Bundle Branch and Fascicular Blocks (Clinical)
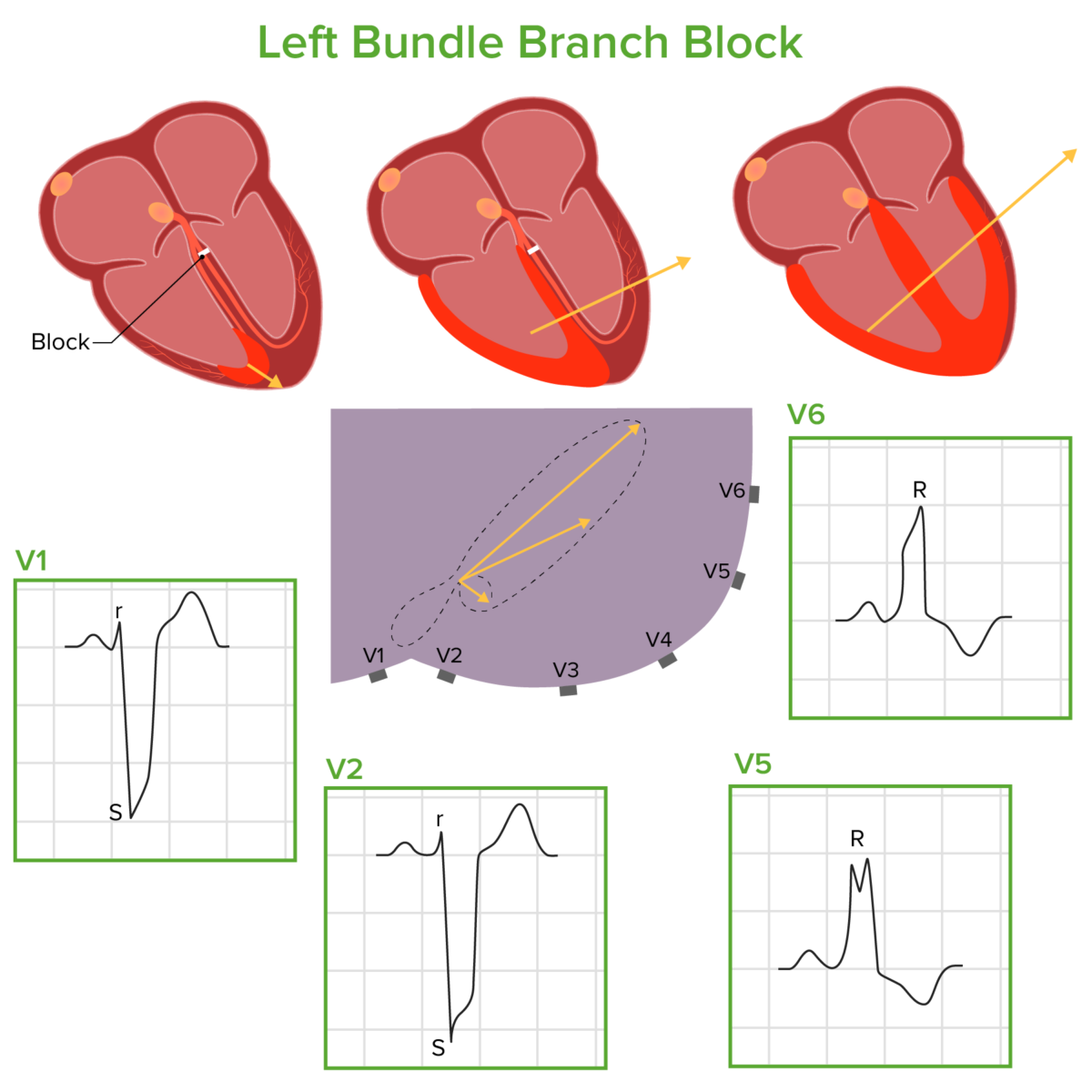
Classification and Epidemiology Classification[8,9] Bundle branch and fascicular blocks are classified on the basis of where the disruption occurs within the His-Purkinje system. Epidemiology[2‒5] Etiology RBBB[2,6] LBBB[3,6] LAFB and LPFB[4,5] These fascicular blocks can occur because of many of the same causes of RBBB or LBBB, most notably: Pathophysiology Normal physiology[2‒5] Bundle branch blocks[2‒5,9] Fascicular […]
Hypoglycemia (Clinical)
Overview Definition[1‒3,5,6] Hypoglycemia is an emergency condition defined as a serum glucose level ≤ 70 mg/dL (≤ 3.9 mmol/L). Classification[3,4] Etiology[1,3] Pathophysiology Glucose homeostasis[6‒8] Serum glucose levels are maintained within the normal range of 71–99 mg/dL owing to a coordinated balance between insulin, glucagon, and the sympathetic nervous system. As the serum glucose level falls, […]
Accidential Hypothermia (Clinical)
Overview Definition[3,12] Hypothermia is a decrease in core body temperature to below 35°C (95°F). The focus of this concept page is primarily on accidental hypothermia. Epidemiology[4,6,7] Etiology[1‒3] Pathophysiology Mechanisms of heat loss[2,5,12] Pathogenesis[1‒5] Clinical Presentation General manifestations[3,5,6,12] The following features may be present, depending on the severity of hypothermia: Stages of hypothermia (by core temperature)[3‒6,12] […]
