What are vital signs?
Vital signs are measurements of the body’s basic functions. Usually, they include:
- Heart rate (pulse)
- Blood pressure
- Respiratory rate
- Oxygen saturation
- Temperature
What is the purpose of vital signs in nursing?
Monitoring clients’ vital signs is a fundamental part of continuously evaluating their physical health. Changes in vital signs can give information about and indicate various changes in a client’s condition and guide the decisions about nursing interventions.
How to take vital signs
- Heart rate: place fingers over pulse point (radial artery), count beats for 30 seconds and double for beats per minute; or apical pulse with the stethoscope for 60 seconds
- Blood pressure: measured with blood pressure cuff and stethoscope
- Respiratory rate: observe the patient’s chest/breath without their awareness to avoid unnatural rates due to self-awareness
- Oxygen saturation: pulse oximeter
- Temperature: orally, rectally, axillary, or tympanic /temporal
When to take vital signs
Vital signs are taken frequently in clinical settings, for example:
- On admission
- In routine checkups
- Before and after surgeries, procedures, medications
- To monitor critical changes in emergency situations
- Based on symptom changes (e.g., patient feeling faint)
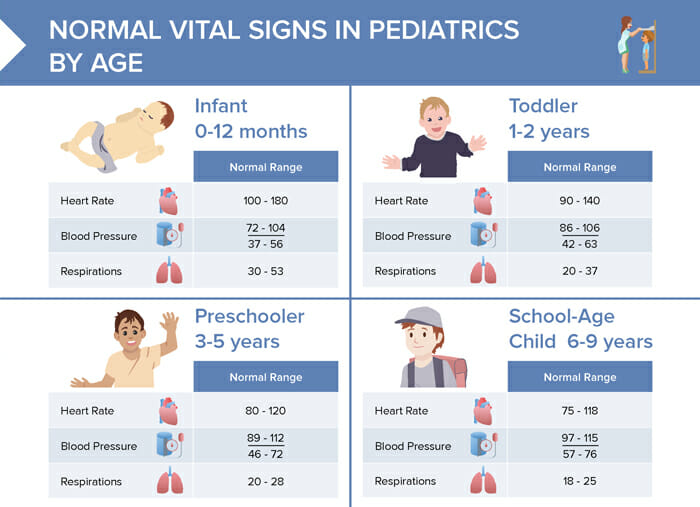
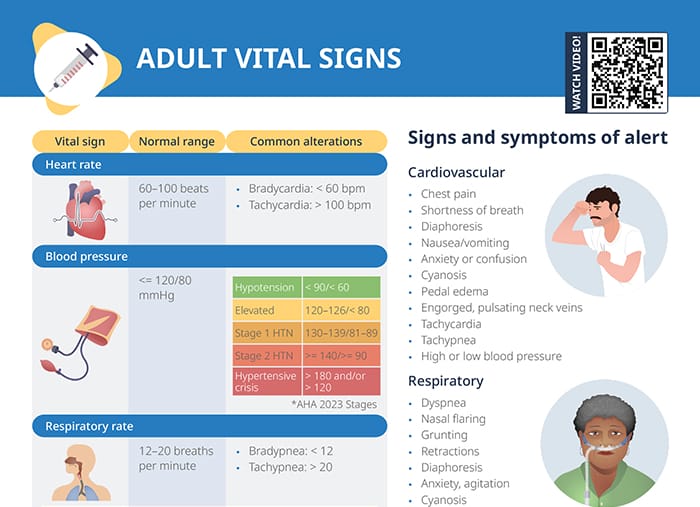
What is a normal heart rate?
The normal range for a resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute.
Common alterations include:
- Bradycardia, defined as less than 60 beats per minute
- Tachycardia, defined as more than 100 beats per minute
What is the normal range for blood pressure?
Ideal blood pressure values are less or equal to 120/80.
Hypotension is noted with findings < 90/< 60 . Blood pressure that is too high is classified b the AHA 2023 stages as follows:
- 120–126/< 80: elevated blood pressure
- 120–126/82–89: stage 1 hypertension
- >= 140/ >= 90: stage 2 hypertension
- > 180 and/or > 120: hypertensive crisis
What is a normal respiratory rate?
A healthy adult with a normal respiratory rate will take between 12 and 20 breaths per minute.
- Bradypnea, less than 12 breaths per minute
- Tachypnea, more than 20 breaths per minute
What is the ideal oxygen saturation?
Oxygen saturation should ideally be 95–100%. Oxygen saturation below 90% means the client is presenting with hypoxemia.
What is a normal temperature for an adult?
The ideal temperature for an adult depends on the mode of measuring:
- Oral: 98.6–99.5°F (37–37.5°C)
- Temporal: 98.4–99.3°F (36.8–37.4°C)
- Axillary: 97.7–99°F (36.5–37.2°C)
- Rectal: 97.8–100.4°F (36.6–38°C)
The body becomes hypothermic when the temperature falls below 95°F (35°C).
Fever is defined as follows:
- Oral: > 100°F/37.8°C
- Temporal/Tympanic: > 100.4°F/37.8°C
- Axillary: > 99°F/37.2°C
- Rectal: > 100.4°F/38°C
Warning signs and symptoms
When checking vital signs and evaluating a patient, there are signs and symptoms of alert to keep in mind that require further attention and intervention:
Cardiovascular signs of alert
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Diaphoresis
- Nausea/vomiting
- Anxiety or confusion
- Cyanosis
- Pedal edema
- Engorged, pulsating neck veins
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnea
- High or low blood pressure
Respiratory signs of alert
- Dyspnea
- Nasal flaring
- Grunting
- Retractions
- Diaphoresis
- Anxiety, agitation
- Cyanosis
- Fatigue
- Orthopnea
- Tripod position
- Tachycardia
- Tachypnea
- Low blood pressure
- Abnormal lung sounds
Neurological signs of alert
- Severe headache
- Altered vision
- Dizziness, loss of balance
- Loss of coordination
- Slurred speech
- Confusion/disorientation
- Memory loss
- Numbness
- Generalized or one-sided muscle weakness
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness