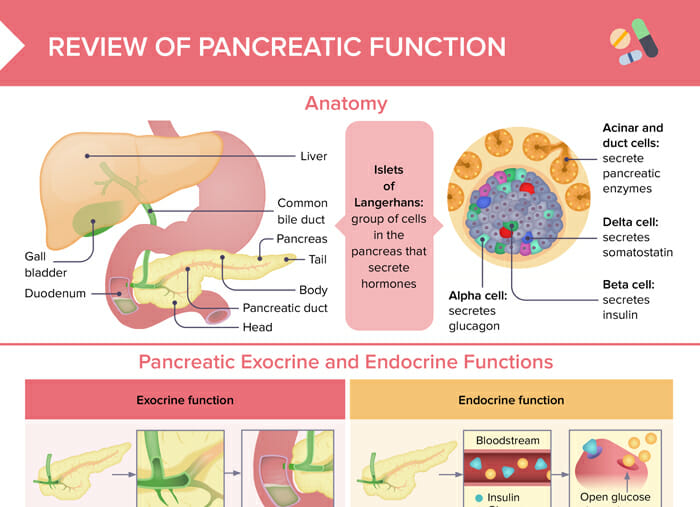
What is glucose?
Glucose is the main carbohydrate used by the body for energy. It is always present in the blood. In order for glucose to be used, it must enter the tissues with the help of insulin.
What is insulin?
Insulin is the hormone responsible for regulating glucose levels in the blood.
How does insulin work?
The function of insulin is to lower blood glucose levels. To achieve that, it is released by the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose levels. Insulin then regulates uptake and storage of glucose by binding to insulin cell receptors (muscles, liver, fat), allowing glucose to enter the cells.
How to control insulin resistance
Risk factors for insulin resistance include Type 2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome, as well as pregnancy. Insulin resistance can be controlled through lifestyle changes such as exercise and dietary changes, as well as medications like metformin.
Insulin vs glucose: at a glance
While glucose is the main carbohydrate (sugar) used by the body cells for energy, insulin is the hormone that regulates its storage and uptake in the body. High levels of glucose lead to hyperglycemia, while high levels of insulin will lead to hypoglycemia.
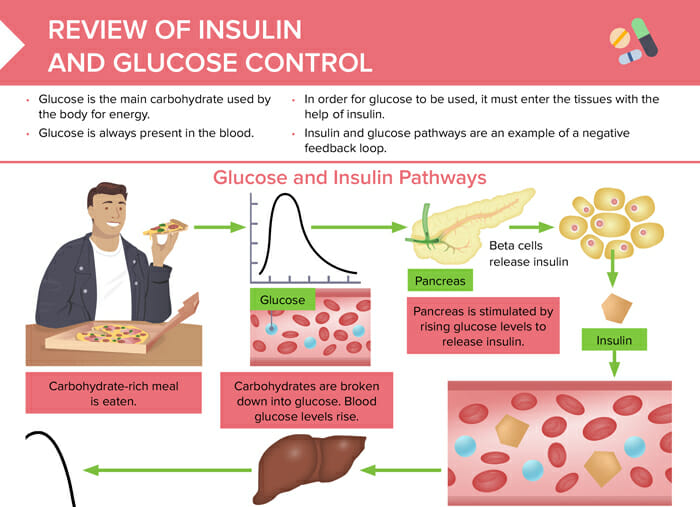
Insulin and glucose control: insulin pathway overview
Glucose and insulin pathways are an example of a negative feedback loop, where rising glucose levels stimulate the pancreas to release insulin, which in turn helps glucose enter tissues and lowers blood glucose levels.
Overview of the steps:
- Person eats carbohydrate-rich meal.
- Carbohydrates are broken down into glucose.
- Blood glucose levels rise.
- Pancreas is stimulated to release insulin into the bloodstream.
- Insulin binds to insulin receptors on cell membranes.
- Liver takes up glucose and stores it as glycogen.
- Glucose leaves bloodstream and enters cell.
- Glucose now can be used for energy in the cells; blood glucose levels normalize, pancreas stops releasing insulin.
What is glucose control solution?
Glucose control solution is often used in diabetes management to evaluate the accuracy of glucose meters and test strips. The liquid has a known concentration of glucose, allowing nurses to double-check that the meters and test strips work correctly.
Which genetically engineered hormone is used to control glucose levels in humans?
Insulin can be genetically engineered (synthetic insulin). It mimics the function of natural insulin and can be used in diabetes management.