Pros and cons of inducing labor
Pros
- Induction can help avoid complications from post-term pregnancy or medical conditions like premature rupture of membranes.
- Augmentation can shorten labor duration, when indicated.
Cons
- Introduces risk factors based on method, e.g. hyperstimulation of the uterus
- Augmentation may increase labor pain.
- Induction may lead to C-section if labor fails to progress.
Related videos
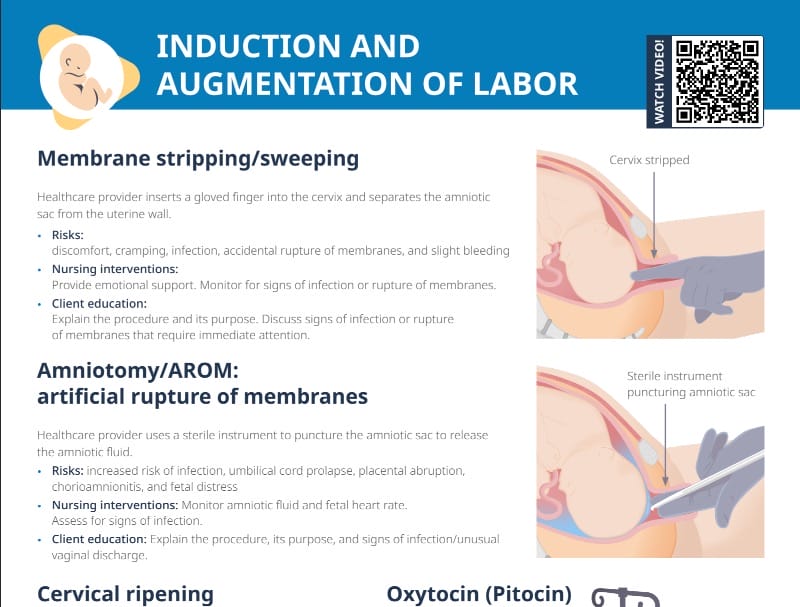
Membrane stripping/sweeping
What is membrane stripping?
Membrane stripping involves the healthcare provider inserting a gloved finger into the cervix to separate the amniotic sac from the uterine wall.
It is important to provide emotional support to the client and to monitor for and educate about signs of infection of rupture of membranes.
Risks
Membrane stripping can come with
- Discomfort and cramping
- Infection
- Accidental rupture of membranes
- Slight bleeding
Amniotomy/artificial rupture of membranes (AROM)
In this method, the healthcare provider uses a sterile instrument to puncture the amniotic sac, releasing the amniotic fluid. Amniotic fluid and fetal heart rate need to be monitored. Assess for signs of infection, and educate the client on the procedure, its purpose, and signs of infection/unusual vaginal discharge.
Risks:
- Increased risk of infection
- Umbilical cord prolapse
- Placental abruption
- Chorioamnionitis
- Fetal distress
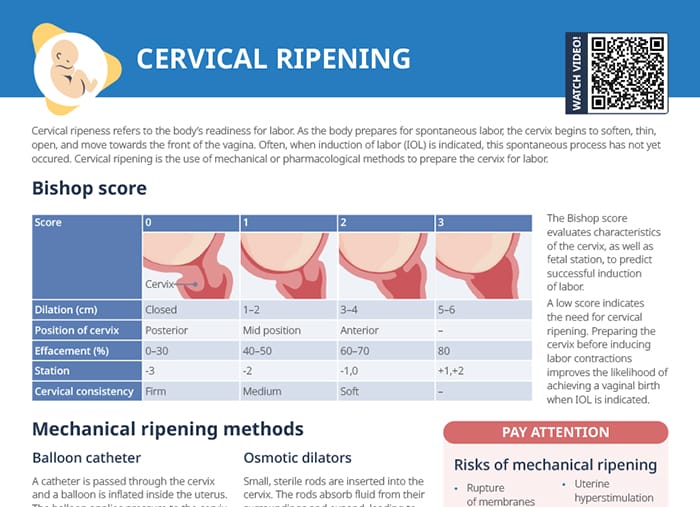
Cervical ripening
What is cervical ripening?
Cervical ripening aids cervix softening for labor dilation. Uterine contractions and fetal heart rate need to be monitored. Assess for uterine hyperstimulation and monitor signs of infection.
How to soften the cervix
This can be done pharmacologically or mechanically:
- Prostaglandin medication administered vaginally or orally to ripen cervix and stimulate contractions
- Mechanical dilation uses a catheter or balloon device inserted into the cervix to dilate it and stimulate contractions.
Does cervical ripening hurt?
Mechanical dilation can involve discomfort and cramping. Educate your client on the procedure and purpose, the potential discomfort, side effects, and signs of infection.
Pharmaceutical ripening is not painful, but involves risks of uterine hyperstimulation leading to fetal distress, uterine rupture, and nausea.
Download: Cervical Ripening Cheat Sheet
Lookup sheet for applying the Bishop score and mechanical and pharmaceutical ripening methods
Oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion
An aqueous solution with oxytocin can be administered intravenously to induce or augment contractions.
Risks
- Uterine hyperstimulation
- Fetal distress
- Uterine rupture
Interventions and client teachings
Titrate oxytocin according to uterine response. Monitor fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. Explain purpose of oxytocin infusion, potential risks such as uterine hyperstimulation, and how to communicate concerns.