Oligohydramnios (Clinical)
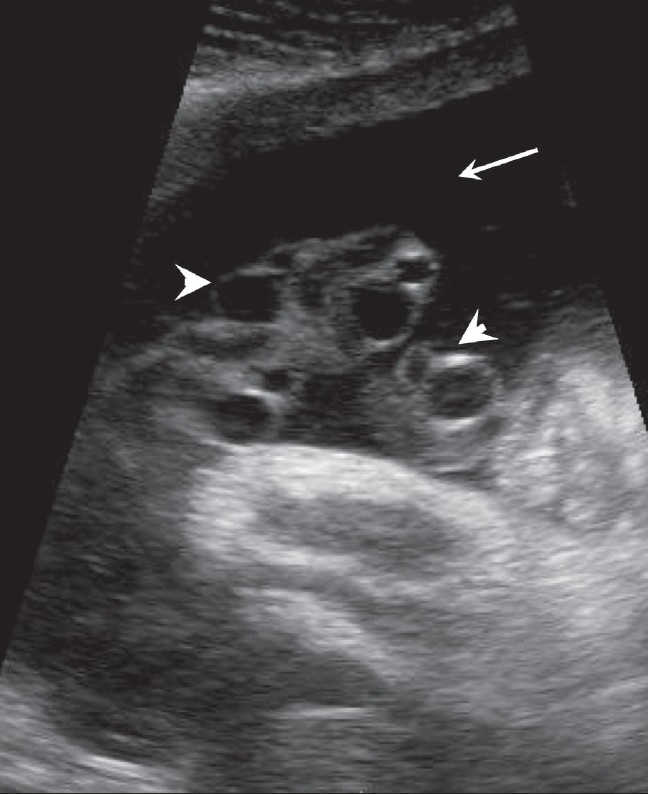
Overview Definition Decreased amniotic fluid volume for gestational age is referred to as oligohydramnios. Oligohydramnios is diagnosed based on ultrasound measurements of amniotic fluid volume and can be defined as either: Anhydramnios is an extreme case of oligohydramnios with no measurable pockets of amniotic fluid present. Epidemiology[4,5,8,9] Pathophysiology and Etiology Normal amniotic fluid production[5,7,9] Amniotic […]
Ectopic Pregnancy (Clinical)
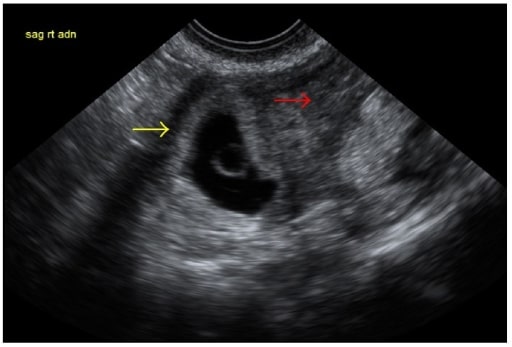
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[5] Etiology[5,8,9,12] Ectopic pregnancy (EP) can occur when the fertilized egg does not enter the uterine cavity by way of the fallopian tube by the 5th to 6th day of gestation. Clinical Presentation Ectopic pregnancy can present before, during, or after rupture. Early on (prior to rupturing), symptoms can be relatively mild, […]
Frostbite (Clinical)
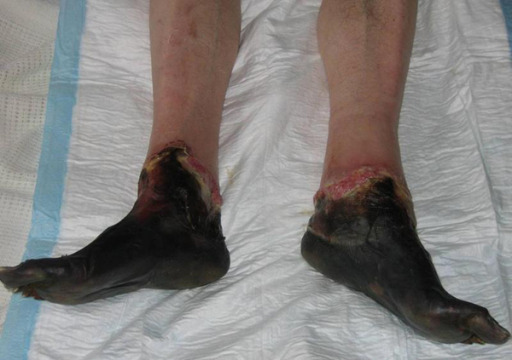
