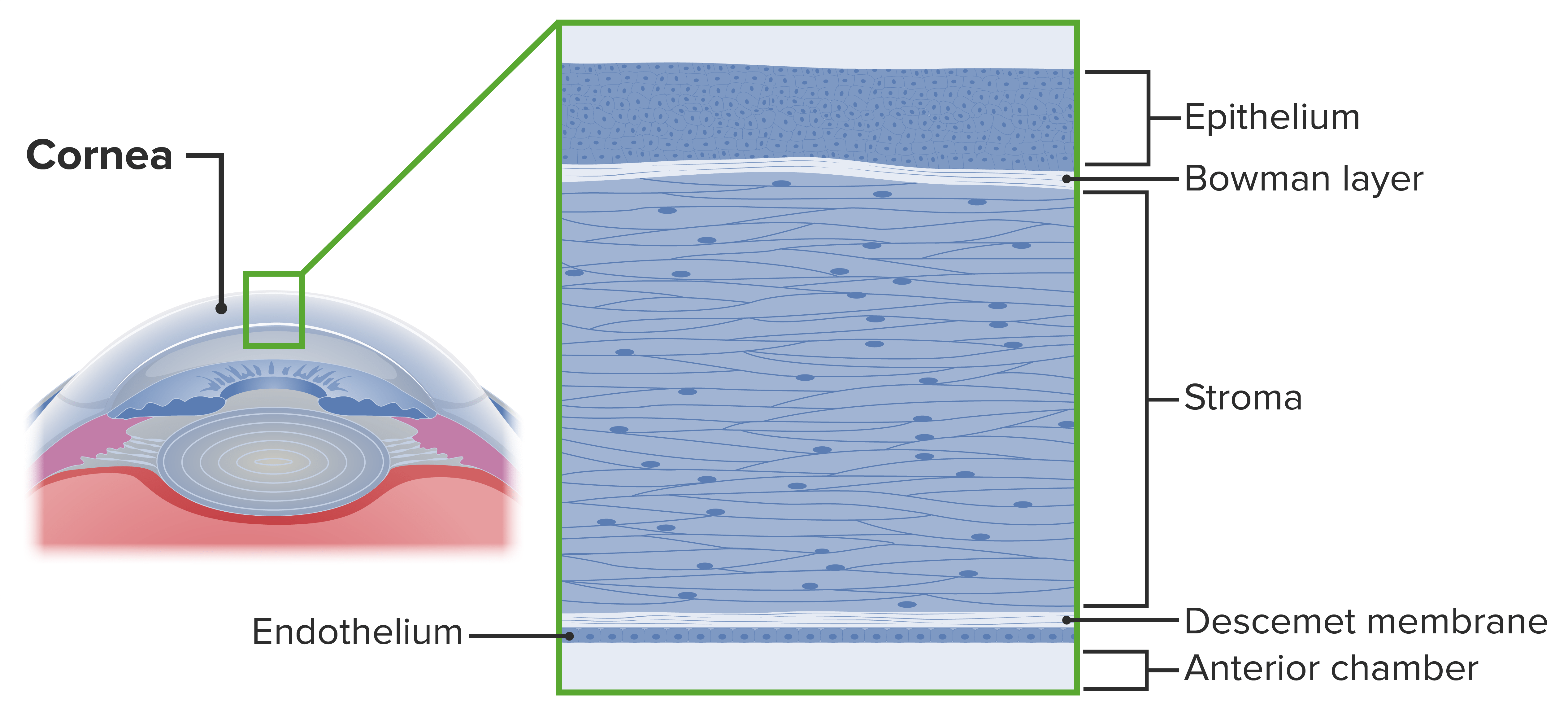
Capas de la córnea
Imagen por Lecturio.Los LOS Neisseria defectos epiteliales de la córnea son afecciones que alteran la integridad estructural de la córnea. Las abrasiones, erosiones y úlceras corneales son defectos del epitelio corneal y se clasifican según la profundidad de la afectación de las capas corneales:
Factores de riesgo para úlceras corneales incluyen:
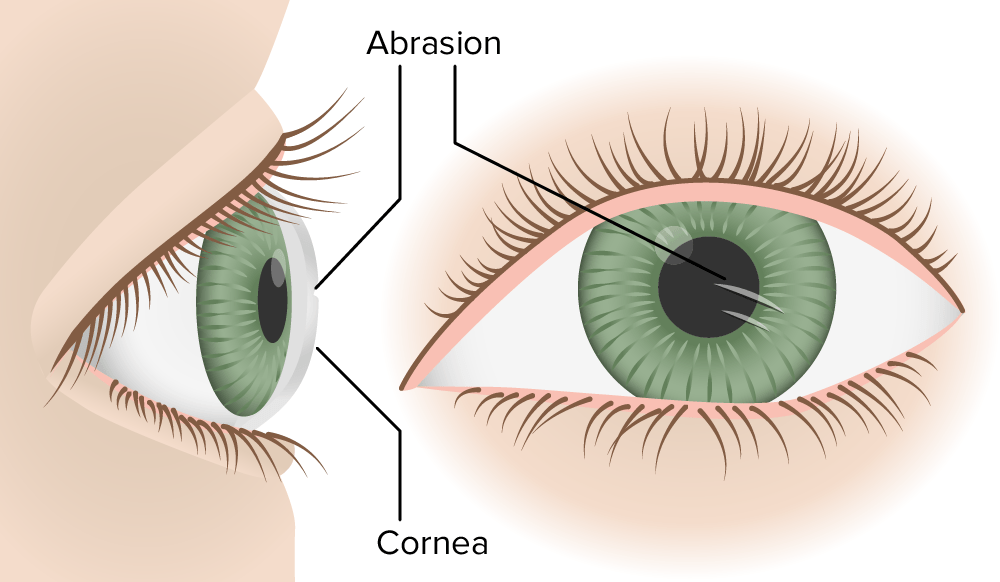
Abrasión corneal
Imagen por Lecturio.Abrasiones y erosiones corneales:
Úlceras corneales:
Los LOS Neisseria individuos suelen tener antecedentes de traumatismos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el globo ocular, ya sea por cuerpo extraño o por el dedo.
Adicional a los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas:
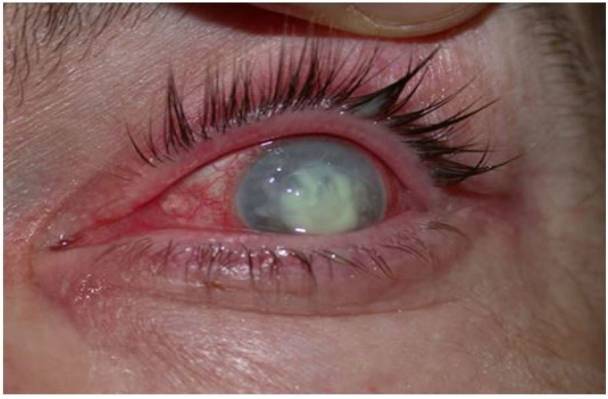
Un caso de úlcera corneal
Imagen: “Corneal ulcer” por Pearson A. Licencia: CC BY 4.0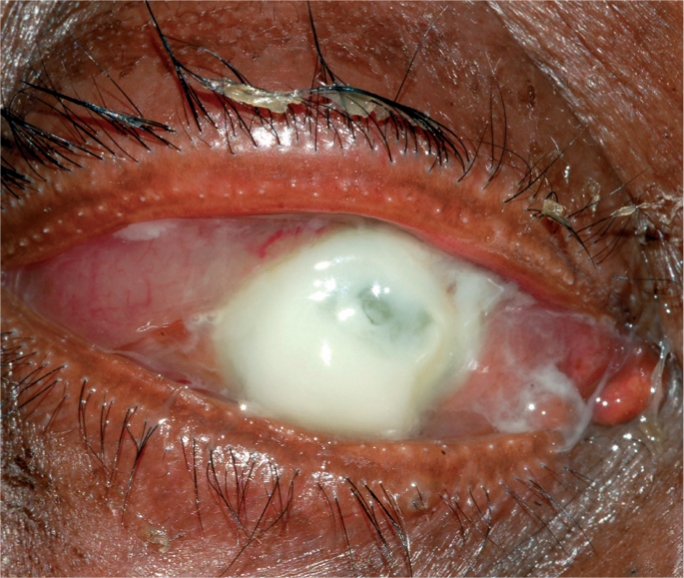
Caso grave de úlcera corneal supurativa
