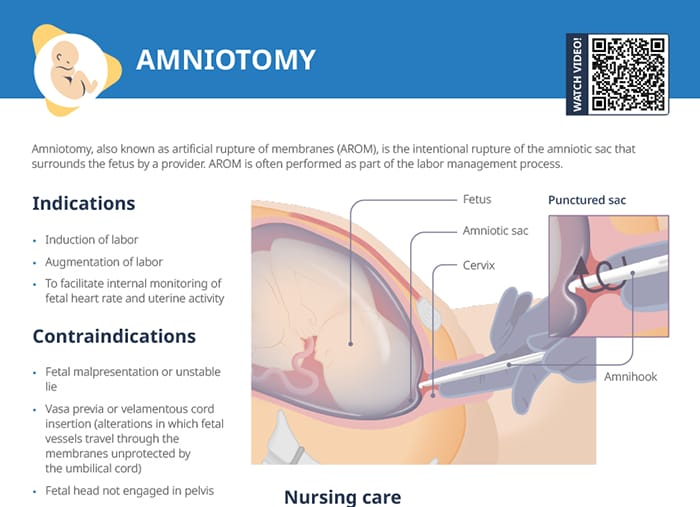
What is an amnioinfusion?
Amnioinfusion is the installation of warmed isotonic fluid (such as normal saline or lactated ringer solution) into the intrauterine cavity.
It is often used to relieve pressure on the umbilical cord and improve fetal status in a pregnant or laboring client.
Indications for amnioinfusion
Oligohydramnios is one of the most common indications for amnioinfusion, which is low amniotic fluid levels.
Amnioinfusion can be indicated when there are variable decelerations during labor, or when membranes rupture preterm/prematurely before the third trimester, to delay the onset of labor.
The restored fluid volume helps to maintain a protective environment for the fetus.
Contraindications
Amnioinfusion is contraindicated if the fetus is in a non-vertex position. Placenta previa and an active genital herpes infection are further contraindications.
Additionally, in cases of severe fetal distress, amnioinfusion is contraindicated as it could delay emergent delivery.
Risks of amnioinfusion
If the catheter is misplaced outside the amniotic cavity, between the membranes and the uterine wall, amnioinfusion could cause placental abruption.
Further risks include:
- Chorioamnionitis: Introducing fluid into the uterus can increase the potential for bacteria to enter the sterile uterine environment. Aseptic technique should be maintained.
- Uterine overdistension: If too much fluid is infused into the amniotic sac, the uterus can get overdistended. This can impair contractions, cause pain, and affect fetal circulation.
- Umbilical cord prolapse: Adding fluid into the amniotic sac can increase the likelihood of the umbilical cord getting displaced into the birth canal, particularly if the baby is not well-engaged in the pelvis.
Procedure
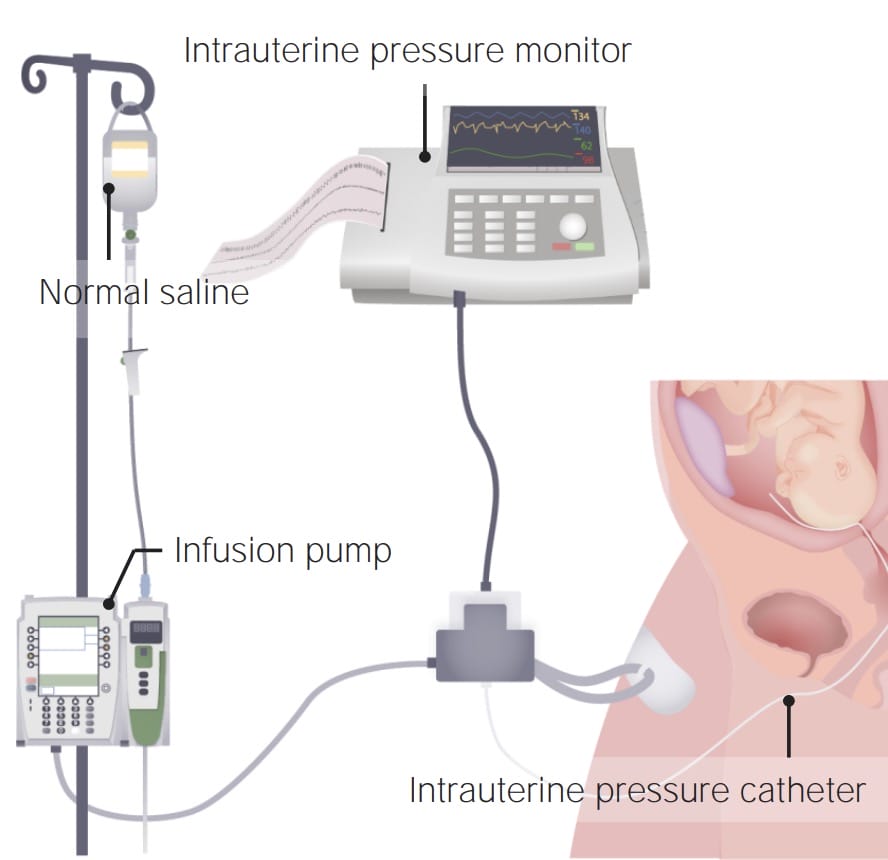
Equipment setup
The equipment needed is:
- An intrauterine pressure monitor
- The infusion pump
- An intrauterine pressure catheter
- Normal saline
Nursing care during the procedure
- Ensure that the client has consented and had all questions answered.
- Assist with amniotomy, catheter placement, and infusion setup as needed. Maintain aseptic technique when handling the catheter and fluid to prevent infection.
- Ensure that fluid is warmed to body temperature.
- Monitor client’s vital signs and fetal heart rate. Encourage relaxation techniques and offer support, as some discomfort might be felt during the procedure.
- Be alert for signs of infection.
- Monitor infusion input and output; avoid uterine overdistension.
- Notify a provider promptly of any change in status.
Amnioinfusion during labor
During labor, amnioinfusion is usually performed to relieve umbilical cord compression. Fetal heart rate and uterine contractions need to be monitored closely, as too much fluid can lead to uterine overdistension or increased intrauterine pressure, which can cause fetal distress.