Kawasaki Disease (Clinical)
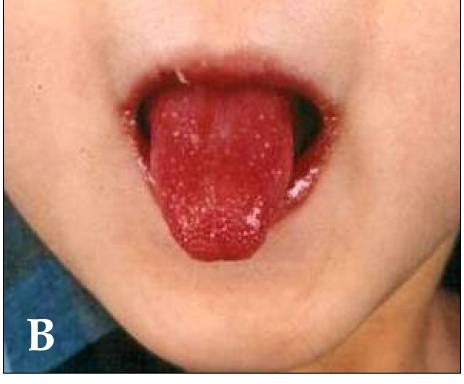
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,2,6] Etiology[1,3–5] The etiology of Kawasaki disease (KD) is unknown. There are several theories: Pathophysiology Kawasaki disease is a systemic, inflammatory illness that affects medium-sized arteries, especially the coronary arteries.[3,4] Clinical Presentation Commonly presenting symptoms[6] Less common manifestations Table: Other manifestations of Kawasaki disease[6] System Manifestations Gastrointestinal Diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, liver […]
Hypothyroidism (Clinical)
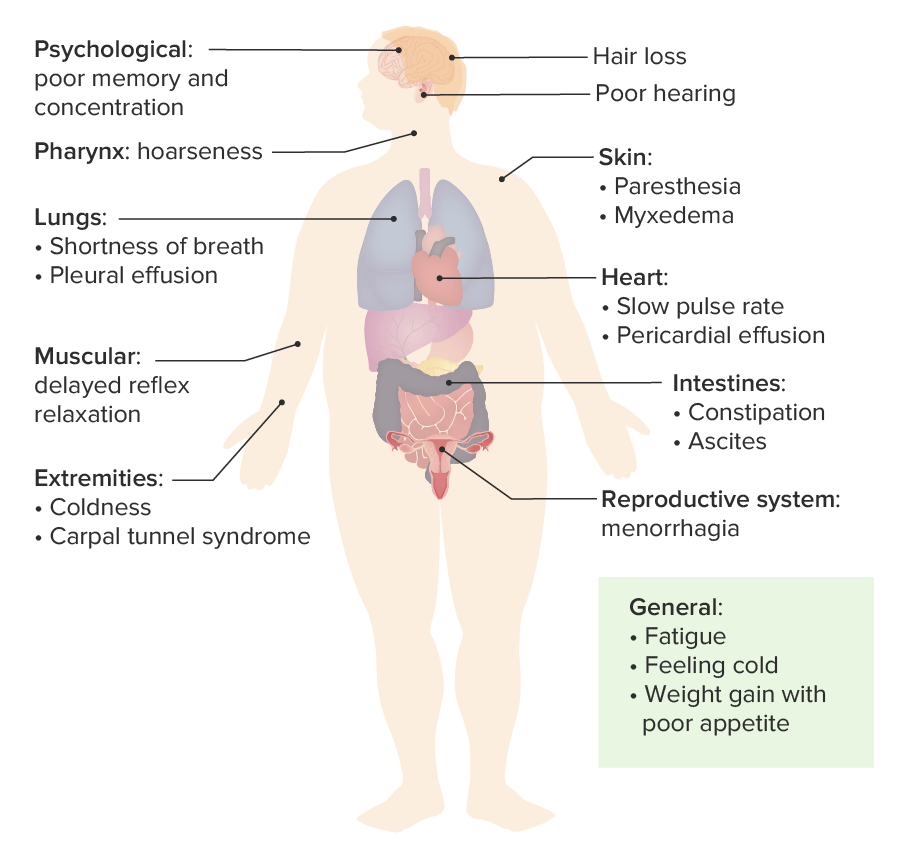
Overview Definition[3,8] Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disorder resulting from thyroid hormone deficiency. Epidemiology[1,2,9] Classification[3,7,8] By onset: By organs affected with disease: Etiology of congenital