Imagen: “A severe bacterial ulcer caused by Pseudomonas sp.” por Srinivasan M. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Anamnesis y examen oftalmológico:
Toma de antecedentes clínicos y un examen oftalmológico:
Examen con lámpara de hendidura:
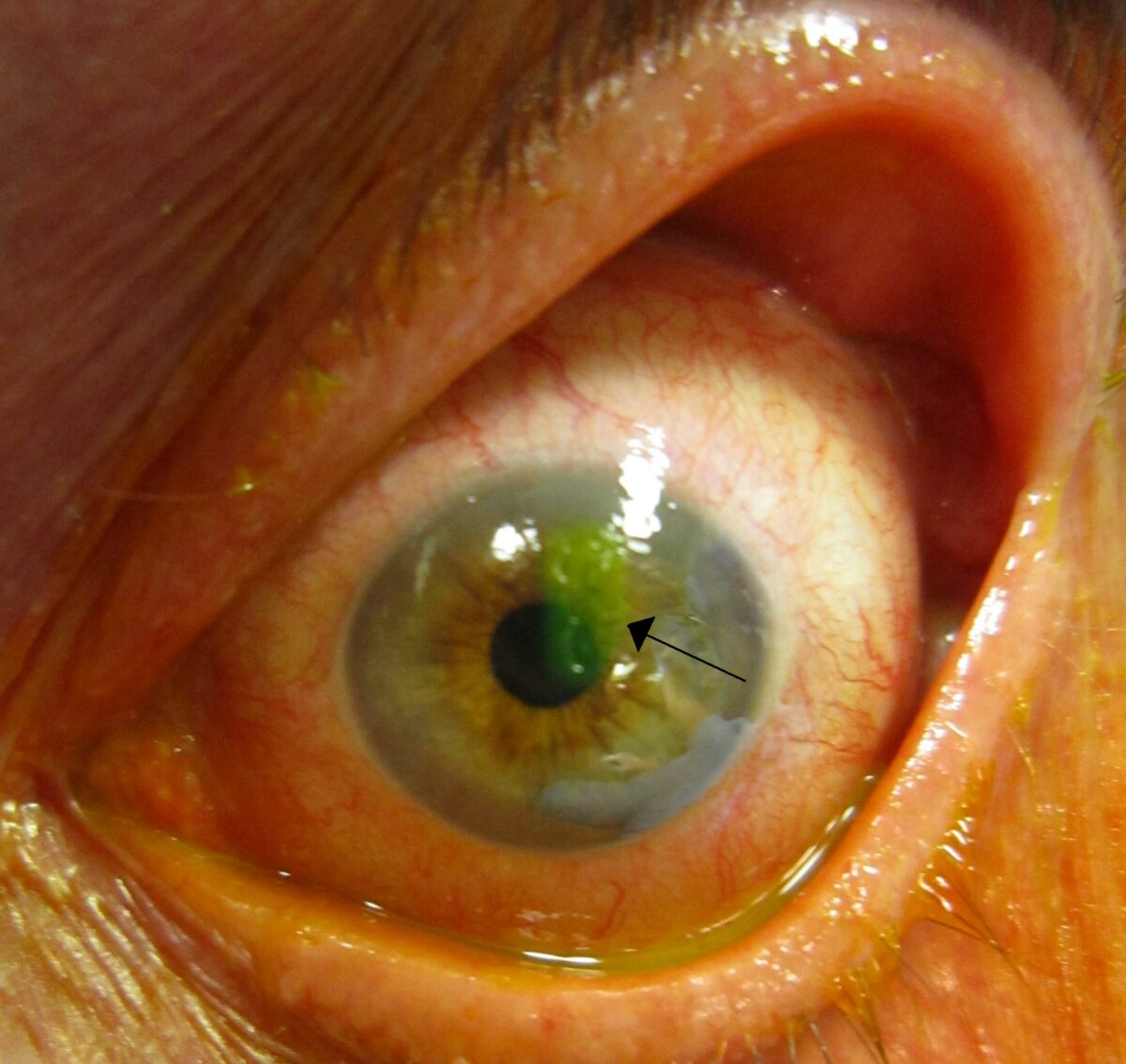
Una abrasión corneal tras la tinción con fluoresceína (flecha)
Imagen: “A corneal abrasion after staining with florescine” por James Heilman. Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0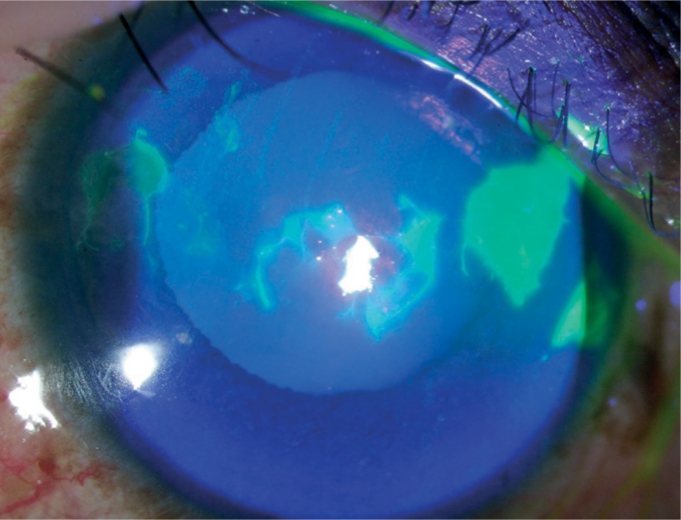
Tinción con fluoresceína:
Las áreas teñidas de verde brillante representan defectos epiteliales
Imagen: “Fluorescein staining” por Upadhyay M.P et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0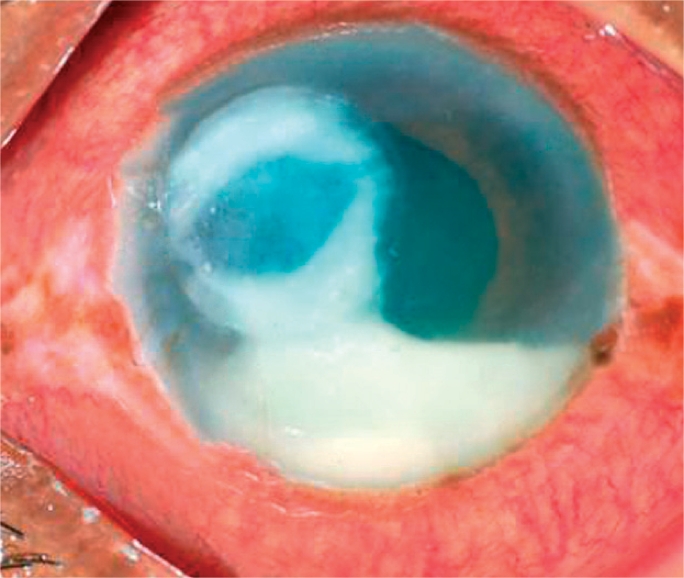
Úlcera corneal bacteriana, con hipopión en la cámara anterior
Imagen: “A bacterial ulcer. The eye is very red and inflamed. Note the ring infiltrate in the cornea and a large hypopyon in the anterior chamber” por Srinivasan M. Licencia: CC BY 2.0