What are topical medications?
Topical medications are treatments applied directly to the body’s surface areas to skin or mucous membranes, used to treat localized conditions or skin disorders. They come in various forms such as creams, ointments, gels, and patches. Topical medications are used for conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, skin infections, inflammation, and localized pain relief.
How should topical medications be applied to the skin?
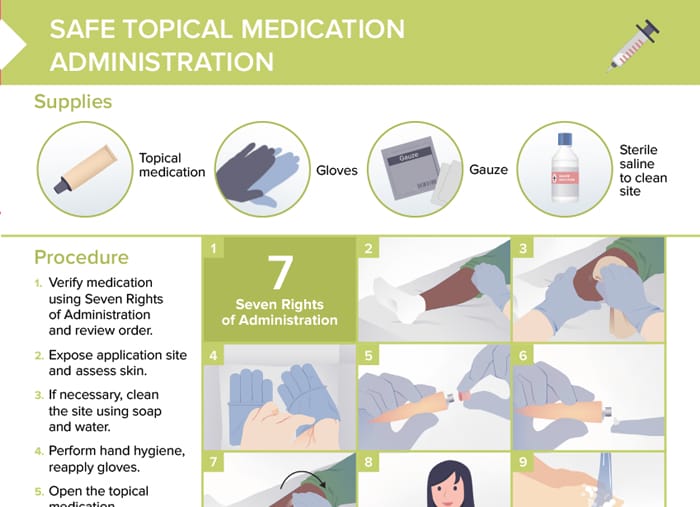
Supplies needed
- Topical medication
- Gloves
- Gauze
- Sterile saline to clean site
Procedure
- Verify medication using Seven Rights of Administration and review order.
- Expose application site and assess skin.
If necessary, clean the site using soap and water.
- Perform hand hygiene, reapply gloves.
- Open the topical medication.
- Apply medication to gloved hand or directly to site.
- Use smooth, gentle strokes to evenly apply medication to affected area.
- Provide client with appropriate follow-up care instructions.
- Remove gloves, perform hand hygiene.
Do topical medications enter the bloodstream?
Since topical medications can enter the bloodstream, but typically in smaller quantities than oral drugs, they primarily affect the area of application and have fewer systemic side effects. The degree of absorption depends on factors like the drug’s chemical properties, concentration, the skin’s health and integrity, and the specific location of application.
The risk for systemic side effects increases if used excessively or on broken skin.
Nursing tips for topical medications
- Do not apply medication to skin that is not intact (unless a HCP order is given to do so).
- Be aware that lotions and creams may interact with medications.
- If skin is dry or flaky, clean the area first and apply medication while skin is damp.
- Do not vigorously rub medication into skin.
- Mucus membranes will absorb medications more rapidly than skin.
- Routinely assess the application site.