O cancro urológico é um termo amplo que envolve o cancro dos tratos urinários masculino e feminino e dos órgãos reprodutivos masculinos. Os fatores de risco para cancro urológico são tabagismo; exposição a produtos químicos como benzidina e beta-naftilamina e arsénico; predisposição genética; e irritação crónica do sistema urinário. A apresentação clínica inclui hematúria indolor, dor no flanco e / ou suprapúbica, disúria e perda de peso significativa inexplicada. O "gold standard" para o diagnóstico é a endoscopia das estruturas urológicas (cistoscopia, cistouretroscopia, ureteropieloscopia) com biópsia. Estudos adicionais incluem exames de imagem radiológicos, que fornecem informações sobre a invasão do tumor Tumor Inflammation e a disseminação da doença para outros locais ou órgãos. O tratamento inclui cirurgia, quimioterapia, radioterapia e tratamento de suporte, dependendo da localização, extensão e histologia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Crescimento de células anormais do revestimento de órgãos dos tratos urinários masculino e feminino e dos órgãos reprodutores masculinos.
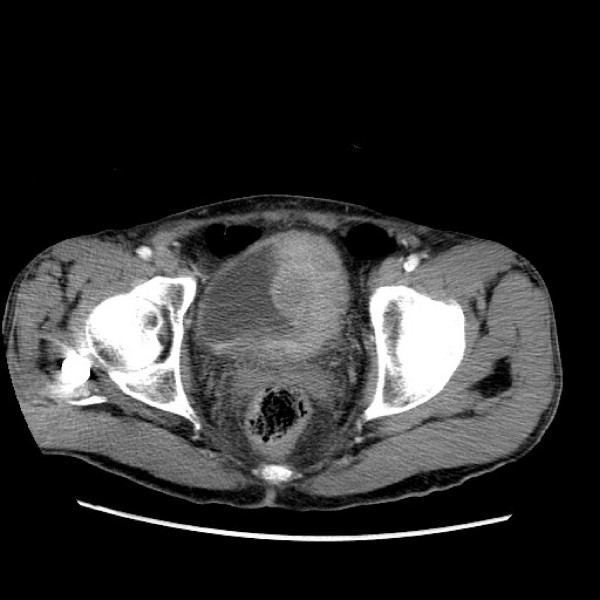
TC do cancro da bexiga:
–Massa de tecido mole lobulada com marcação no lado esquerdo da bexiga.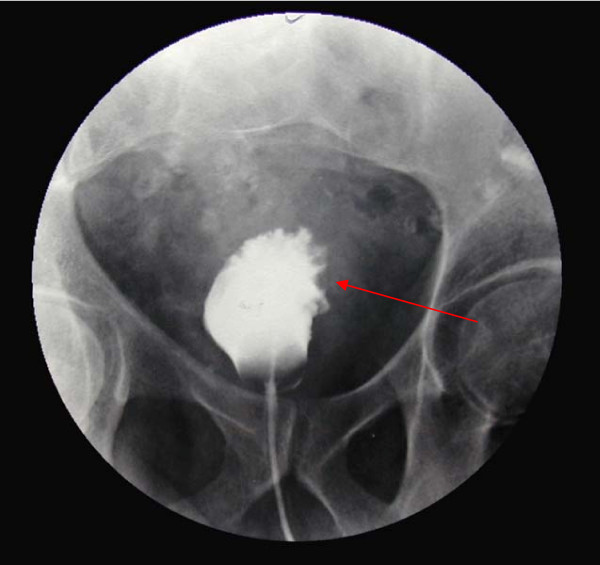
Cistograma (fase da pielografia intravenosa) mostra espessamento trabecular acentuado em indivíduo com carcinoma da bexiga.
Imagem: “Cystogram showing marked trabecular thickening” por Gaurav K, Fitch J, Panda M. License: CC BY 2.0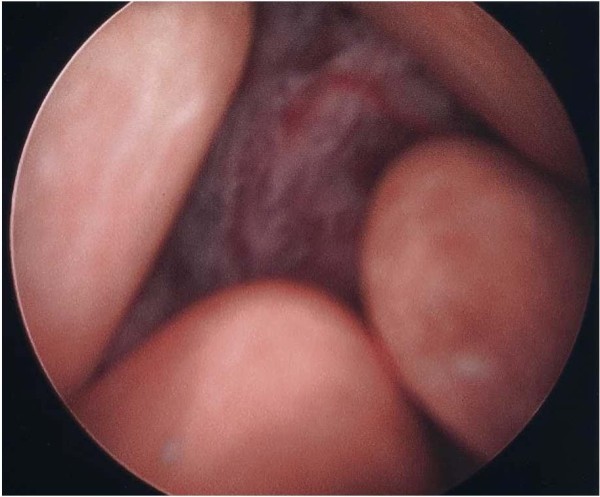
Imagem cistoscópica que mostra uma massa na bexiga e vários cálculos
Imagem: “Cystoscopy showing a bladder mass and multiple calculi.” por Cho JH, Holley JL. Licença: CC BY 2.0Os estadios patológicos do cancro da bexiga são baseados no sistema de estadiamento TNM.