Overview Definition Frostbite is injury to tissue resulting from cold exposure at temperatures below 0°C (32°F). Frostbite exists on the severe end of a spectrum, with frostnip and pernio at the milder end. Epidemiology[1,2,4] Pathophysiology[1,2,4] Frostbite injury results from: 4 phases: Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis The diagnosis of frostbite is clinical and should be distinguished […]
Nephrolithiasis (Clinical)
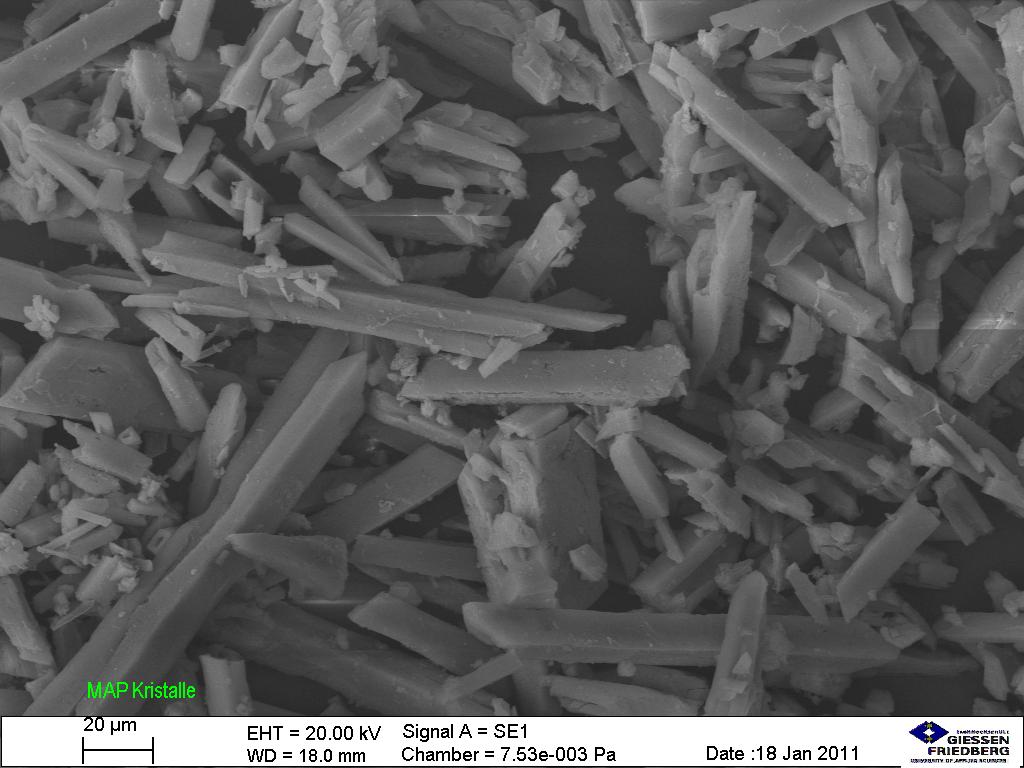

Overview Definition[15,18] Nephrolithiasis (also known as kidney stones, urolithiasis, or urinary calculi) is the formation of stones anywhere along the urinary tract. Classification[1,2,15,18] There are 5 main types of kidney stones: Epidemiology[18] Etiology[2,3,18] Nephrolithiasis occurs when normally soluble material supersaturates the urine and crystal formation begins. Risk factors[2,3,18] Pathophysiology Underlying medical (including genetic) and environmental […]
Carotid Artery Stenosis (Clinical)
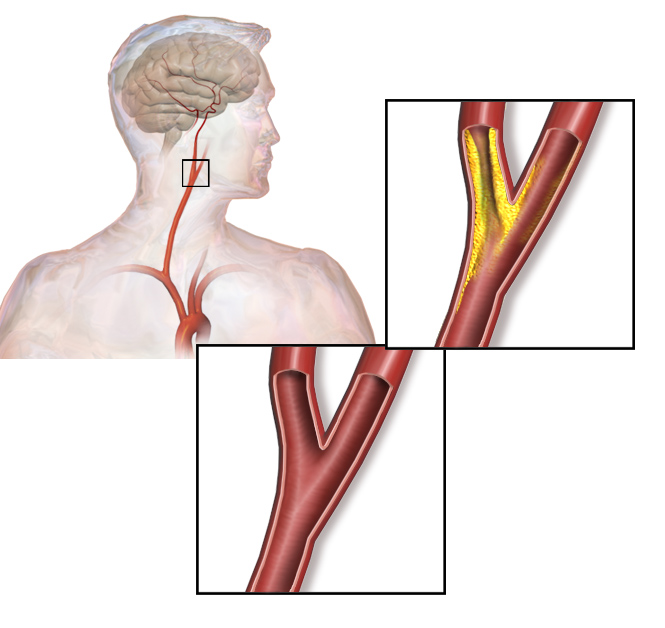
Overview Definition Carotid artery stenosis is a narrowing of the common and internal carotid arteries (ICAs) secondary to atherosclerosis. Epidemiology[1–3,5] Etiology[5] Pathophysiology Carotid stenosis can cause symptoms from a state of low flow or embolization. Low flow results from progressive narrowing of the carotid artery: Embolization: Clinical Presentation Asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis: carotid atherosclerosis without […]
Endometriosis (Clinical)
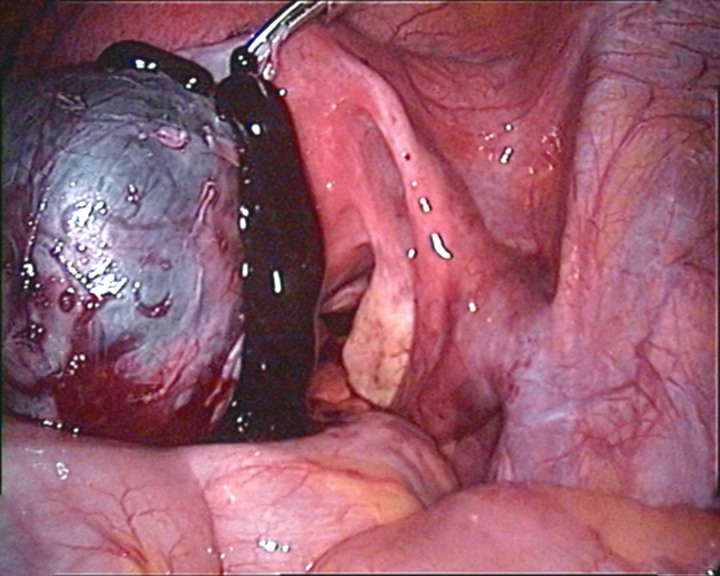
Overview Definition[8] Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrial glands and stroma implant outside of the uterus. These implants can be highly inflammatory but are generally not malignant. Epidemiology[1–3,9] Risk factors[3,13–15] Pathophysiology Contributing factors[3,14,15] Theories about the establishment of implants[2,3,9,13–15] Sites of ectopic implantation[8,9] Histologic phenotypes[3,7] There are 3 primary phenotypes that can be identified […]
Septic arthritis (Clinical)
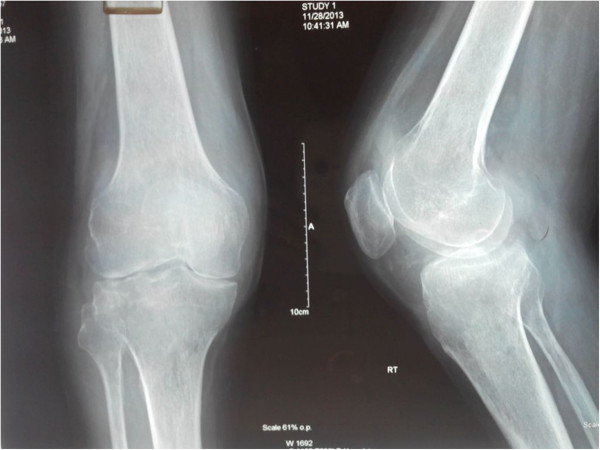
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,9] Etiology[1,7] The majority of septic arthritis infections are monomicrobial. Common organisms include: Risk factors[1,3,5,7,11] Table: Most common organisms in septic arthritis, based on some notable underlying risk factors Risk factors Infectious agents No specific risk factor S. aureus Prosthetic joint replacement S. aureus (particularly MRSA) S. epidermidis (creates biofilms on prosthetics) […]
Mastitis (Clinical)
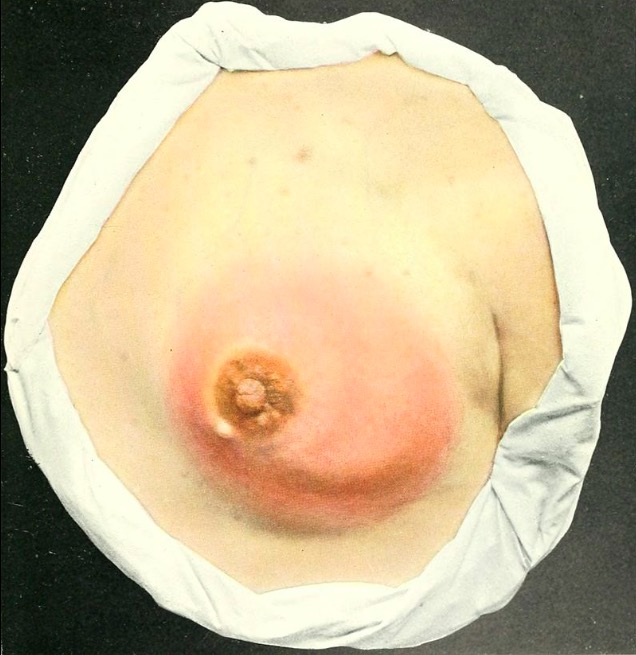
Overview Definition Mastitis refers to inflammation of the breast that may or may not be associated with infection. Classification[3–5] Epidemiology[1,2,4,5] Etiology and Pathophysiology Lactational mastitis[4,6,7] Non-lactational mastitis[1,2,5,9] Periductal mastitis: IGM: Clinical Presentation General[3–5] Lactational mastitis[4,7] Periductal mastitis[2,5,9] IGM[1,5] Diagnosis Lactating mothers[6,7] Non-lactating women[1,9] Periductal mastitis: IGM: Management Lactational mastitis Non-lactational mastitis Periductal mastitis: IGM: Differential […]
Erythema Infectiosum (Clinical)
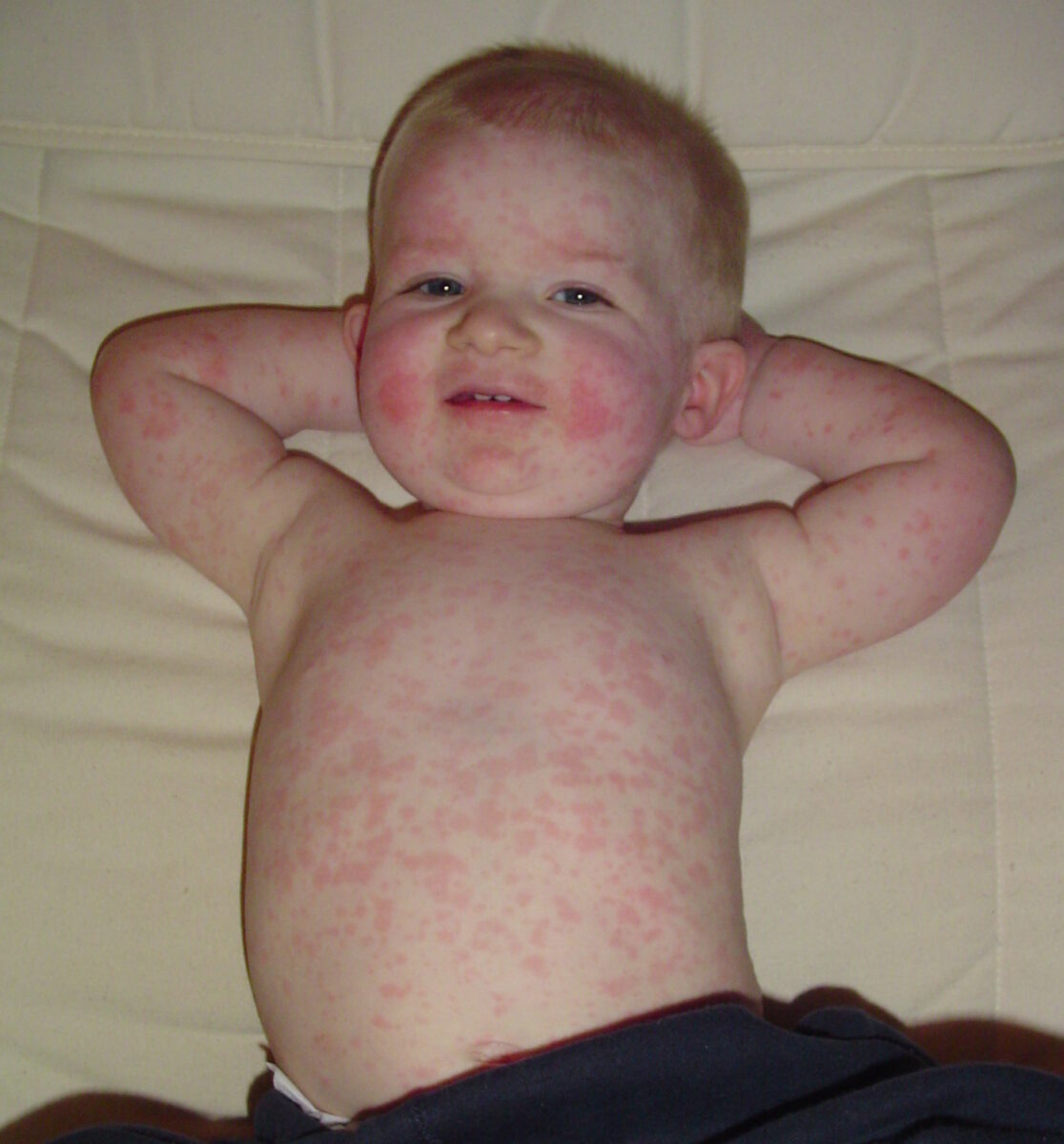
