Achalasia
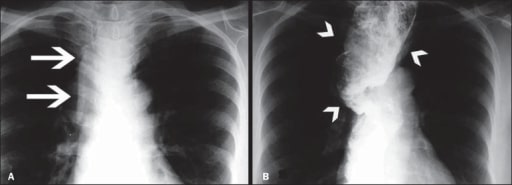
Overview Definition Anatomy and physiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Pathologic process Proposed factors that contribute to the pathogenesis Clinical Presentation and Complications Clinical presentation Complications Diagnosis Diagnostic approach Esophageal manometry Other diagnostic tests Management Approach to management Management options Differential Diagnosis References
Cirrhosis
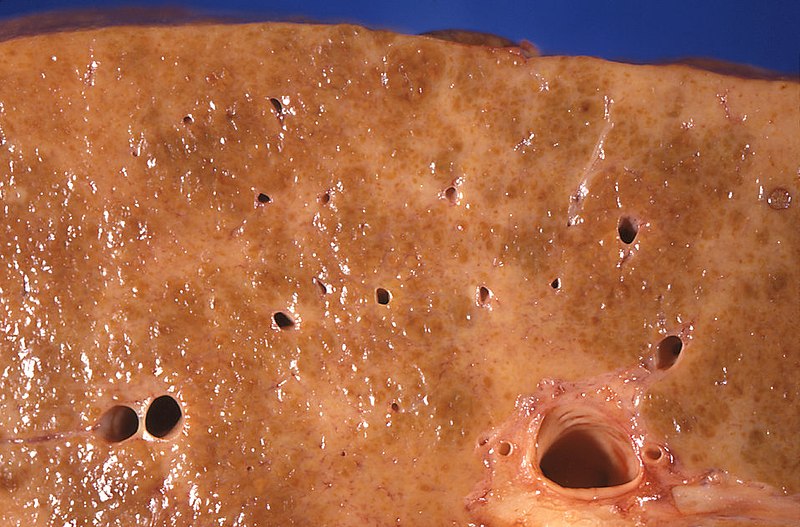
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Two most common causes of cirrhosis: Overview of potential causes: Pathophysiology General Cirrhosis is liver damage that is characterized by diffuse distortion of the basic liver architecture and replacement with scar tissue and regenerative nodules. Secondary effects Classification The Child-Pugh score is used to estimate life expectancy. It serves as […]
Ulcerative Colitis
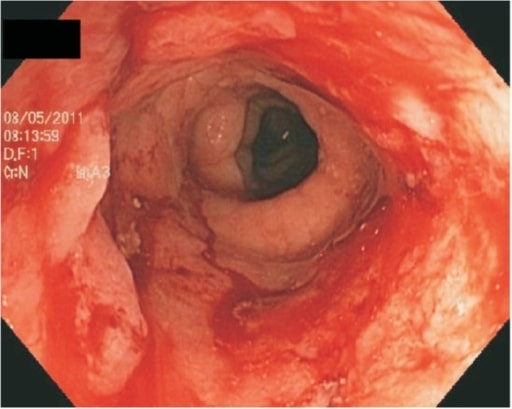
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Risk factors An increased risk of developing ulcerative colitis (UC) may be associated with the following: Pathophysiology The exact pathophysiology is unknown, but is likely associated with a combination of dysregulation of the intestinal epithelium and the immune system. The inflammation invariably involves the rectum and may extend proximally through the […]
Jaundice
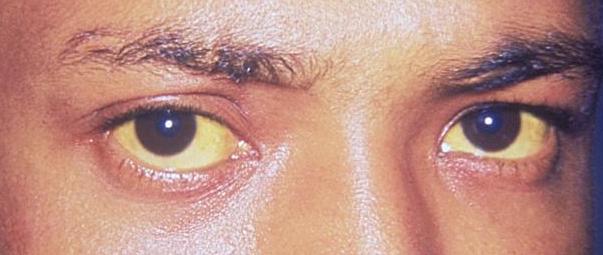
Definition Pathophysiology Jaundice is caused by an elevation of serum bilirubin (hyperbilirubinemia), which can be caused by: Mnemonic Common causes of hyperbilirubinemia can be remembered with the mnemonic HOT Liver: Etiology Etiologies of jaundice can be broken down as conditions that cause either an elevation in indirect, direct, or mixed hyperbilirubinemia (see table below). Causes […]
Autoimmune Hepatitis
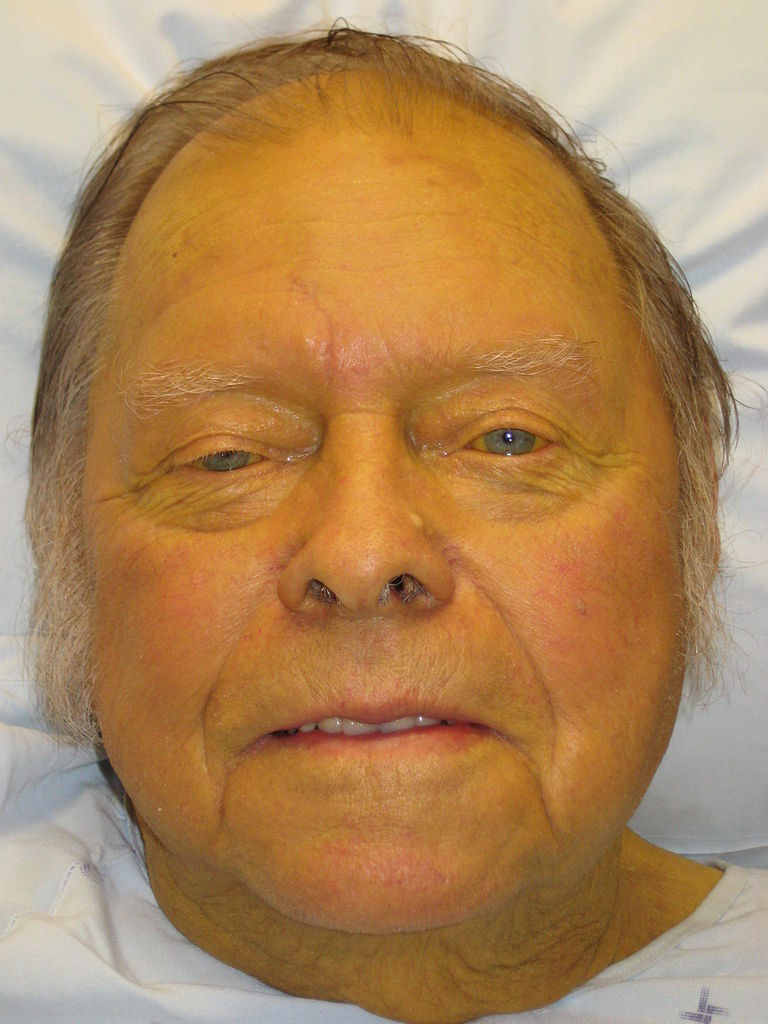
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Associated with other autoimmune conditions (e.g., Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, Graves’ disease, diabetes mellitus, rheumatoid arthritis, celiac disease, Sjogren’s syndrome) Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a differential diagnosis for any patient presenting with at least one of the following: Autoimmune hepatitis is a diagnosis of exclusion, so […]
Wilson Disease
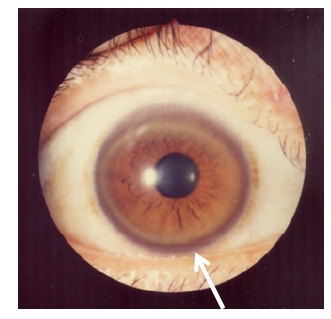
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Wilson disease usually presents in children and young adults. It rarely manifests after 40 years of age. Manifestations are primarily hepatic, neurologic, and psychiatric and may include: Mnemonic Clinical presentation of Wilson disease: ABCD Diagnosis and Management Diagnosis Management Prognosis Differential Diagnosis References