Geriatric Care and Screening (Clinical)
Caring for Older Adults Geriatric population[5] Assessment of older adults[19] Care for older adults is a team-based approach that involves various professionals (e.g., physicians, social workers, nutritionists, physical therapists) working together to assess the following: Physical Health Nutrition[5] Alcohol, tobacco, and substance use[5] Tobacco use: Marijuana/cannabis use:[22,23] Physical activity[8] Medication Management Considerations[11] Beers criteria[24] Table: […]
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (Clinical)
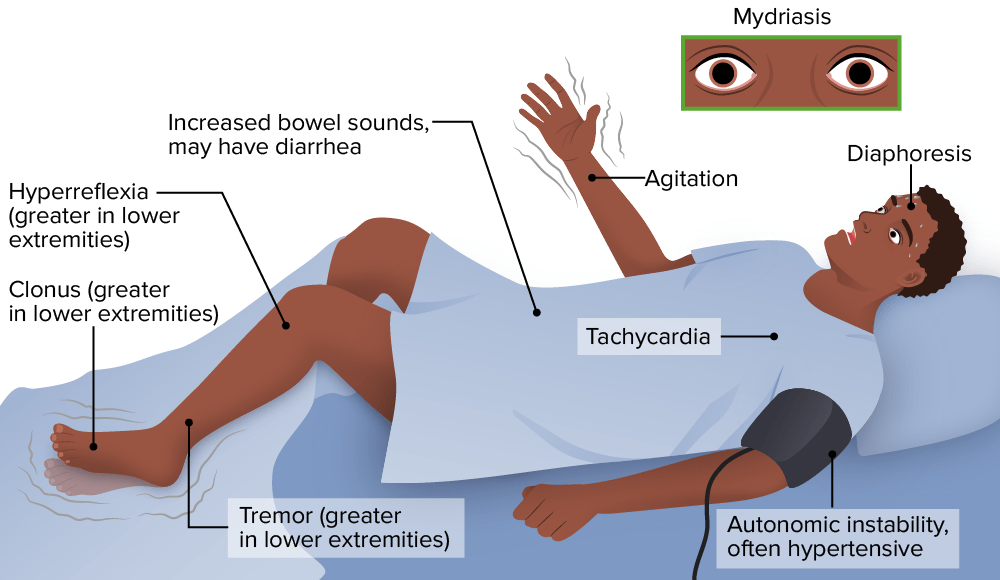
Overview Definition[1-3] Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) is a life-threatening neurologic disorder associated with the use of antipsychotics that presents as a classic tetrad: Epidemiology[3,5,7,11] Etiology[2,3] NMS is an idiosyncratic reaction to neuroleptic (antipsychotic) drugs. Risk factors[5-7] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology[1-3] Clinical presentation[2-5] Cardinal features of the neuroleptic malignant syndrome include: Other signs and symptoms […]
Giant cell arteritis (Clinical)
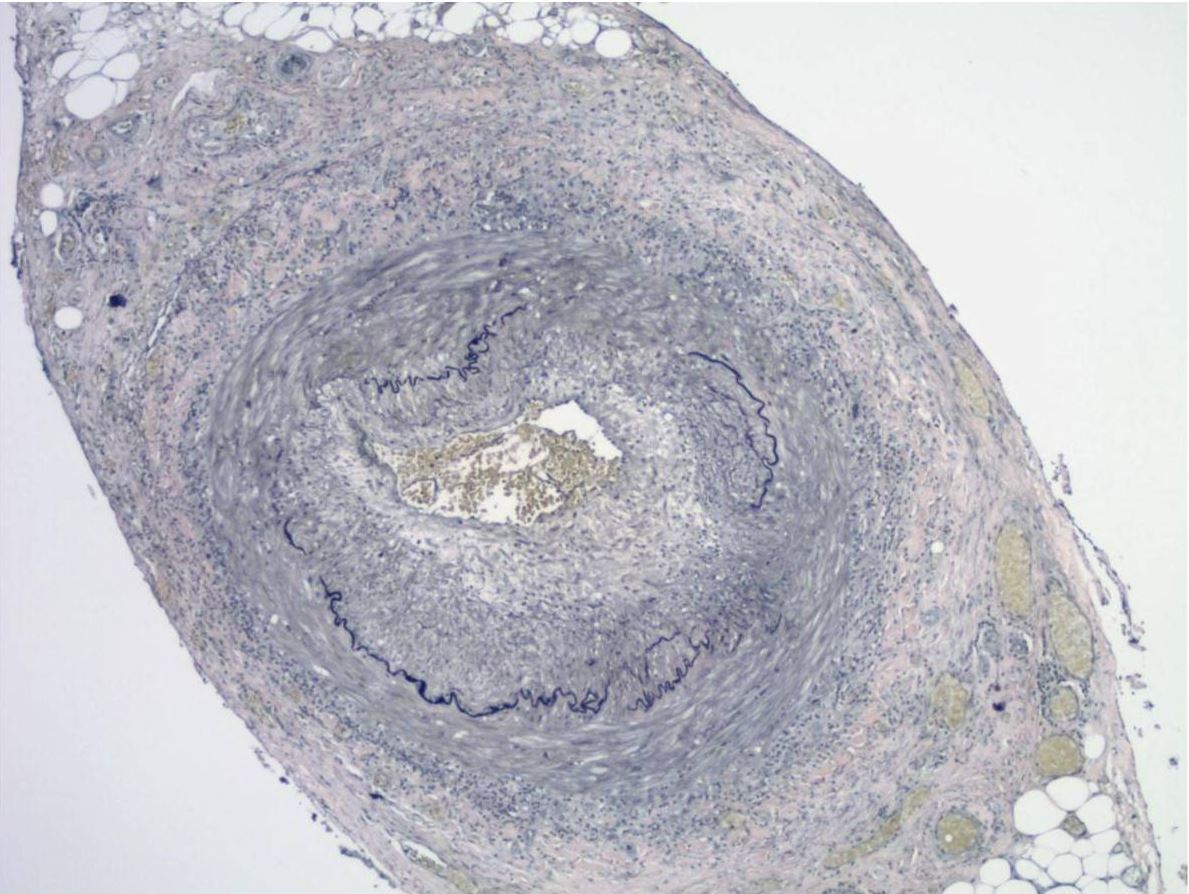
Overview Epidemiology[1,5,6,7] Etiology[1,6] Pathophysiology[1,6,7] Giant cell arteritis (GCA) is caused by a complicated cascade of vascular inflammation, damage, and dysfunctional repair: Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations[6,8,10,13] Symptom onset is typically subacute, developing over weeks to months. More abrupt presentations, with symptoms arising over a few days; occurs in a minority of cases. Physical exam[6,8,10,13] Diagnosis Diagnostic […]
Dog and Cat Bites (Clinical)
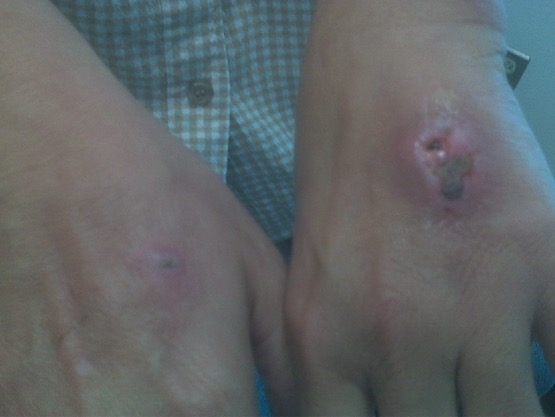
Overview Epidemiology[1,3,4] International data are lacking, but statistics in the United States include: Table: Demographics based on animal Dog bites Cat bites Approximately 90% of all animal bites Approximately 10% of all animal bites Men > women Women > men Children > adults Adults > children Less often result from provocation More often result from […]
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning (Clinical)

Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation The symptoms of CO poisoning are varied and nonspecific. The severity of the clinical presentation of CO poisoning depends on the amount of CO in the inhaled