Peptic Ulcer Disease (Clinical)
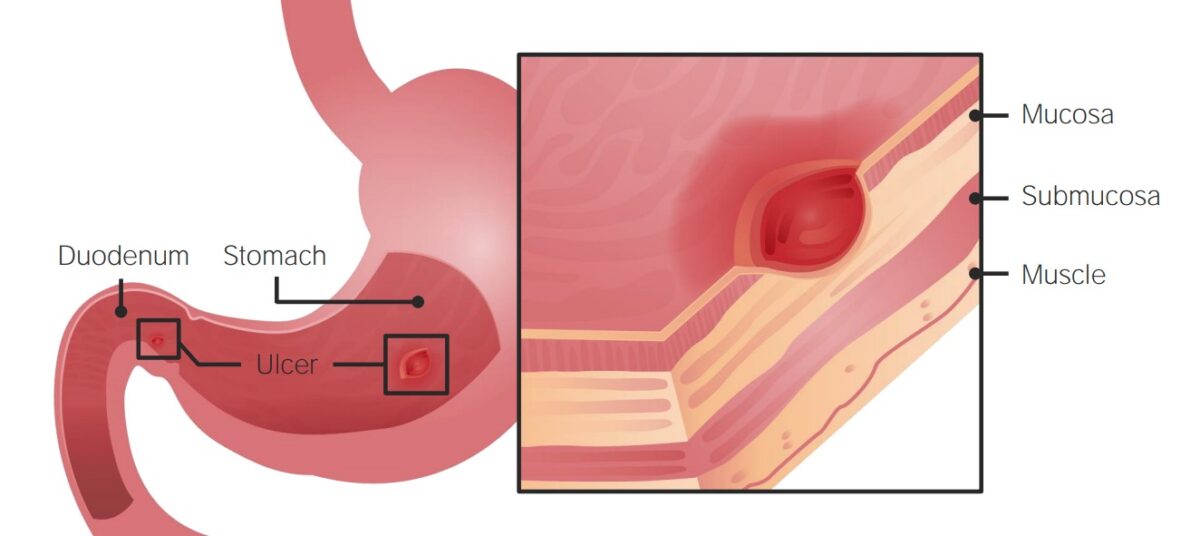
Overview Definition Peptic ulcers are mucosal defects > 5 mm in diameter that penetrate the muscularis mucosae in the wall of the stomach or duodenum. Epidemiology[2,3] Etiology[1-3,13] Risk factors[5–7,13] Pathophysiology Classification[2,3,13] Pathophysiology[3,8,13] PUD results from an imbalance in offending agents (acid, pepsin) and defense mechanisms, which leads to mucosal erosion. Clinical Presentation PUD may be […]
Labial and Genital Herpes (Clinical)
Definition Genital herpes is a mucocutaneous ulcerative disease caused by either herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 or 2.[1,2,10] HSV-1: HSV-2: Types of infections: Epidemiology Etiology Causative agent: herpes simplex virus[1] Transmission[1,2,10] Risk factors[1,2,10] Pathophysiology First infection[1] Primary infection and non-primary infections occur when the virus travels through tiny breaks or even microscopic abrasions in […]
Myocarditis (Clinical)
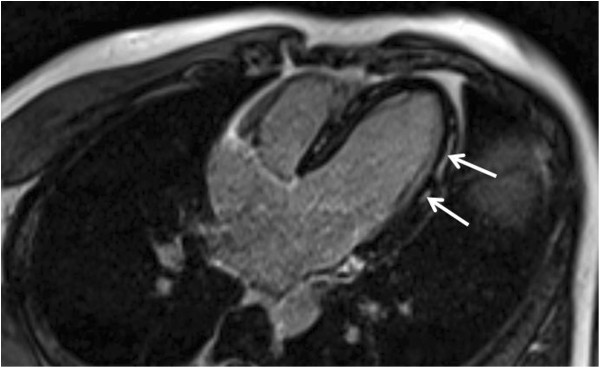
Overview Definition Myocarditis is an inflammatory disease of the myocardium. Epidemiology[5,11] Etiology[2,10,11] The most frequent causes of myocarditis are presumed viral infections, cardiotoxins such as those found in chemotherapy regimens and recreational drugs, and immune system activation. Infectious causes of infectious myocarditis[2,10,11] The following table summarizes the infectious causes of myocarditis. Keep in mind that […]
Cervical Cancer Screening (Clinical)
Overview Cervical cancer[6,12] Epidemiology[1,6,12] Risk factors[12] Screening Rationale Strategies for Screening Screening strategies can be done independently or concurrently (co-testing). Cervical Cancer Screening for Average-Risk Individuals The following recommendations are for average-risk individuals.[1-7] This group includes individuals who are fully vaccinated against HPV. Cervical Cancer Screening for Special Populations High-risk individuals[1,3,6,7] Certain conditions have a […]
Vitiligo (Clinical)
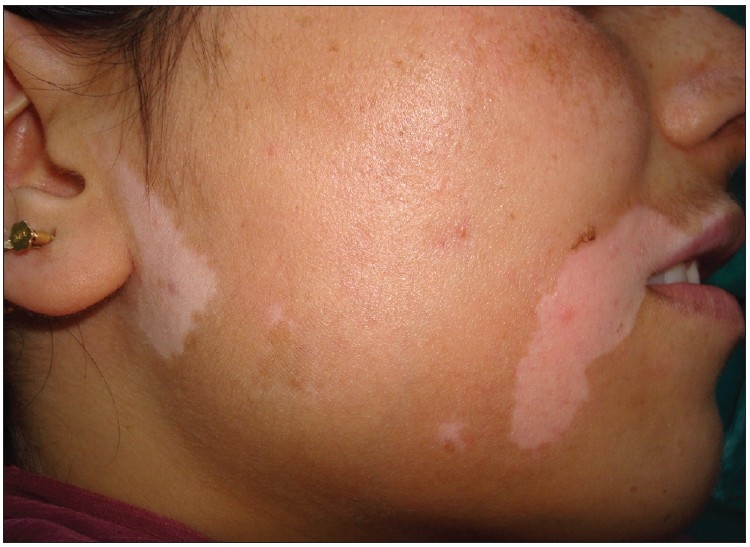
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Vitiligo is a progressive skin condition in which there is destruction of melanocytes resulting in the loss of skin pigmentation. Epidemiology[1] Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology[1,3,8] The cause of vitiligo is unknown but is postulated to be a result of multiple factors. Pathophysiology[1,8] Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation Vitiligo results in […]
Atrioventricular block (AV block) (Clinical)
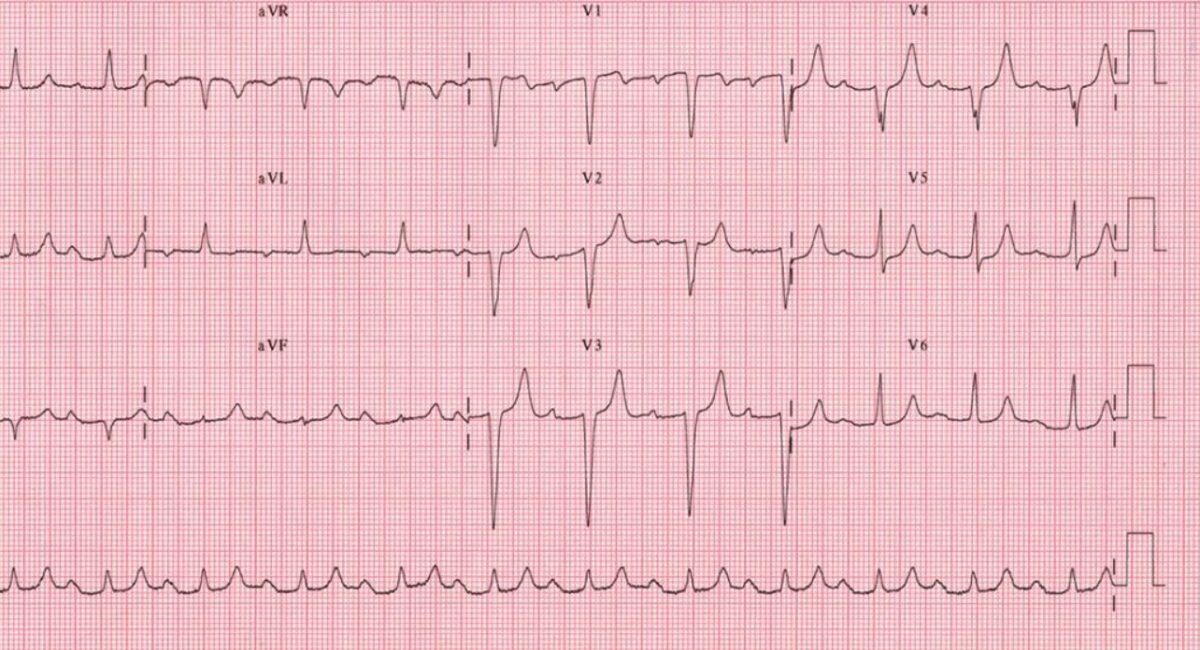
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1] Etiology[1,2,7,10] Pathophysiology and Classification Atrioventricular (AV) block is a delay, or interruption, in the electrical impulse as it passes from the atria to the ventricles through the AV node or the His-Purkinje system. Atrioventricular block is classified based on the severity of the disruption. 1st-degree AV block[1,7,10] 2nd-degree AV block[1,4,5,7,10] 2nd-degree […]
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (Clinical)
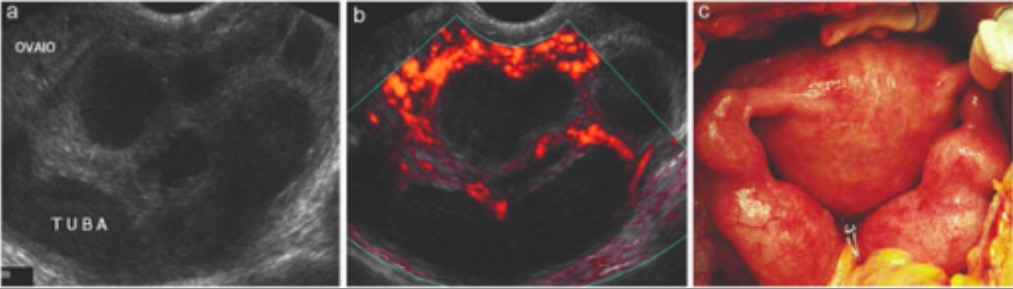
Overview Definition Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an acute upper genital tract infection in women that affects the uterus, fallopian tubes/oviducts, ovaries, and possibly the adjacent pelvic organs. Epidemiology[4,5] Etiology[1,4,5,7] Pathophysiology Normal pelvic protection[2,4] Pelvic infection[2‒4] Clinical Presentation Symptoms typically occur rather acutely over several days, though subclinical or chronic PID may develop more slowly, […]
Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (Clinical)
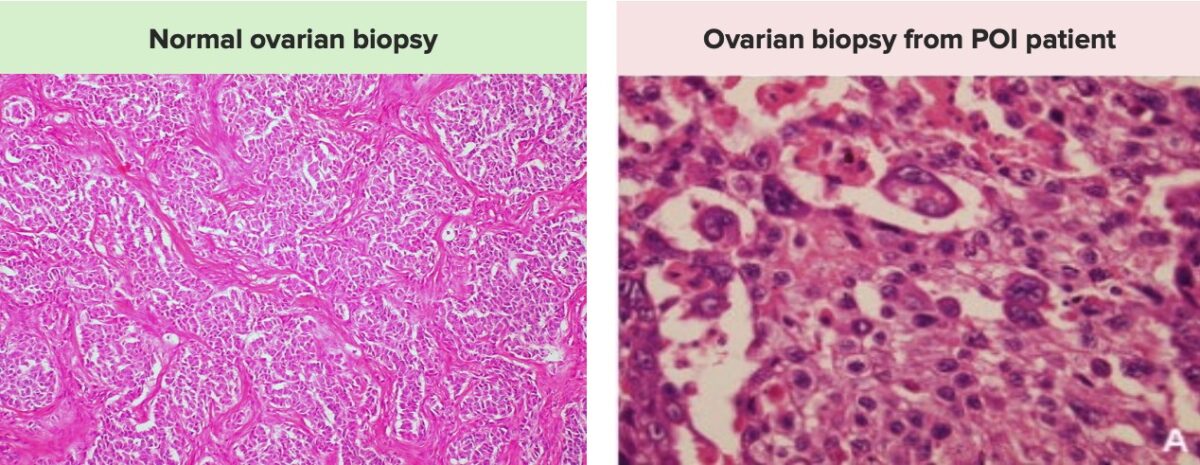
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Primary ovarian insufficiency is the depletion or dysfunction of ovarian follicles resulting in cessation of ovulation and menses prior to age 40. Epidemiology[1,4,6] Pathophysiology Normal physiology of hypothalamic–pituitary–ovarian (HPO) axis[2,4,6] Hypothalamus: Pituitary: Ovary: Clinical importance of functioning HPO axis in younger women: Pathophysiology of POI[2,4,6] Etiology Primary ovarian insufficiency can be […]
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (Clinical)
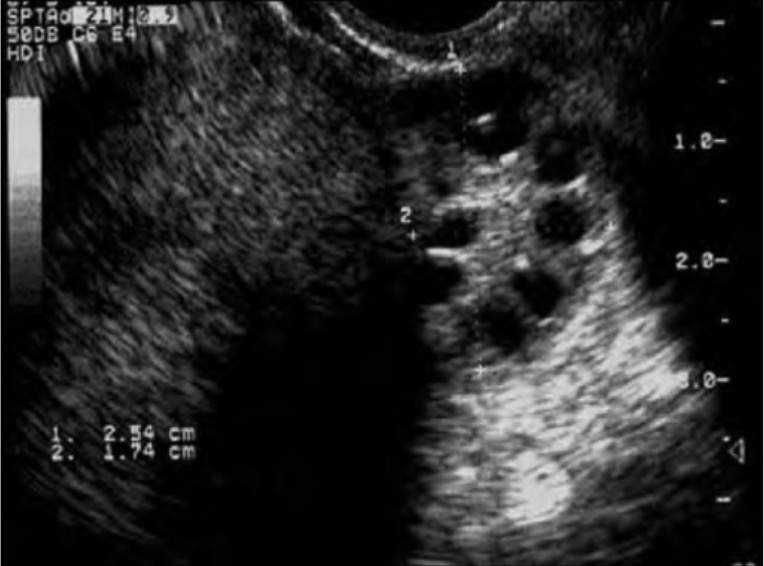
Epidemiology and Pathophysiology Epidemiology Pathophysiology The exact mechanisms are unknown, but thought to be complex and include both genetic and environmental factors. Metabolic syndrome and obesity are often, but not always, present and likely contribute to the pathophysiology in some individuals. Clinical Presentation Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) should be suspected in any reproductive-age female with […]
Epiglottitis (Clinical)
Epidemiology Etiology Epiglottitis can be bacterial, viral, fungal, or noninfectious. In previously healthy children, most causes are bacterial.[1,3,9] Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Management Management may vary based on practice location. The following information is based on US and UK guidelines. Airway management[2,3,8,9] Epiglottitis is an airway emergency, especially in the pediatric population. Preparation for early tracheal […]