|
Tumor
Tumor
Inflammation (T) categoria |
Descrição |
|---|---|
| Tx | O tumor Tumor Inflammation primário não pode ser avaliado. |
| T0 | Sem evidência de tumor Tumor Inflammation primário |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Lesões papilares ou exofíticas não invasivas |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ (“tumor plano”) |
| T1 | O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade a lâmina própria (ou submucosa). |
| T2 | O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade a camada muscular própria. |
| T2a: O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade a muscular própria superficial (metade interna). | |
| T2b: O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade a muscular própria profunda (metade externa). | |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade a gordura perivesical. |
| T3a: invasão microscópica | |
| T3b: invasão macroscópica (massa extravesical) | |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade 1 dos seguintes: estroma prostático, vesículas seminais, útero, vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy, parede pélvica, parede abdominal. |
| T4a: O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade o estroma prostático, o útero, a vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy (órgãos adjacentes). | |
| T4b: O tumor Tumor Inflammation invade a parede pélvica, a parede abdominal ou outros órgãos. |
| Categoria do nódulo (N) | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Nx | Os gânglios linfáticos não podem ser avaliados. |
| N0 | Sem metástases nos gânglios linfáticos |
| N1 | Metástase de gânglio linfático único na pelve (perivesical, obturador, ilíaco interno e externo ou gânglios sacrais) |
| N2 | Múltiplas metástases em gânglios linfáticos regionais na pelve (perivesical, obturador, ilíaca interna e externa ou metástases em gânglios sacrais) |
| N3 | Metástase para os gânglios ilíacos comuns |
| Categoria da metástase (M) | Descrição |
|---|---|
| M0 | Sem metástases à distância |
| M1 | Metástases à distância |
| M1a: metástase à distância limitada a gânglios além dos gânglios ilíacos comuns | |
| M1b: metástase à distância de gânglios não linfáticos |
| Estadiamento | T | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0a | Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio 0is | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio II | T2a | N0 | M0 |
| T2b | N0 | M0 | |
| Estadio IIIA | T3a, T3b, T4a | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio IIIA | T1 – T4a | N1 | M0 |
| Estadio IIIB | T1 – T4a | N2, N3 | M0 |
| Estadio IVA | T4b | Qualquer N | M0 |
| Estadio IVA | Qualquer T | Qualquer N | M1a |
| Estadio IVB | Qualquer T | Qualquer N | M1b |
Crescimento anormal de células no revestimento interno do ureter / ureteres, dos quais> 90% são carcinomas uroteliais.
Tumor ureteral observado no exame endoscópico do ureter.
Imagem: “Ureteral tumour with elective indication for endoscopic treatment” por Niţă G, Georgescu D, Mulţescu R, Draguţescu M, Mihai B, Geavlete B, Persu C, Geavlete P. Licença: CC BY 2.0O estadiamento aplica-se ao cancro que envolve a pelve renal e o ureter.
| Categoria T | Descrição |
|---|---|
| TX | O tumor Tumor Inflammation primário não pode ser avaliado. |
| T0 | Sem evidência de tumor Tumor Inflammation primário |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Lesões papilares ou exofíticas não invasivas |
| Tis | CIS CIS Multiple Sclerosis |
| T1 | Invasão tumoral do tecido conjuntivo subepitelial |
| T2 | Invasão tumoral da camada muscular |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Somente para o ureter: invasão além da camada muscular para a gordura periureteral. Apenas para a pelve renal: invasão além da camada muscular para a gordura peripélvica ou parênquima renal |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invasão tumoral de órgãos adjacentes ou do rim para a gordura perinéfrica |
| Categoria do nódulo | Descrição |
|---|---|
| NX | Os gânglios linfáticos não podem ser avaliados. |
| N0 | Sem metástases nos gânglios linfáticos |
| N1 | Metástase ≤ 2 cm (gânglio único) |
| N2 | Metástase> 2 cm (gânglio único ou múltiplos gânglios) |
| Categoria M | Descrição |
|---|---|
| M0 | Sem metástases à distância |
| M1 | Metástases à distância |
| Estadio | T | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0a | Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio 0is | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio II | T2 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio III | T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio IV | T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | NX, N0 | M0 |
| Qualquer T | N1, N2 | M0 | |
| Qualquer T | Qualquer N | M1 |
O tratamento do cancro ureteral depende do local, tamanho e extensão do cancro, sendo que a cirurgia fornece tratamento curativo.
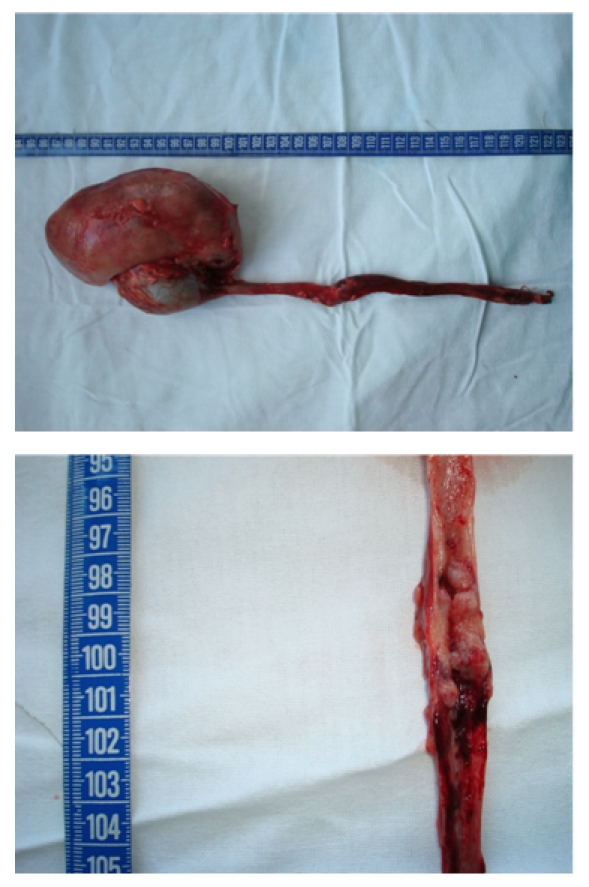
Nefroureterectomia no cancro ureteral
Imagem: “Nephroureterectomy (with endoscopic desinsertion) for ureteral tumours” por Niţă G, Georgescu D, Mulţescu R, Draguţescu M, Mihai B, Geavlete B, Persu C, Geavlete P. Licença: CC BY 2.0O cancro uretral é uma doença maligna extremamente rara (<1% de todas as doenças malignas geniturinárias) que envolve o crescimento anormal de células no revestimento da uretra.
O cancro uretral tem um início insidioso e pode permanecer assintomático por muito tempo. Os sintomas variam entre homens e mulheres:
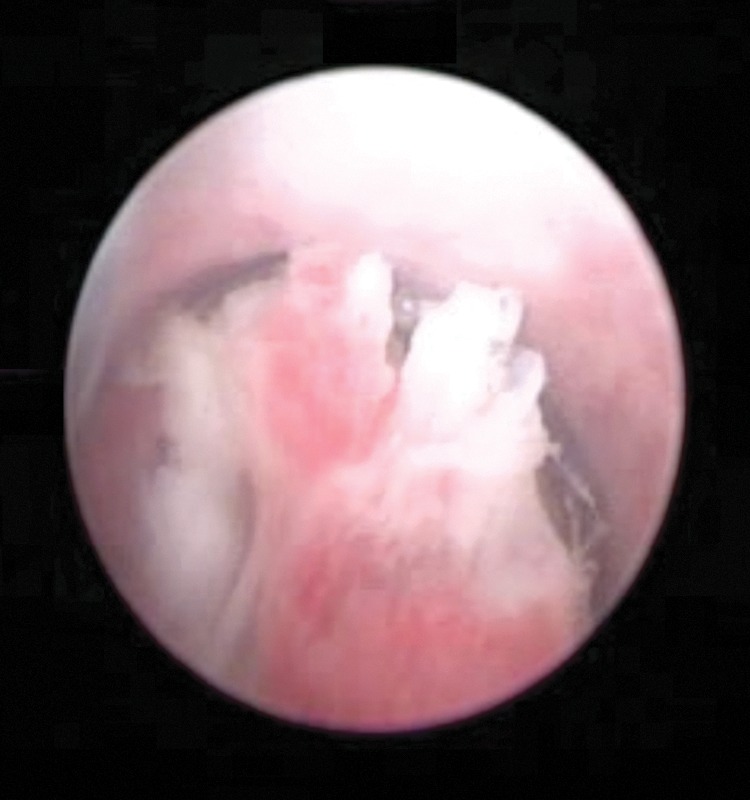
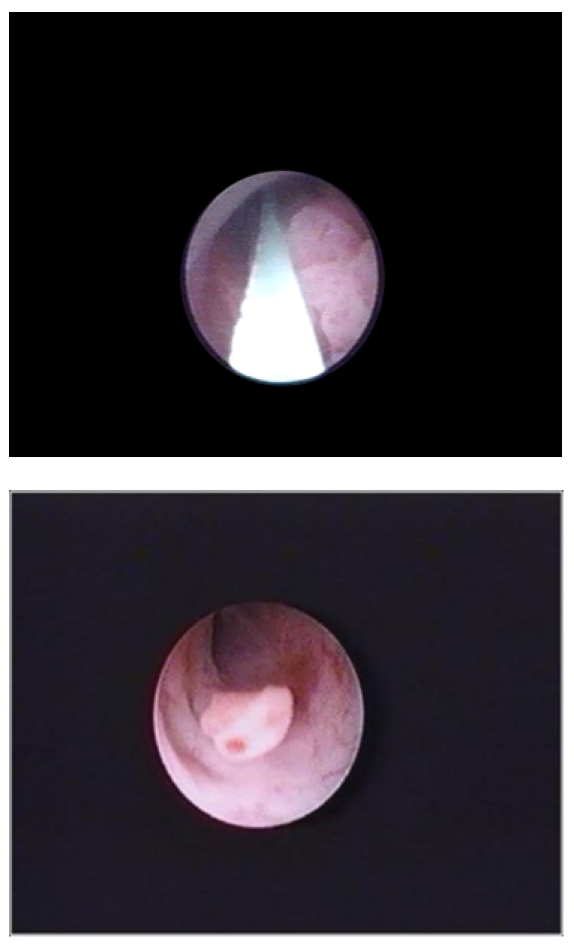
Vídeo de uretrocistoscopia que mostra um tumor papilar na uretra bulbar
Imagem: “Video urethrocystoscopy showing papillary tumor at the level of bulbar urethra.” por Journal of Endourology Case Reports. Licença: CC BY 4.0O estadiamento do cancro uretral é feito segundo os critérios do TNM.
| Categoria T | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Tx | O tumor Tumor Inflammation primário não pode ser avaliado. |
| T0 | Sem evidência de tumor Tumor Inflammation primário |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Carcinoma papilar não invasivo |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ Carcinoma in situ A lesion with cytological characteristics associated with invasive carcinoma but the tumor cells are confined to the epithelium of origin, without invasion of the basement membrane. Leukoplakia |
| T1 | Invasão tumoral do tecido conjuntivo subepitelial |
| T2 | Invasão tumoral do corpo esponjoso ou músculo periuretral |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Invasão tumoral do corpo cavernoso ou vagina Vagina The vagina is the female genital canal, extending from the vulva externally to the cervix uteri internally. The structures have sexual, reproductive, and urinary functions and a rich blood supply, mainly arising from the internal iliac artery. Vagina, Vulva, and Pelvic Floor: Anatomy anterior |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invasão tumoral de outros órgãos adjacentes |
| Categoria T | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Tx | O tumor Tumor Inflammation primário não pode ser avaliado. |
| T0 | Sem evidência de tumor Tumor Inflammation primário |
| Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | Carcinoma papilar não invasivo |
| Tis | Carcinoma in situ (envolve a uretra prostática ou, os ductos periuretrais ou prostáticos sem invasão do estroma) |
| T1 | Invasão tumoral do tecido conjuntivo subepitelial imediatamente subjacente ao urotélio |
| T2 | Invasão tumoral do estroma prostático em redor dos ductos (estendendo-se diretamente da superfície urotelial ou invadindo os ductos prostáticos) |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Invasão tumoral da gordura periprostática |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Invasão tumoral dos órgãos adjacentes |
| Categoria N | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Nx | Os gânglios linfáticos regionais não podem ser avaliados. |
| N0 | A metástase de gânglio linfático regional não está presente. |
| N1 | Metástase de gânglio linfático regional único na região inguinal ou pelve ou gânglio pré-sacral |
| N2 | Múltiplas metástases de gânglios linfáticos na região inguinal ou pelve ou gânglio pré-sacral |
| Categoria M | Descrição |
|---|---|
| M0 | Sem metástase à distância |
| M1 | Metástase à distância |
| Estadio | T | N | M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0a | Ta TA Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio 0is | Tis | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio I | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| Estadio II | T2 | M0 | |
| Estadio III | T1, T2 | N1 | M0 |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | N0, N1 | M0 | |
| Estadio IV | T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | N0, N1 | M0 |
| Qualquer T | N2 | M0 | |
| Qualquer T | Qualquer N | M1 |
A doença localizada (até T2) é geralmente tratada com cirurgia, enquanto as condições localmente avançadas são tratadas com terapia multimodal.
Os seguintes diagnósticos diferenciais são considerados tendo em conta um indivíduo que apresenta hematúria: