Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH)
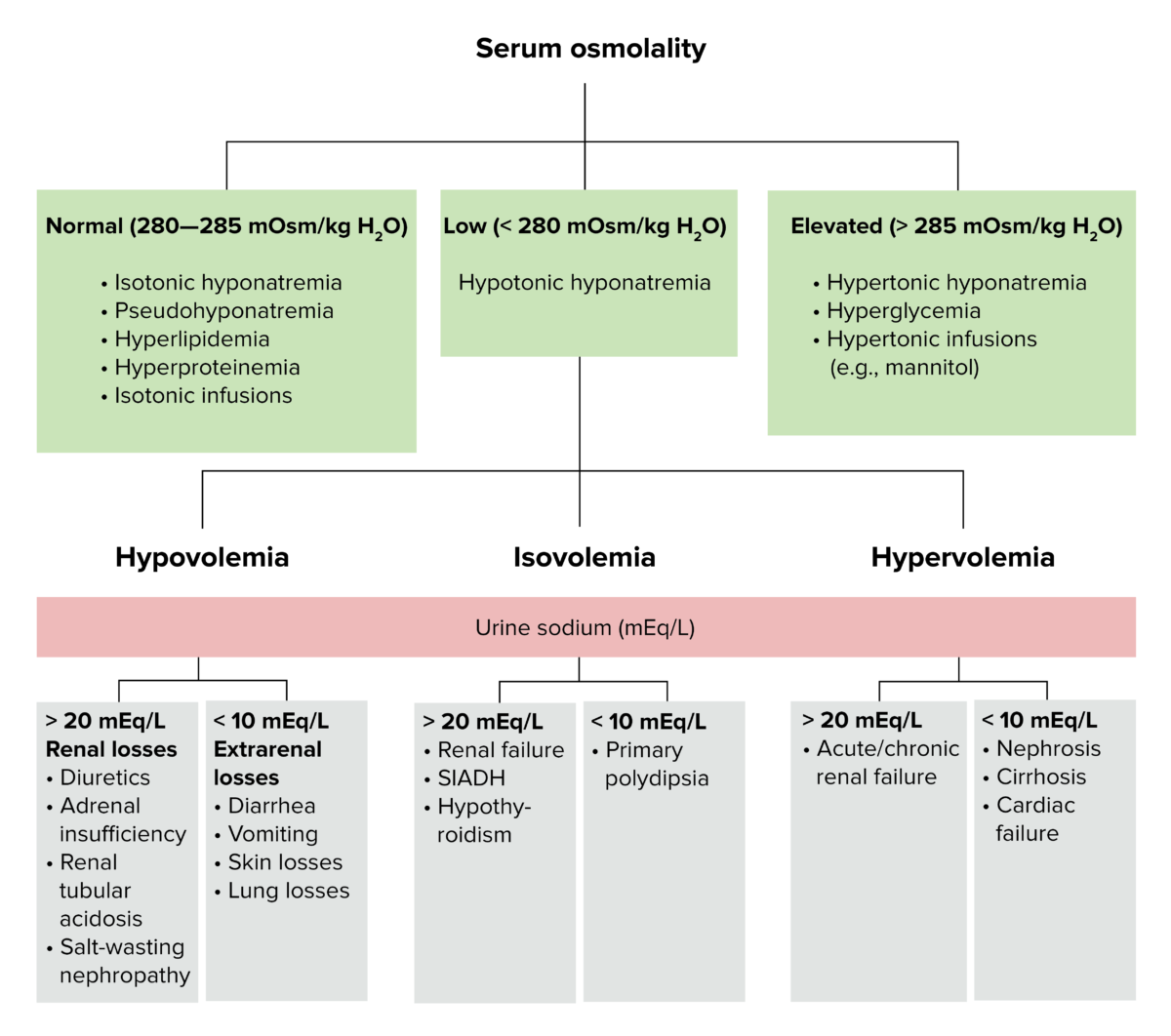
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Source Secreted in response to Function Etiology and Pathophysiology Table: Causes of acquired SIADH Major causes Examples Central nervous system causes Stroke Subarachnoid hemorrhage Infection: Meningitis Encephalitis Trauma Neoplasms Small cell lung cancer Head and neck cancers Pulmonary causes Pneumonia Tuberculosis Atelectasis Medications Carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine SSRIs Vincristine, vinblastine, vinorelbine, cisplatin MAOIs Haloperidol […]
Hyperprolactinemia
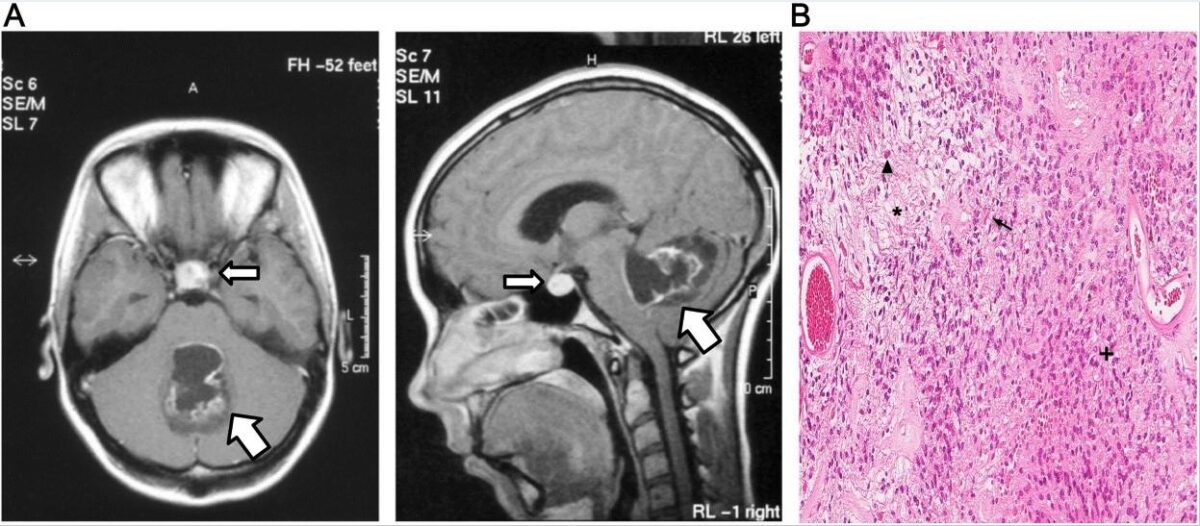
