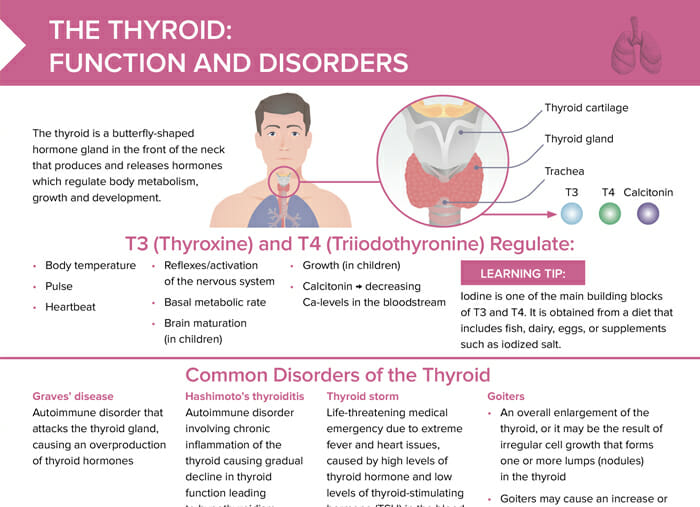
What is the thyroid?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped hormone gland in the front of the neck that produces and releases hormones which regulate body metabolism, growth and development.
What is the function of the thyroid hormones?
T3 (thyroxine) and T4 (triiodothyronine) regulate:
- Body temperature
- Pulse
- Heartbeat
- Reflexes/activation of the nervous system
- Basal metabolic rate
- Brain maturation (in children)
- Growth (in children)
- Calcitonin → decreasing Ca levels in the bloodstream
Tip: Iodine is one of the main building blocks of T3 and T4. It is obtained from a diet that includes fish, dairy, eggs, or supplements such as iodized salt.
Are thyroid issues hereditary?
Thyroid disorders can have a hereditary component, although they are also influenced by environmental factors, lifestyle, and other medical conditions. If a patient has a family history of thyroid disorders, they may be at higher risk and may benefit from more frequent screening.
Common thyroid disorders
- Grave’s disease: autoimmune disorder that attacks the thyroid gland, causing an overproduction of thyroid hormones
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: involves chronic inflammation of the thyroid causing gradual decline in thyroid function → hypothyroidism
- Thyroid storm: life-threatening medical emergency due to extreme fever and heart issues, caused by high levels of thyroid hormone and low levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in the blood
- Goiters: overall enlargement of the thyroid, or the result of irregular cell growth that forms one or more lumps (nodules) in the thyroid; may cause an increase of decrease in hormones
What is hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism means an underactive thyroid producing not enough hormones.
Common symptoms are:
- Fatigue
- Weight gain
- Constipation
- Depression
- Numbness/tingling
- Muscle weakness
- Dry, scaly skin
- Brittle hair and nails
- Loss of sexual drive
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Sensitivity to cold temperatures
What is hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is an overactive thyroid, producing too many hormones.
Symptoms include:
- Rapid and/or irregular heartbeat
- Mood disorders
- Fatigue related to sleep issues
- Irregular or light menstrual cycle
- Sweating and/or warm skin
- Puffiness or bulging of the eyes
- Weight loss
- Restlessness and hyperactivity
- Diarrhea
- Tremor
Can thyroid issues cause headaches?
While headaches are not among the primary symptoms of hypo- or hyperthyroidism, they can be associated with the conditions:
- In hypothyroidism, a reduced metabolism may cause increased pressure in the brain, leading to headaches.
- In hyperthyroidism, increased heart rate and blood pressure can contribute to headaches or migraines.
Do men have thyroid issues?
Thyroid disorders are less common in men than in women and therefore may be more likely to be overlooked, however, they can affect everyone.