Overview Definition Erythema infectiosum is an illness caused by parvovirus B19, which presents with fever and a characteristic rash. Epidemiology[1–3] Pathophysiology Mode of transmission[3,4,15] Incubation[3,14,15] The incubation period is 4–21 days. Pathogenesis[3,7] Clinical Presentation Initial prodromal symptoms (viremia)[3,5,14,15] Later symptoms (viremia resolved)[3,5,14,15] Complications[4–6,8,13,14] Diagnosis and Management Diagnostic approach[4,10,13–15] Treatment Erythema infectiosum is generally a self-limited […]
Gonorrhea (Clinical)
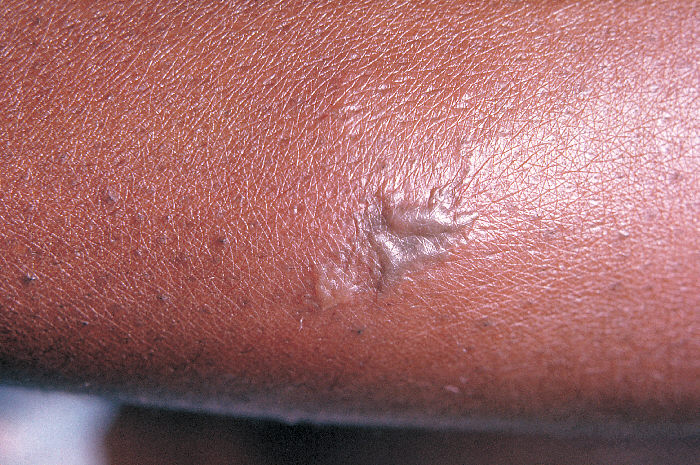
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[2,3,5,8] Etiology[1,2,8] Gonorrhea is caused by the pathogen Neisseria gonorrhoeae (N. gonorrhoeae): Risk factors: Pathophysiology Transmission[1,2] Virulence factors[1,6,8] Pathogenesis[1,6,8,12] Antimicrobial resistance[2,13] Clinical Presentation Urogenital infection in men[2,3,9,17,18] Urogenital infection in women[2,3,9,17,18] Infections in individuals following genital reconstructive surgery (GRS)[17] Extragenital infections[2,3,9] Disseminated gonococcal infection[3,10,17] Clinical presentation in children[2,21] Newborn infections: After the […]