El síndrome urémico hemolítico es un fenómeno clínico que se observa con mayor frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria niños y que consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una tríada clásica de anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica microangiopática, trombocitopenia y lesión renal aguda. El síndrome urémico hemolítico es una de las principales causas de lesión renal aguda en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños y se asocia con mayor frecuencia a un pródromo de enfermedad diarreica causada por bacterias productoras de toxinas tipo Shiga. Los LOS Neisseria análisis de laboratorio confirman una anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica microangiopática (hemoglobina < 8 g/dL, esquistocitos y Coombs directo negativo), trombocitopenia (recuento de plaquetas < 140 000/mm³) y lesión renal aguda (creatinina y nitrógeno de urea Urea A compound formed in the liver from ammonia produced by the deamination of amino acids. It is the principal end product of protein catabolism and constitutes about one half of the total urinary solids. Urea Cycle (BUN, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sangre elevados). El tratamiento del síndrome urémico hemolítico implica principalmente terapia de soporte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome urémico hemolítico es una enfermedad de los LOS Neisseria capilares (microangiopatía) que provoca la formación de coágulos de sangre, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types causada por la destrucción de los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estos capilares coagulados ( anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types hemolítica), lesión renal aguda y disminución de las plaquetas (trombocitopenia).
La etiología se clasifica como adquirida (infecciosa o no infecciosa) o hereditaria.
La fisiopatología del síndrome urémico hemolítico secundario a la toxina Shiga ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia sido bien descrita.
Otras formas de síndrome urémico hemolítico:
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas suelen aparecer entre 5–7 días posterior a la diarrea y pueden incluir:
El diagnóstico es clínico, basado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tríada clásica de:
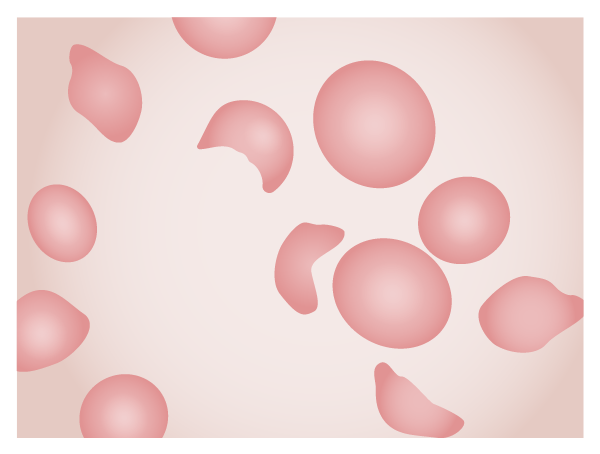
Microfotografía de un frotis de sangre de un paciente con síndrome urémico hemolítico. Obsérvense los esquistocitos, fragmentos de eritrocitos que quedan tras la lesión mecánica de las células en la microvasculatura.
Imagen por Lecturio.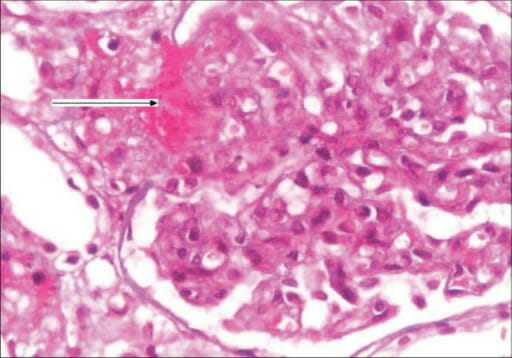
Biopsia renal del síndrome hemolítico urémico (SHU): Biopsia renal que muestra el glomérulo con un aumento de la matriz mesangial, edema focal de las células endocapilares, arteriolas con trombos de plaquetas y fibrina (flecha) y necrosis fibrinoide (tinción H&E, 400x).
Imagen: “F0002: Kidney biopsy showing glomerulus with increase in mesangial matrix, focal endocapillary cell swelling and arterioles with platelet fibrin thrombi (arrow), and fibrinoid necrosis. (H&E stain, magnification ×400)” por G. Lakshminarayana, R. Rajesh, A. Jojo, G. Kurian, and V. N. Unni. Licencia: CC BY 2.0El tratamiento del síndrome urémico hemolítico se realiza principalmente mediante terapias de soporte.
Hay que tener en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuenta que el tratamiento con antibióticos durante las enfermedades diarreicas sanguinolentas causadas por bacterias productoras de toxina Shiga se asocia con un mayor riesgo de desarrollar síndrome urémico hemolítico.