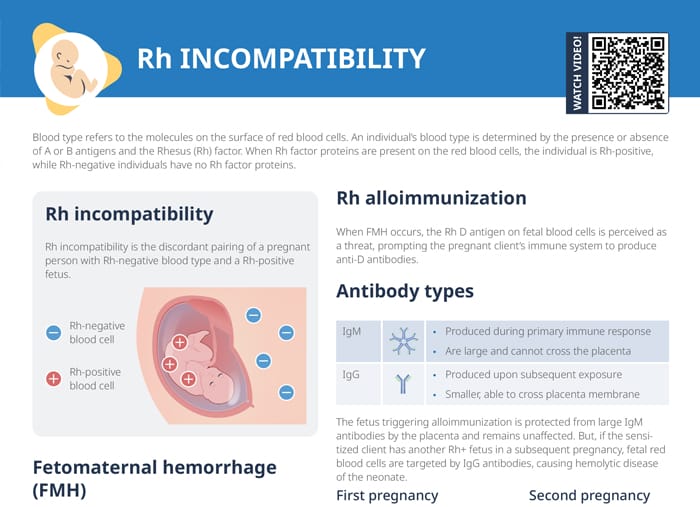
Bleeding during pregnancy
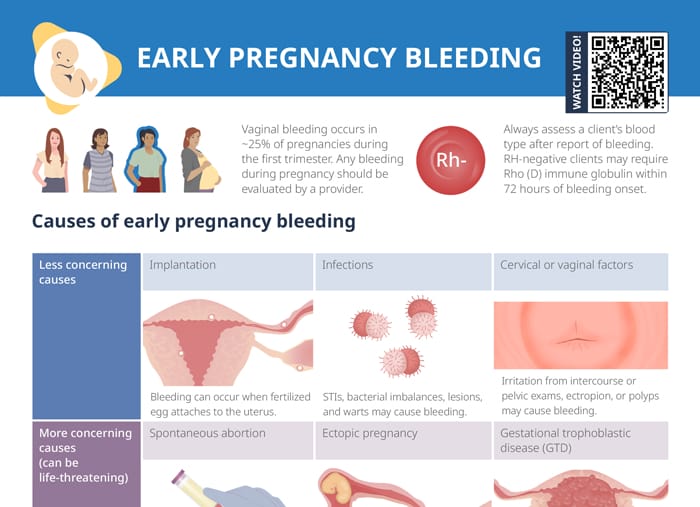
Vaginal bleeding occurs in about 25% of pregnancies during the first trimester. All bleeding in pregnancy should be evaluated by a provider.
Nursing tip: Always assess a client’s blood type after a report of bleeding. RH-negative clients may require Rho (D) immune globulin within 72 hours of bleeding onset.
Causes of early pregnancy bleeding
Less concerning causes
- Implantation bleeding: Bleeding might occur when the fertilized egg attaches to the uterus.
- Infections: STIs, bacterial imbalances, lesions, and warts may cause bleeding.
- Cervical or vaginal factors: Irritation from intercourse or pelvic exams, ectropion, or polyps may cause bleeding.
Serious causes (potentially life-threatening)
- Spontaneous abortion: occurs in 10–15% of confirmed pregnancies
- Ectopic pregnancy: occurs in 0.5–2% of pregnancies
- Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD): occurs in less than 0.5% of pregnancies
Related videos
Nursing assessment of a client who is bleeding during early pregnancy
Assessment
- Timing of when bleeding began
- Any vaginal symptoms (discharge, odor, burning)
- Pain location, quality (including shoulder pain)
- Amount of bleeding, color
- LMP or due date if client has been seen by MD
- Presence of clots
- Presence of pregnancy symptoms
- Signs of infection
- Signs of shock, hypovolemia
- Anticipate labs, ultrasound, pelvic examination
Client education around early pregnancy bleeding
Educate your client on when to call a provider, including signs of an ectopic pregnancy. Provide appropriate education and empathy: bleeding can be emotionally distressing to clients.
Reinforce the importance of follow-up care for clients experiencing miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, or GTD.
Patient questions around bleeding during pregnancy
“If I have implantation bleeding, will a pregnancy test be positive?”
Even if clients experience implantation bleeding, a pregnancy test might not immediately be positive. Implantation bleeding occurs when a fertilized egg attaches to the lining of the uterus, which typically happens about 10 to 14 days after conception. The body starts producing human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), the hormone detected by pregnancy tests, after implantation. It usually takes a few days after implantation for hCG levels to become high enough to be detected by a pregnancy test. Advise clients to wait a few days and retest for a more accurate result.
“Can you take a pregnancy test during implantation bleeding?”
Advise clients on the ideal time when to take a pregnancy test after implantation bleeding. The accuracy of a test during implantation bleeding might be affected and a test after a missed period (typically a few days to a week after implantation) is more reliable.
“How much bleeding is normal in early pregnancy?”
A small amount of spotting or light bleeding is relatively common and often not a cause for concern. Spotting might be pink, red, or brown, can happen at any time, and is usually much lighter than a menstrual period. Promote calmness in clients while educating them about warning signs and when to contact a provider. To be on the safe side, encourage clients to report all bleeding to a healthcare provider.
“When is spotting during pregnancy concerning?”
Warning signs about pregnancy bleeding include:
- Heavy bleeding (similar or heavier than menstrual period)
- Accompanying symptoms (e.g., cramps, pain, dizziness, passing tissue – could indicate miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy)
- Persistent bleeding
Educate clients to immediately contact their healthcare provider if they experience the above symptoms.
“How to stop bleeding during pregnancy?”
Advise clients to not try to stop bleeding on their own, but consult their healthcare provider about all spotting and bleeding during pregnancy to ensure optimal care.
Immediate measures in the time before seeing the provider can include:
- Monitoring the bleeding (track amount, report other symptoms)
- Trying to get rest to feel more comfortable and reduce risk of further complications
- Avoiding to insert anything into the vagina and abstaining from intercourse until a healthcare provider has evaluated the bleeding