As síndromes de neoplasia endócrina múltipla são doenças hereditárias autossómicas dominantes caracterizadas por 2 ou mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome tumores produtores de hormonas envolvendo os órgãos do sistema endócrino. Existem diferentes tipos de MEN, nomeadamente a MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia–4. A síndrome MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia está associada à mutação do gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia e implica uma predileção por hiperparatiroidismo primário, adenomas hipofisários (pituitários) e tumores pancreáticos (os 3 P's). Devida à mutação do proto-oncogene RET, a síndrome MEN2 pode ser posteriormente categorizada como MEN2A e MEN2B. O carcinoma medular da tiroide e o feocromocitoma são condições frequentes. A variante MEN2A está associada ao hiperparatiroidismo primário, enquanto a MEN2B (também considerada MEN3) se associa a neuromas e ao fenótipo marfanoide. A entidade mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome recente e rara, MEN4 MEN4 Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, tem características da MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, mas resulta de mutações no CDKN1B. O diagnóstico é clínico e os tumores são detetados com base em exames de imagem e nos níveis das hormonas correlacionadas. Os testes Testes Gonadal Hormones genéticos desempenham um papel crucial nas síndromes MEN2 para determinar o tratamento posterior. O tratamento depende dos tumores presentes e da mutação genética.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
As síndromes de neoplasia endócrina múltipla (MEN) são doenças genéticas caracterizadas pela presença de ≥ 2 tumores endócrinos.
| MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia | MEN2A e MEN2B | MEN4 MEN4 Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Padrão | Autossómica dominante | Autossómica dominante | Autossómica dominante |
| Mutação genética | Gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia no cromossoma 11 (11q13) | Proto-oncogene RET no cromossoma 10 (10q11.2) | CDKN1B no cromossoma 12 (12p13) |
| Características clínicas |
|
MEN2A
MEN2B
|
|
| Tratamento |
|
|
|
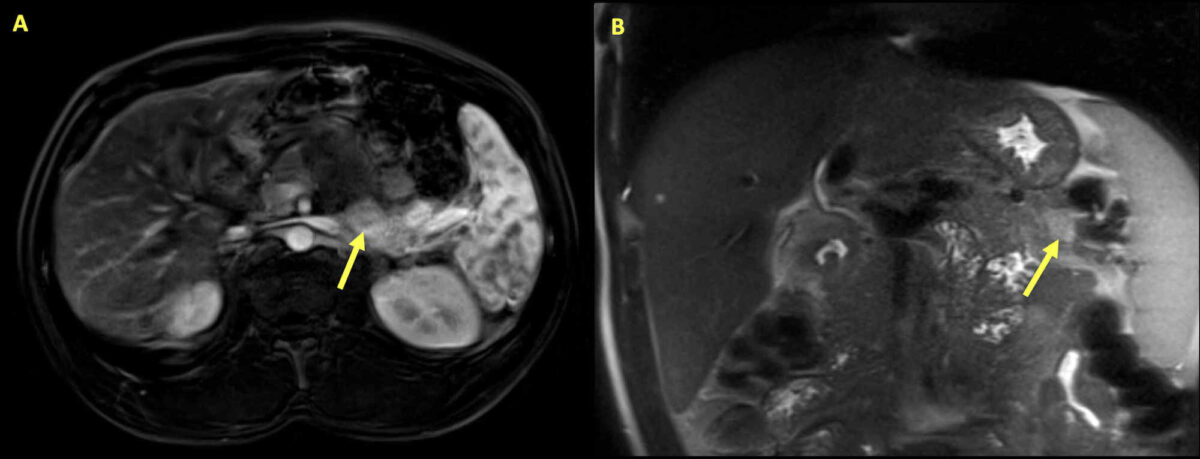
Insulinoma:
Ressonância magnética do abdómen de um homem de 34 anos que se apresentou com hipoglicemia e hipercalcémia. Veem-se múltiplas lesões pancreáticas, com as setas a destacar a maior lesão. A massa é uma área de 2,8 cm x 1,3 cm no pâncreas, de realce variável e restrição à difusão, consistente com um insulinoma.
As análises posteriores revelaram níveis elevados de paratormona (PTH) intacta. Com hiperparatiroidismo primário e insulinoma, foi realizado o teste genético, que mostrou mutação no gene MEN1, o que confirmou a presença da síndrome MEN1.
No sentido de recordar os locais de desenvolvimento de tumores na MEN1 MEN1 A form of multiple endocrine neoplasia that is characterized by the combined occurrence of tumors in the parathyroid glands, the pituitary gland, and the pancreatic islets. The resulting clinical signs include hyperparathyroidism; hypercalcemia; hyperprolactinemia; cushing disease; gastrinoma; and zollinger-ellison syndrome. This disease is due to loss-of-function of the men1 gene, a tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 11 (locus: 11q13). Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia, lembrar os 3 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation:
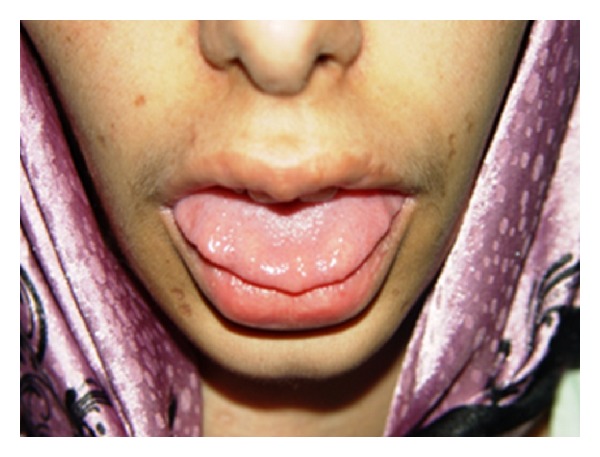
Neoplasia endócrina múltipla (MEN) 2B:
A imagem mostra neuromas no terço anterior da língua num doente com MEN2B
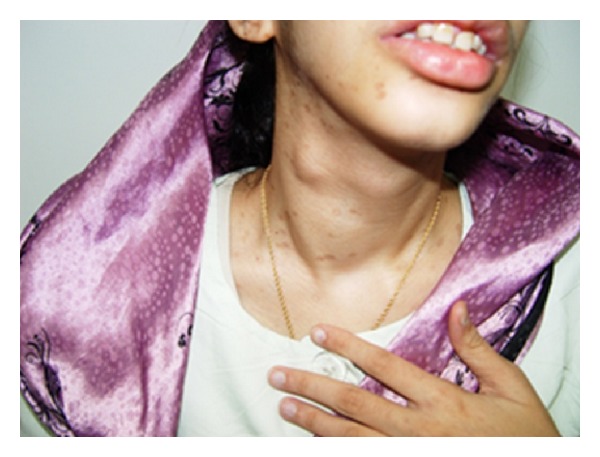
Neoplasia endócrina múltipla (MEN) 2B:
O doente da imagem apresenta um bócio com um nódulo da tiroide no lobo direito. A biópsia revelou posteriormente um carcinoma medular da tiroide.
No sentido de recordar os locais de desenvolvimento de tumores na MEN2, lembrar os 3 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation: