El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de Epstein-Barr ( EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology lineal de ADN de doble cadena que pertenece a la familia Herpesviridae Herpesviridae A family of enveloped, linear, double-stranded DNA viruses infecting a wide variety of animals. Subfamilies, based on biological characteristics, include: alphaherpesvirinae; betaherpesvirinae; and gammaherpesvirinae. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2. Este virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de alta prevalencia se transmite principalmente a través del contacto con las secreciones orofaríngeas de un individuo infectado. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology puede infectar a las células epiteliales y a los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B, donde puede experimentar la replicación lítica o la latencia. La infección inicial puede presentarse como mononucleosis Mononucleosis Infectious mononucleosis (IM), also known as "the kissing disease," is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Its common name is derived from its main method of transmission: the spread of infected saliva via kissing. Clinical manifestations of IM include fever, tonsillar pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy. Mononucleosis infecciosa, y la reactivación (a menudo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes seropositivos) puede causar leucoplasia vellosa oral. Una característica importante de las infecciones por EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus es la capacidad de transformar los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B, lo que proporciona inmortalización y proliferación. Así, el EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus está asociado a trastornos linfoproliferativos y neoplasias, como el linfoma de Burkitt, el linfoma de Hodgkin, la linfohistiocitosis hemofagocítica, la enfermedad linfoproliferativa postrasplante, ciertos cánceres gástricos y el carcinoma nasofaríngeo.
Last updated: Dec 29, 2025
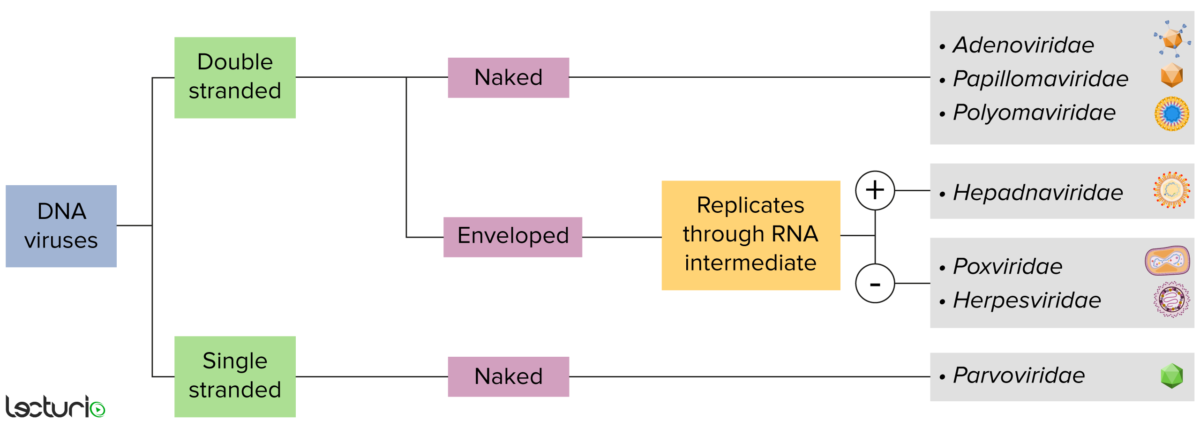
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como de cadena simple o doble. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que suele tomarse de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
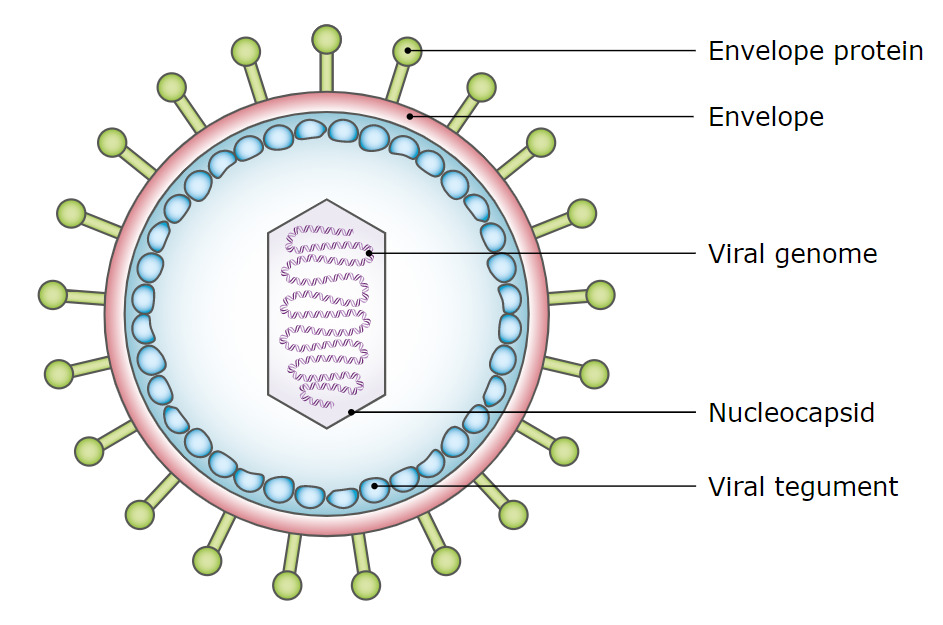
Diagrama simplificado de la estructura del virus de Epstein-Barr
Imagen: “Simplified diagram of the structure of EBV” por Ben Taylor. Licencia: Dominio Público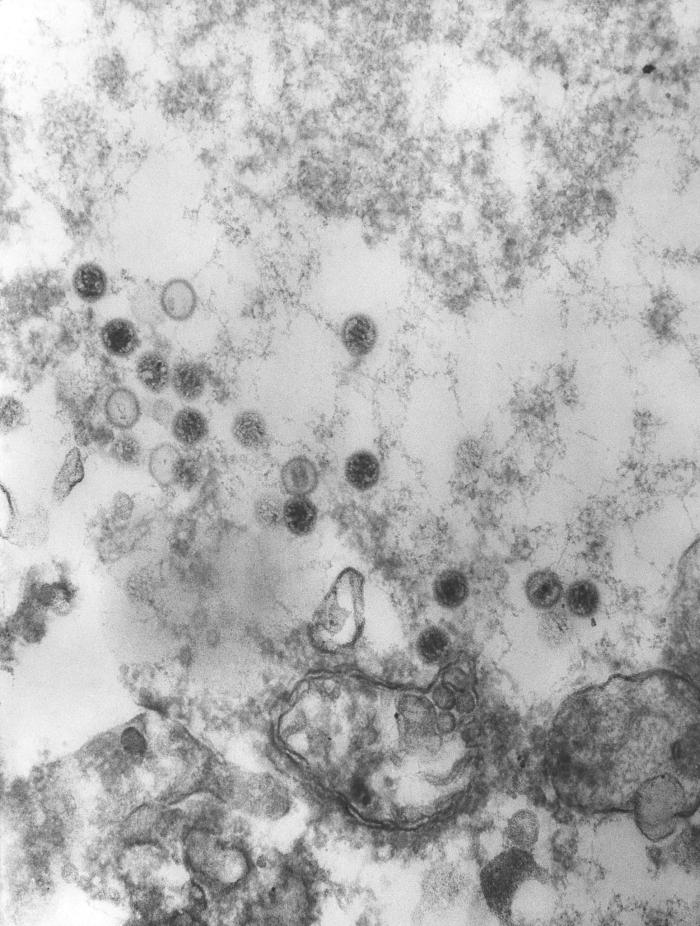
Imagen de microscopía electrónica de transmisión que muestra la presencia de numerosos viriones del virus de Epstein-Barr (EBV), miembros de la familia de los virus Herpesviridae:
En el núcleo de su cápside proteica, el EBV contiene un genoma lineal de ADN de doble cadena.
Los LOS Neisseria humanos son el único reservorio.
Entrada a las células:
Latencia:
Replicación lítica:
Tipos de células infectadas:
Infección primaria:
Trastornos linfoproliferativos:
Patogénesis de la infección por norovirus
Imagen de Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0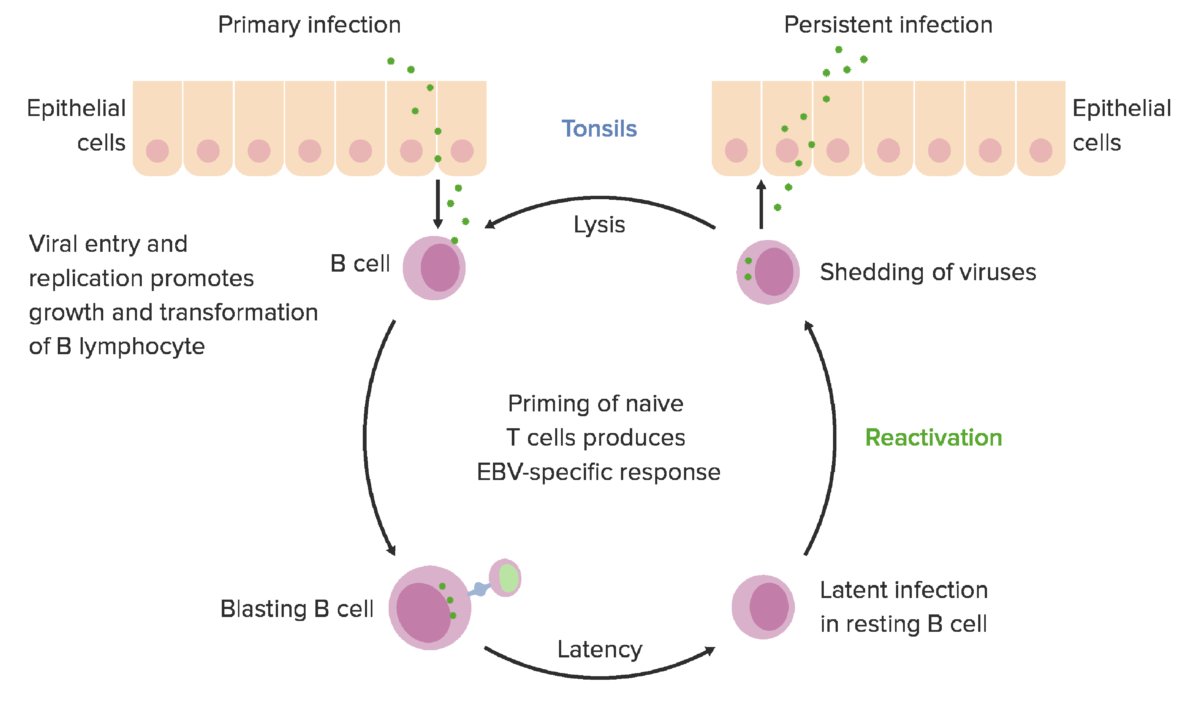
El EBV puede infectar tanto a los linfocitos B como a las células epiteliales orofaríngeas:
El virus entra en los linfocitos B uniéndose al receptor celular CD21, lo que permite la fusión de la envoltura viral con la membrana celular.
El ciclo lítico da lugar a la producción de viriones infecciosos tanto en los linfocitos B como en las células epiteliales orofaríngeas. En los linfocitos B, la replicación lítica normalmente solo tiene lugar después de la reactivación desde la latencia, mientras que en las células epiteliales orofaríngeas, la replicación lítica suele seguir directamente a la entrada del virus.
Durante la replicación lítica, la ADN polimerasa viral se encarga de sintetizar el genoma viral. Esto contrasta con la latencia, en la que la ADN polimerasa de la célula huésped copia el genoma viral. Sin embargo, la latencia no da lugar a la producción de viriones, ya que solo se expresa una parte de los genes del EBV.
Presentación:
Diagnóstico:
Tratamiento:
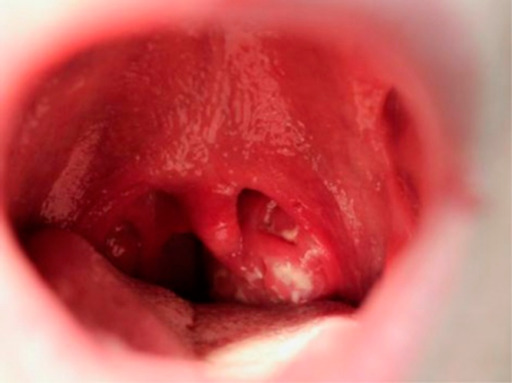
Mononucleosis infecciosa:
Faringitis que muestra una amigdalitis exudativa y una úvula agrandada en un estudiante universitario de 19 años, 5 días después del inicio de la mononucleosis infecciosa
La leucoplasia vellosa oral está causada por la reactivación del EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus latente y se produce sobre todo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes VIH positivos.
Presentación clínica:
Diagnóstico:
Tratamiento:
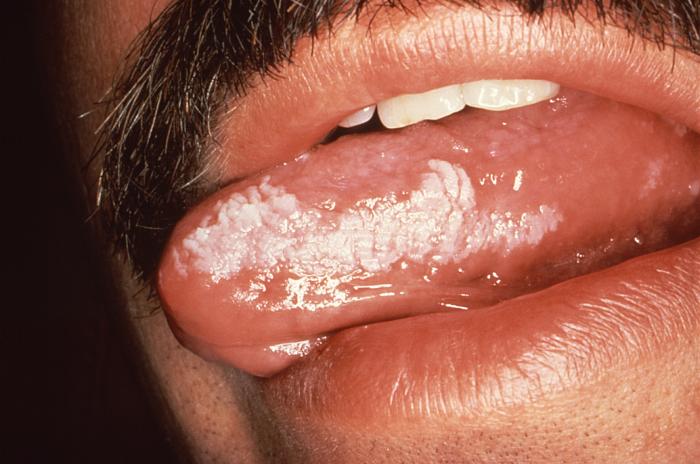
Mancha blanca y vellosa en la lengua de un paciente debido a una leucoplasia vellosa oral
Imagen: “Advanced oral hairy leukoplakia (OHL)” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público| Enfermedad | Características | Presentación Clínica | Tratamiento |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linfoma de Burkitt |
|
|
|
| Linfoma de Hodgkin | Células Reed-Sternberg |
|
|
| Linfohistiocitosis hemofagocítica |
|
|
|
| Enfermedad linfoproliferativa postrasplante |
|
|
↓ Terapia inmunosupresora |
| Carcinoma nasofaríngeo |
|
|
|
| Carcinoma gástrico asociado al AL Amyloidosis EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus |
|
|
|
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum total se conocen 115 especies diferentes de herpesvirus que se agrupan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 familias:
| HHV | Nombre común | Células objetivo primarias | Sitio de latencia | Presentación clínica* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 (grupo alfa) |
VHS-1 | Células mucoepiteliales | Ganglios de la raíz dorsal |
|
|
2 (grupo alfa) |
VHS-2 |
|
||
|
3 (grupo alfa) |
VZV |
|
||
|
4 (grupo gamma) |
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus |
|
Linfocitos B de memoria |
|
|
5 (grupo beta) |
CMV |
|
Células progenitoras hematopoyéticas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la médula ósea |
|
|
6A, 6B (grupo beta) |
Virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology herpes humano tipo 6 ( HHV-6 HHV-6 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7) | Linfocitos T | Monocitos | Roséola |
|
7 (grupo beta) |
HHV-7 HHV-7 Human herpesvirus (HHV)-6 and HHV-7 are similar double-stranded DNA viruses belonging to the Herpesviridae family. Human herpesviruses are ubiquitous and infections are commonly contracted during childhood. Human Herpesvirus 6 and 7 | Linfocitos T | ||
|
8 (grupo gamma) |
KSHV |
|
Linfocitos B | Sarcoma de Kaposi Kaposi A multicentric, malignant neoplastic vascular proliferation characterized by the development of bluish-red cutaneous nodules, usually on the lower extremities, most often on the toes or feet, and slowly increasing in size and number and spreading to more proximal areas. The tumors have endothelium-lined channels and vascular spaces admixed with variably sized aggregates of spindle-shaped cells, and often remain confined to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, but widespread visceral involvement may occur. Hhv-8 is the suspected cause. There is also a high incidence in AIDS patients. AIDS-defining Conditions |