Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (Clinical)
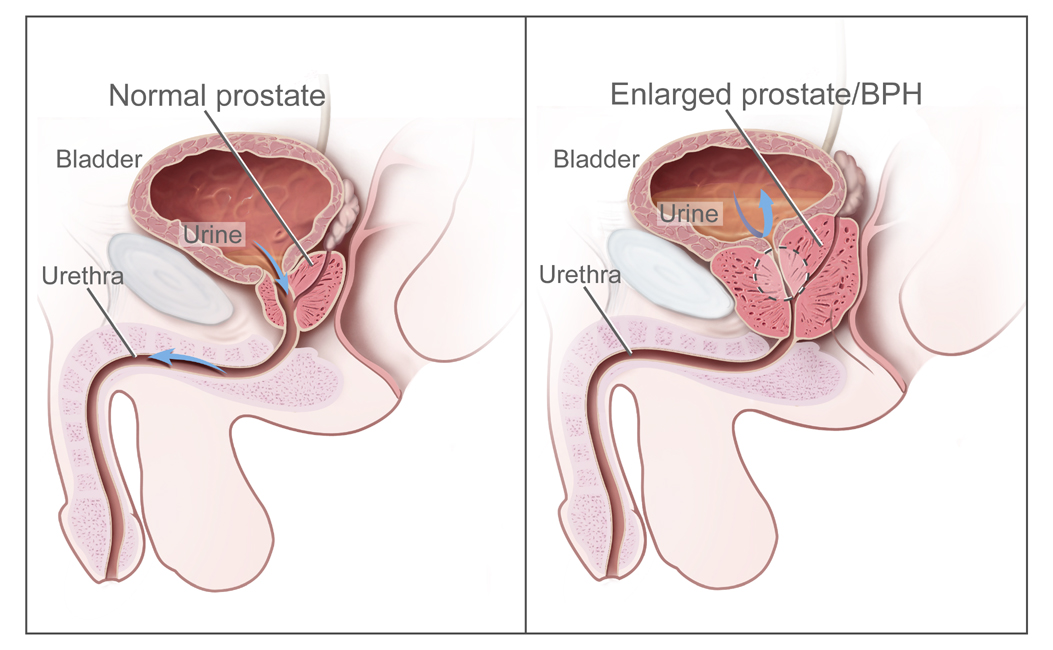
Overview Definition[2] Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a histologic diagnosis with an increase in the total number of stromal and epithelial cells within the transition zone of the prostate gland. The overall size of the prostate gland does not correlate with the degree of symptoms. Benign prostatic hyperplasia occurs with bladder outlet obstruction (BOO), leading […]
Hypoparathyroidism (Clinical)

Overview Definition Hypoparathyroidism is a condition associated with insufficient secretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia are the pathognomonic biochemical features of hypoparathyroidism and result directly from a lack of PTH action on the kidney. Epidemiology[3,10] Etiology[2,4,10,11] Pathophysiology Normal physiology of PTH[1,2,10] Effects of hypoparathyroidism[10] Clinical presentation Acute hypoparathyroidism[7,10,11] Chronic hypoparathyroidism[8,10,11,15] Physical exam[7,10,12] Diagnosis […]
Barrett Esophagus (Clinical)
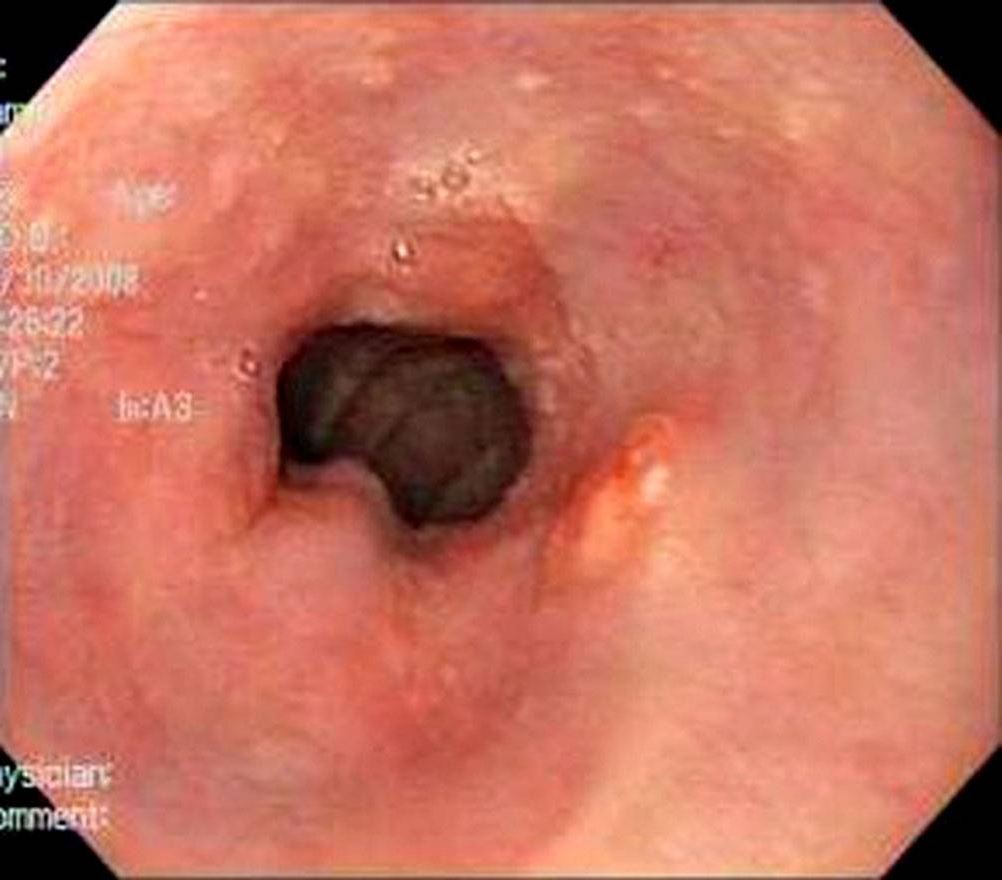
Epidemiology and Risk Factors Epidemiology[3,4,8] Risk Factors[1,2,8] Pathophysiology Mucosal injury[9] Metaplasia[9,11] Dysplasia[9] Progression to cancer[9,13] Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis Clinical presentation[1,8] Diagnosis[1–5,11,12] Screening recommendations: Procedure of choice is esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD): Management The management of Barrett esophagus has been addressed in several society guidelines, and there is considerable disagreement among experts. The information here is based […]
Urinary Incontinence (Clinical)

Overview Definition Urinary incontinence (UI) is the involuntary leakage of urine. Epidemiology[1,3] Etiology and risk factors[2,4,6,7,20,28] Consequences of urinary incontinence[23,28,29] Pathophysiology and Classification Normal bladder function[11,23] Incontinence pathophysiology and classification[28,29] Alterations in bladder and/or urethral sphincter pressures lead to UI. Clinical Presentation and Diagnosis General approach Focus the history on symptoms consistent with incontinence based […]