Overview Definition Hyperprolactinemia means abnormally high levels of prolactin (PRL) in the blood. Normal PRL levels (may vary according to the lab): < 23.5–25 ng/mL or μg/L for non-pregnant women 80–400 ng/mL or μg/L for pregnant women < 20–21.5 ng/mL or μg/L for men Epidemiology Occurs in < 1% of the general population The most […]
Diabetes Insipidus
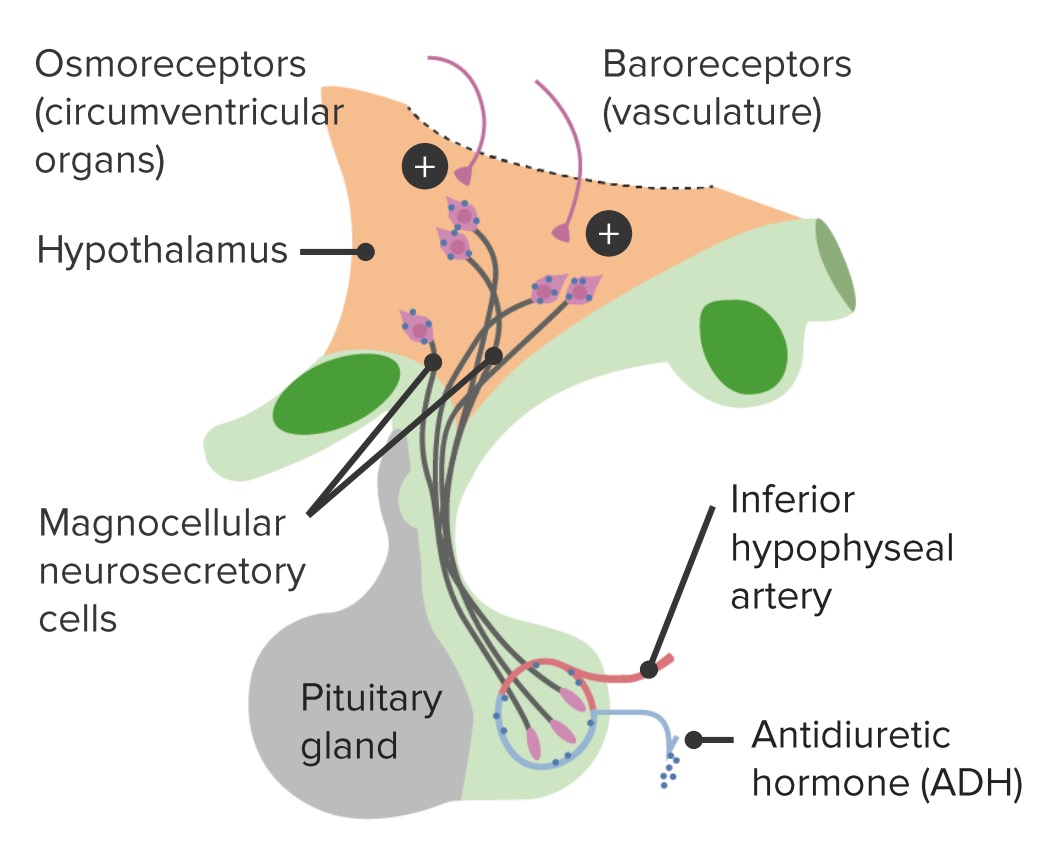
Epidemiology Pathophysiology Role of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Antidiuretic hormone is also called vasopressin. Function: Antidiuretic hormone regulates serum osmolality and blood pressure. Production: Central DI Central diabetes insipidus is caused by the insufficient production of ADH from the hypothalamus or insufficient release from the posterior pituitary gland. Nephrogenic DI Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus is caused by an insufficient response […]