air, the duration of the exposure, and the general state of health of the affected individual. Mildly to moderately CO-intoxicated individuals[1–3,5] Severely CO-intoxicated individuals[1–3,5] […]
Malignant Hyperthermia (Clinical)

Overview Definition[1,2] Malignant hyperthermia (MH) is a hypermetabolic response in a patient exposed to a volatile anesthetic or succinylcholine resulting in fever, muscle rigidity, rhabdomyolysis, and pulmonary and cerebral edema. Epidemiology[2,5] Etiology[2,4] Triggering substances: “Safe” anesthetics for patients with previously diagnosed malignant hyperthermia: Pathophysiology[1,2] Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Symptoms may appear at any point during […]
Serotonin Syndrome (Clinical)
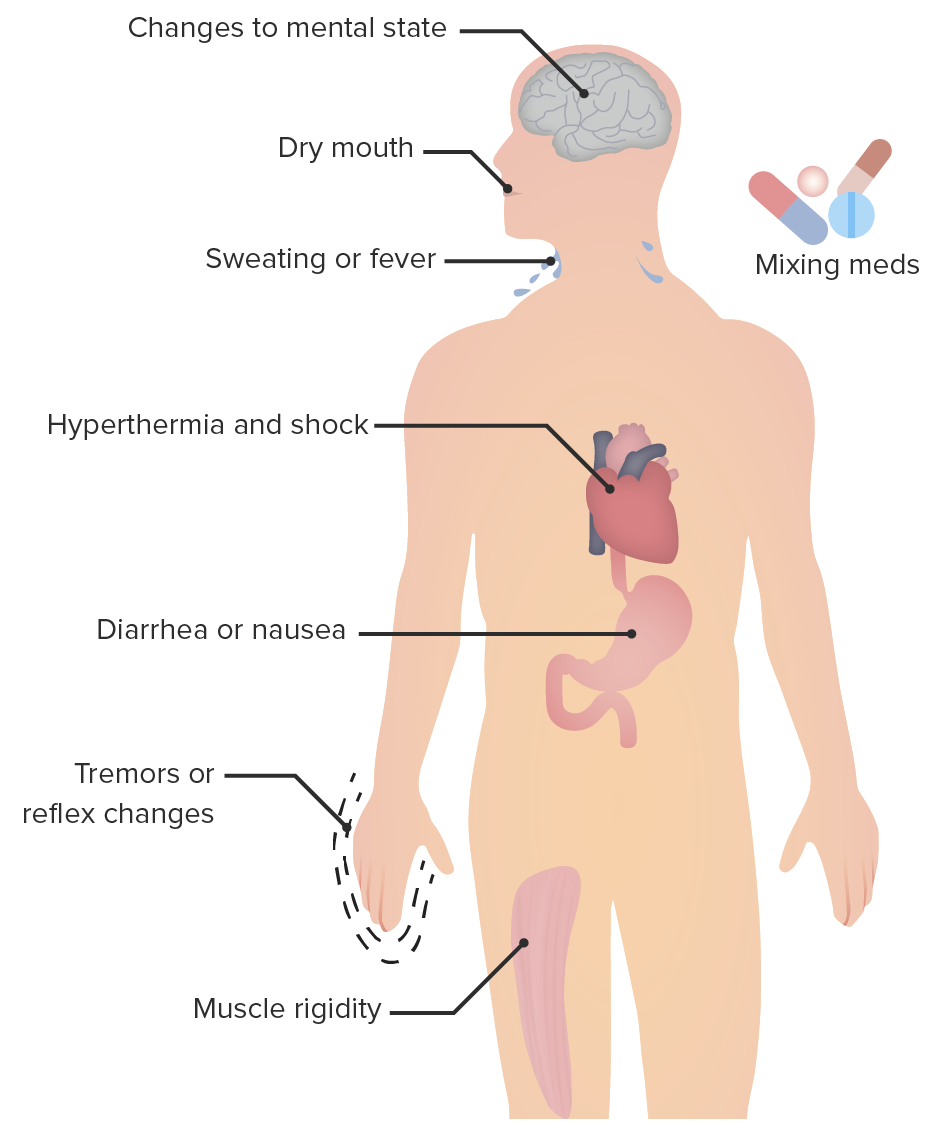
Overview Definition[4] Serotonin syndrome is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by large increases in serotonergic activity due to exposure to serotonin agonists. Defining symptoms include altered mental status, autonomic instability, and neuromuscular abnormalities (tremors, myoclonus). Epidemiology[4,6] Etiology[6] Serotonin syndrome occurs secondary to use of therapeutic medication, drug interactions, or overdose. Pathophysiology Serotonin syndrome occurs from […]