Long QT syndrome (Clinical)
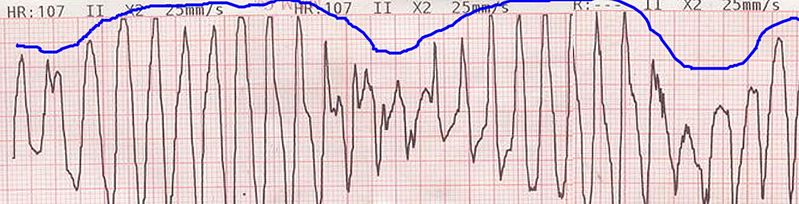
Definitions Etiology Congenital long QT syndrome[6,13,17] Pathophysiology: Types of congenital LQTS: Variety of associated conditions: Acquired long QT syndrome[1–3,17] Clinical Presentation Congenital long QT syndrome[6,7,17] Acquired long QT syndrome[6,7,13] Diagnosis The diagnosis of long QT syndrome can be made via an ECG of the patient and/or 1st-degree relatives. A careful medication review is indicated for […]
Lipid Disorders (Clinical)
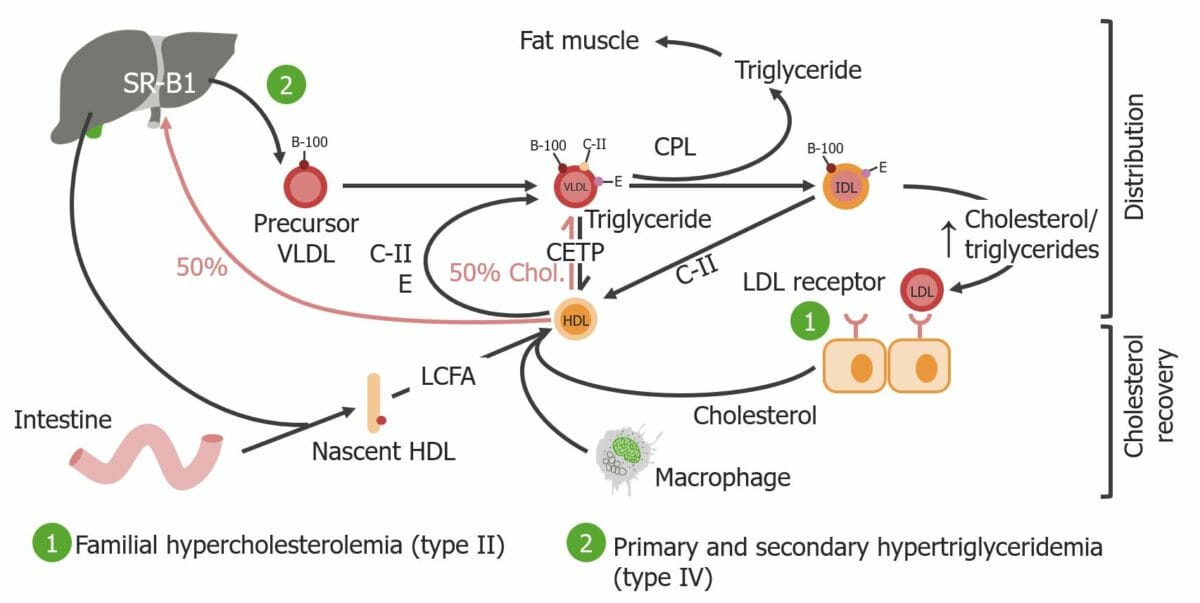
Overview Definition[17] Dyslipidemia: abnormal amounts of lipids in the blood Epidemiology[20] Pathophysiology[17] Etiology and Classification Lipid disorders are due to a combination of diet and lifestyle habits coupled with a genetic predisposition. Etiology[3,17] Causes of dyslipidemia can be divided into primary (familial) and secondary (acquired) causes. Primary causes: Secondary (acquired) causes: Table: Fredrickson classification for […]
Hepatic Encephalopathy (Clinical)
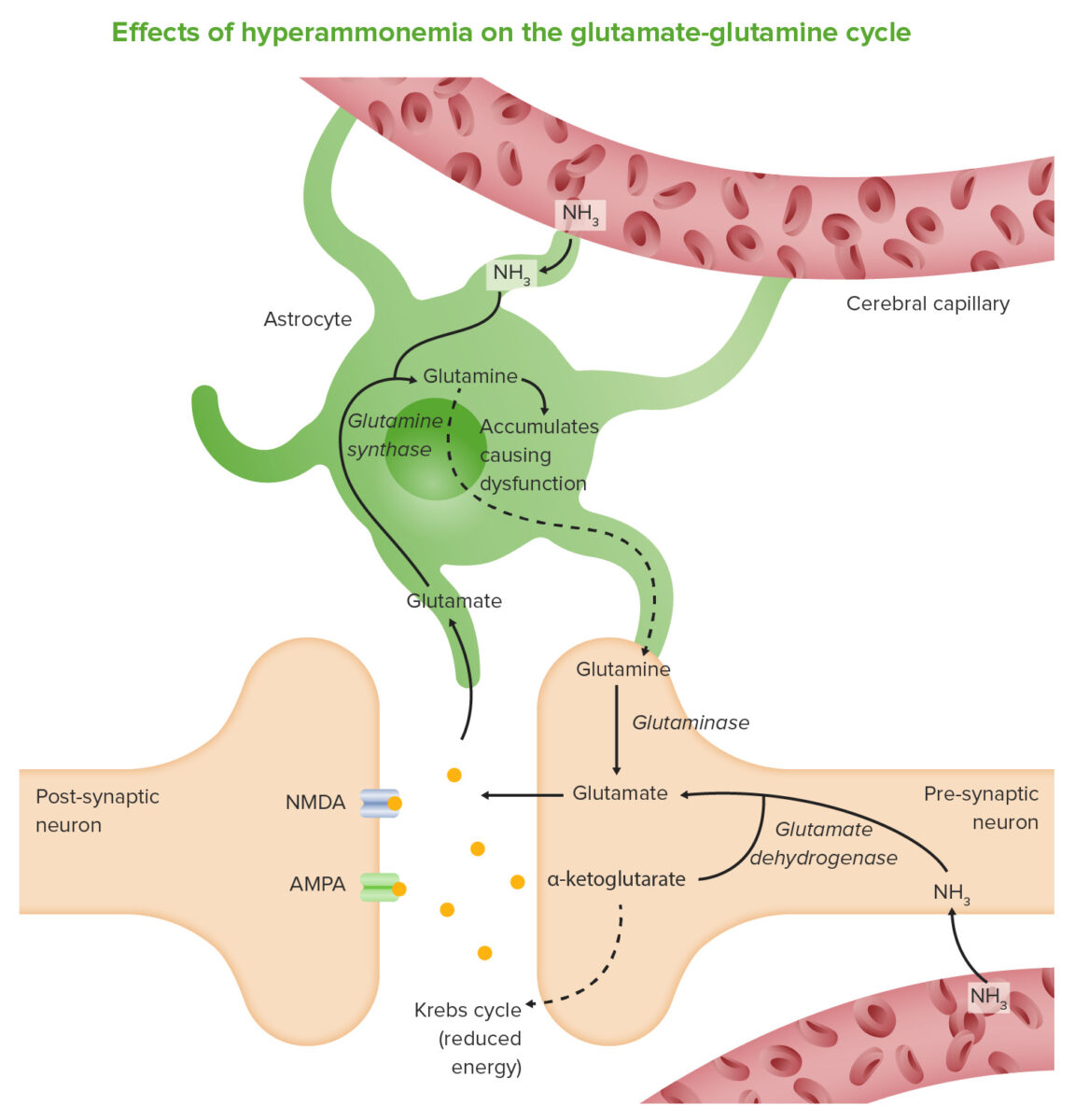
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[4,5,10] Etiology[4,10] Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is seen in patients with severe liver disease or liver failure, and can be exacerbated by: Mnemonic Precipitating factors for hepatic encephalopathy can be remembered by the mnemonic “HEPATICS”: Pathophysiology Normal physiology:[2,10] Liver disease allows disruption of normal ammonia regulation through:[2,4,10] Impaired brain function results from a […]
Gastrointestinal Bleeding (Clinical)
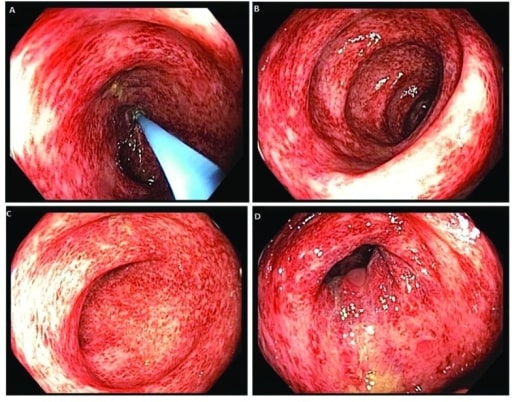
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[1,2,8,16] Etiology UGIB (proximal to the ligament of Treitz):[7,16] LGIB (distal to the ligament of Treitz):[15] Clinical Presentation Clinical manifestations[3,6,17] Physical exam[17] Diagnosis and Management The approach to evaluating patients with GI bleeding depends on its severity and whether the patient is able to undergo endoscopic evaluation. Diagnosis and management are often […]
Gastritis (Clinical)
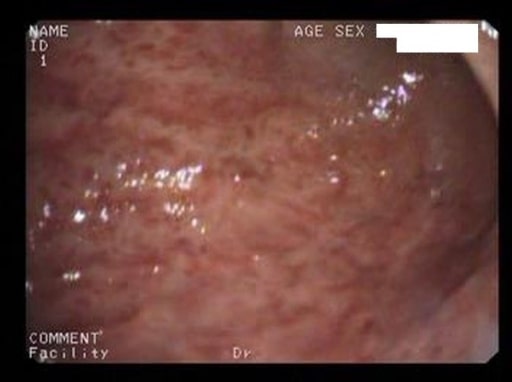
Overview Definition Gastritis is the inflammation of gastric mucosa associated with mucosal injury. Gastropathy refers to a disease of the stomach associated with reactive or hyperplastic epithelial changes with only minimal or no inflammation. Etiology[10] Gastritis is usually due to an infection or an immune-mediated process, but it can also be caused by substances that […]
Cystic Fibrosis (Clinical)
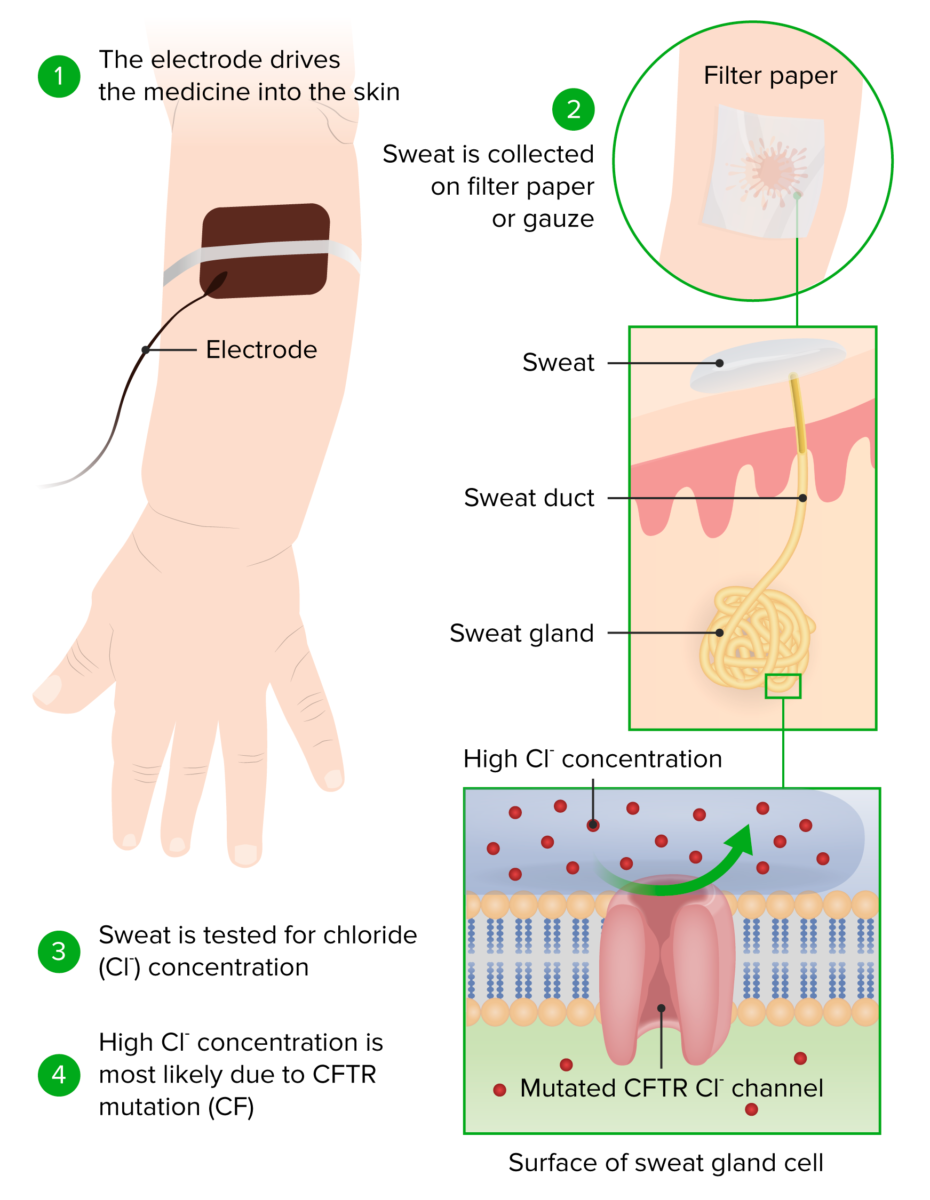
Epidemiology Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology[1–3] Pathophysiology[2,3] Impact on organ systems Clinical Presentation Respiratory system[2–4] Gastrointestinal system[2–4] Table: Gastrointestinal manifestations of cystic fibrosis Small intestine Thick secretions impair absorption, increasing the risk of obstruction. Fails to pass meconium within 48 hrs of life in newborn Constipation, abdominal pain Bowel obstruction, unable to pass gas, abdominal distention, […]