hypothyroidism[1,8] Etiology of acquired hypothyroidism[2,3] Pathophysiology Hypothalamic–pituitary–thyroid axis[2] Clinical Presentation Underlying processes of manifestations[7,9] Congenital hypothyroidism[1,10] Acquired hypothyroidism Common signs and symptoms:[8,9] In the elderly: Myxedema coma: Diagnosis Congenital hypothyroidism Mandatory […]
Hyperglycemic Crises (Clinical)
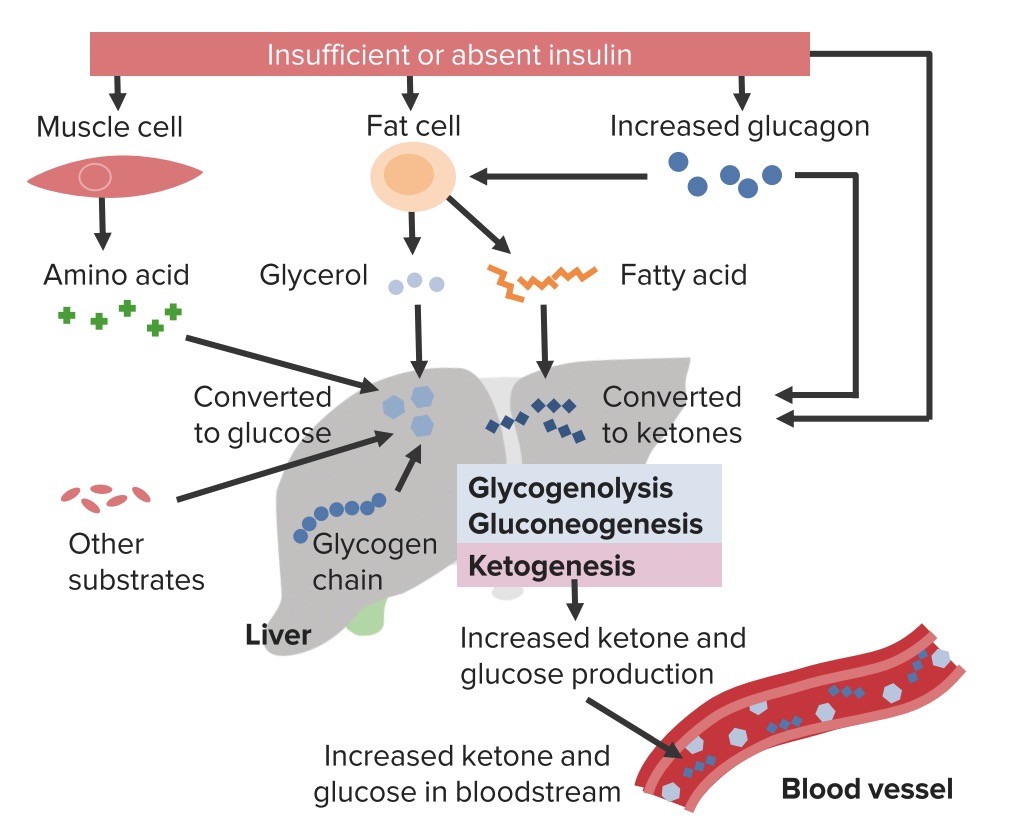
Overview Definition Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) are serious, acute complications of diabetes mellitus. Epidemiology[3–5] Etiology[1–4,6] Pathophysiology Normal physiology[3–5] The normal response to increased serum glucose involves the release of insulin by pancreatic beta cells. This leads to: Pathophysiology of DKA[4,5,8] Pathophysiology of HHS[4,5,8] Clinical Presentation Clinical presentation of DKA[2,4,6,9] Clinical presentation […]
Breast Cancer Screening (Clinical)
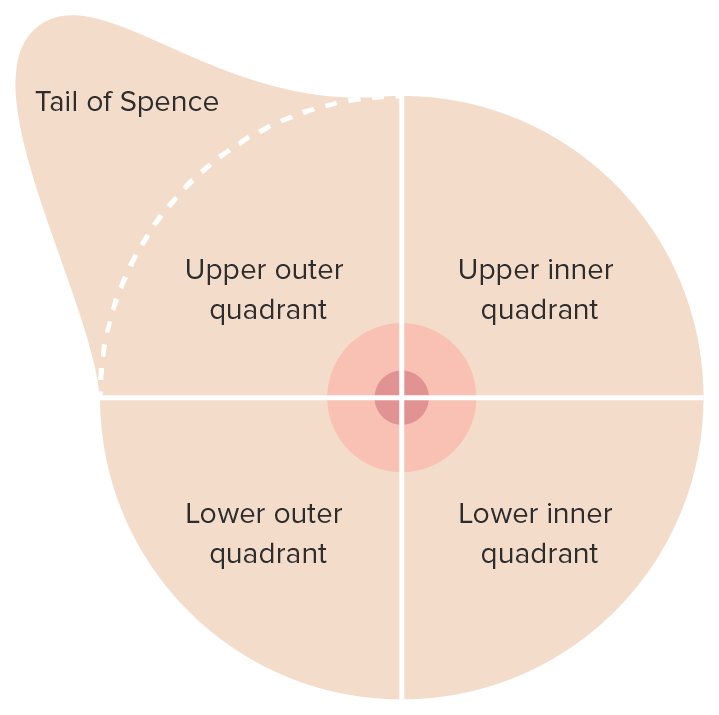
Overview Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Epidemiology[4,5,8,12] Overview of screening process[4,12] Risk factors for breast cancer[1,4,12] Mnemonic: BReast-CAncer 1 and 2: BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the mutated genes in breast cancer. Initial risk assessment[3,4,12,20] Details of the patient’s medical and personal history […]
Conjunctivitis (Clinical)
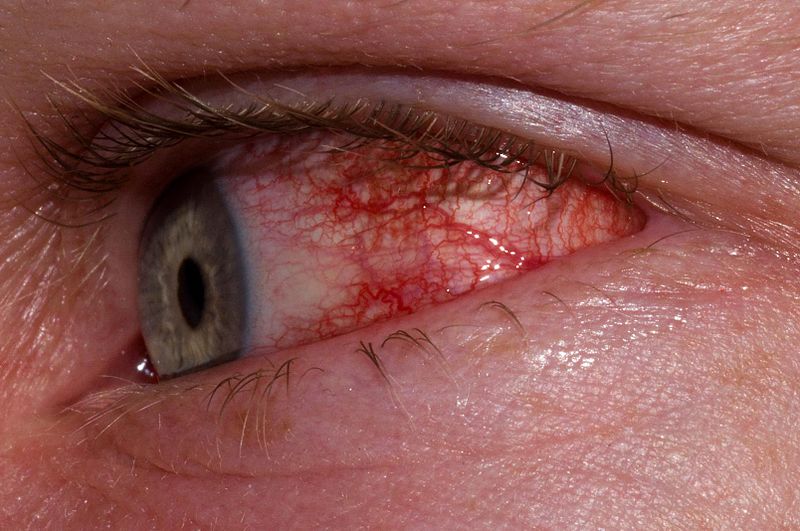
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,3] Etiology Infectious conjunctivitis Noninfectious conjunctivitis Clinical Presentation Patients can present with some or all of the following symptoms:[1 –3] Table: Clinical presentation of conjunctivitis based on etiology Viral conjunctivitis Bacterial conjunctivitis Allergic conjunctivitis Discharge Clear, watery discharge Thick, purulent yellow, white, or green discharge with severe crusting (eyes glued shut upon awakening) […]
Parkinson Disease (Clinical)
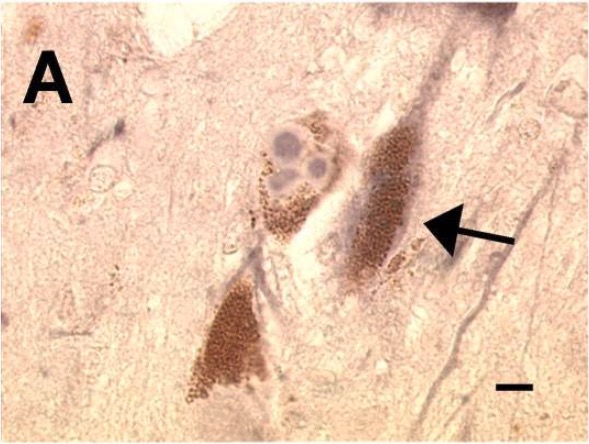
Overview Definition Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder affecting the CNS with cardinal features of resting tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability. Epidemiology[2,8] Etiology The etiology of PD is unclear but depends on various genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors[2,8] Pathophysiology Compensatory mechanisms in the brain may temporarily decrease the effects of […]
Acetaminophen Overdose (Clinical)
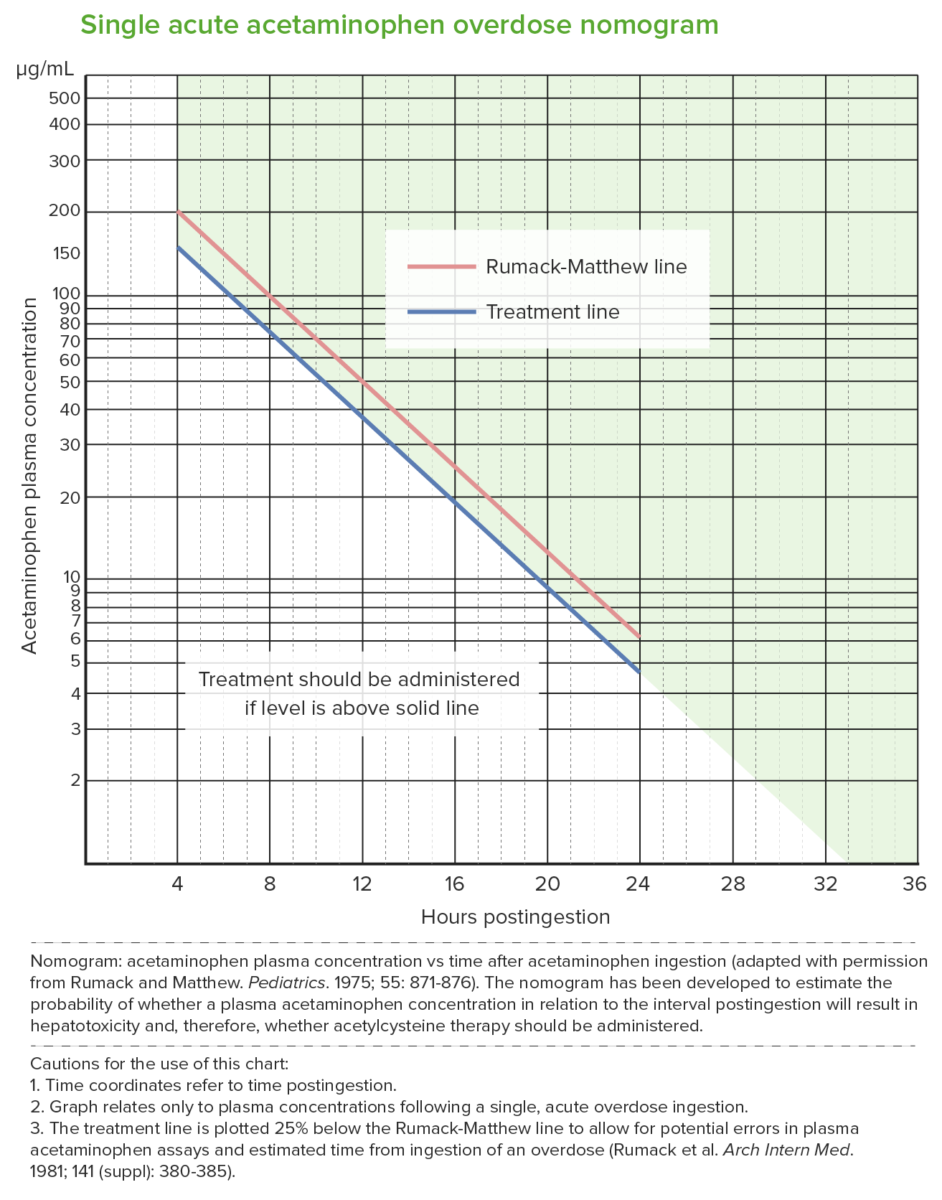
Epidemiology Pathophysiology Pharmacokinetics[1,12] Normal metabolism[1,2,4,12] Pathogenesis[1,2,4,12] Clinical Presentation The clinical course of APAP poisoning is often divided into 4 stages, which are classified according to duration since time of ingestion.[12] Diagnosis Evaluation[1,2,3,9,12] Rumack-Matthew nomogram[1,2,12] Management Treatment approach Entails supportive care, limiting drug absorption, and treatment of toxic effects: N-acetylcysteine (NAC) Acute overdose Rule of 150[6] […]
Myasthenia Gravis (Clinical)
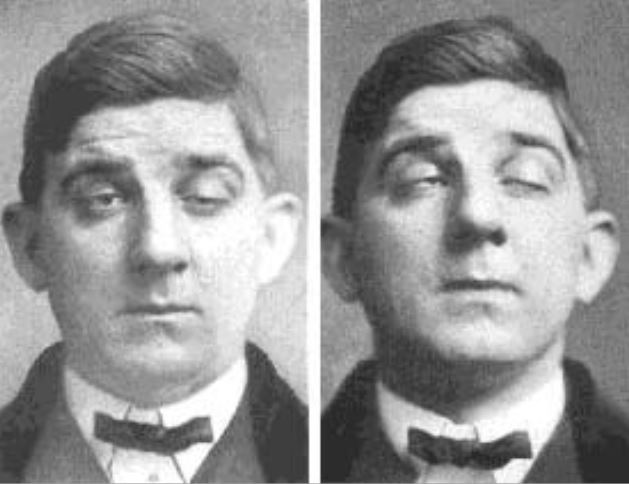

Overview Definition[5–7] Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune disorder in which antibodies attack the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) complex at the neuromuscular junction. Epidemiology[4,5] Etiology[3,6] Classification and Pathophysiology Classification[4] Based on clinical presentation: Based on serologic profile of antibodies: Presence of antibodies against either AChR, MuSK, or LRP4 is referred to as seropositive MG: Classification […]
Erectile Dysfunction (Clinical)
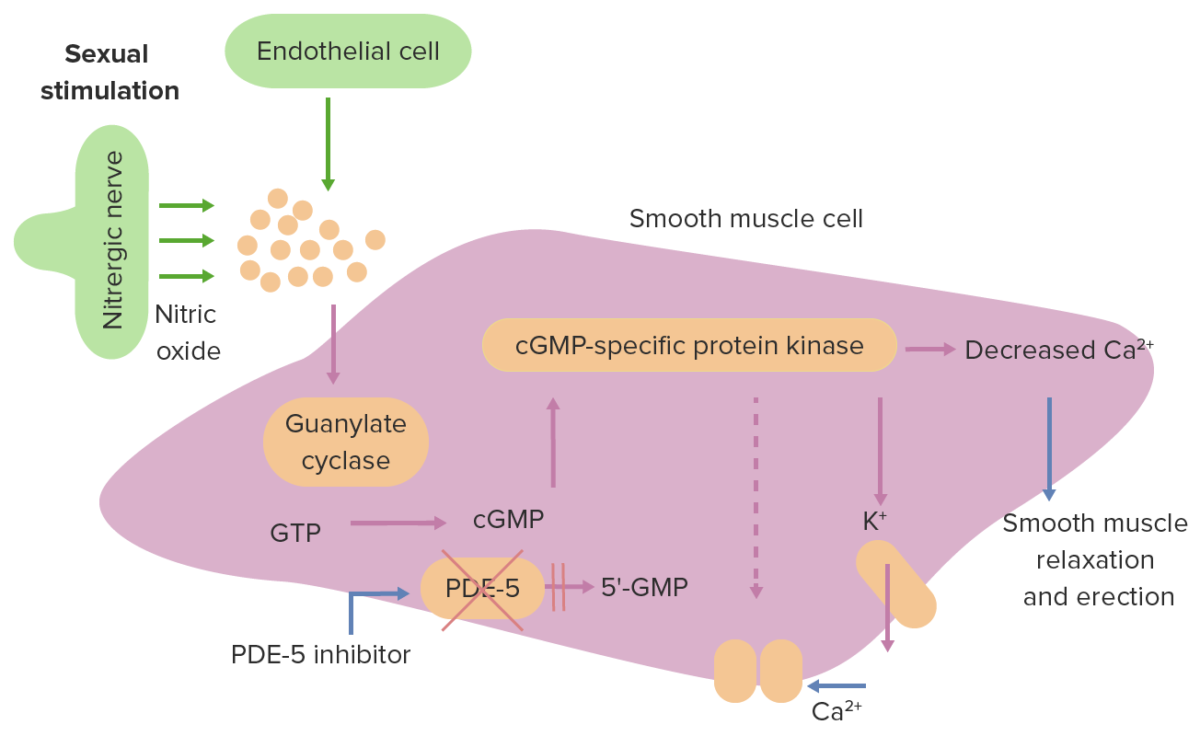
Overview Definition[1–4] Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the recurrent failure to achieve or maintain consistent rigid penile erection for satisfactory sexual intercourse. Clinical importance: Epidemiology[1,3,4] Globally, at least 150 million men suffer from ED: Prevalence of ED is closely related to increased age and presence of other systemic comorbidities. Etiology[1–4] Erectile dysfunction is a multifactorial disease […]
Meningitis (Clinical)
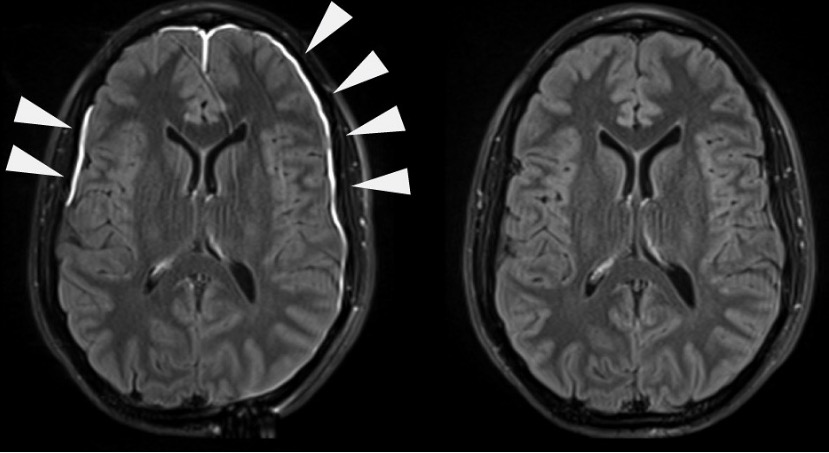
Overview Definition Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes of the brain and the spinal cord, collectively called the meninges, that is commonly caused by an acute infection. Epidemiology[3] Etiology Meningitis can be of infectious (most common) or noninfectious origin. Infectious meningitis can be community- or hospital-acquired. Infectious meningitis[1–6,15] Bacterial meningitis: Viral meningitis: Fungal meningitis: Parasitic […]