El síndrome de Sturge-Weber es un trastorno neurocutáneo congénito que se presenta con una marca de nacimiento facial llamada mancha en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum vino de oporto, anomalías neurológicas como convulsiones y anomalías oculares como glaucoma Glaucoma Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by typical visual field defects and optic nerve atrophy seen as optic disc cupping on examination. The acute form of glaucoma is a medical emergency. Glaucoma is often, but not always, caused by increased intraocular pressure (IOP). Glaucoma. No todos estos síntomas tienen que estar presentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un individuo afectado y algunos pueden desarrollarse más adelante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vida. Si bien la afección es congénita, no se hereda, ya que la mutación causante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen GNAQ es somática y esporádica. El diagnóstico se sospecha con base a los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la neuroimagenología, y se confirma mediante pruebas genéticas. El tratamiento está dirigido al AL Amyloidosis control de los LOS Neisseria síntomas y la prevención de las convulsiones y la hemiparesia.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La incidencia es aproximadamente 1 de cada 20,000 a 50,000 recién nacidos vivos.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas generalmente se deben al AL Amyloidosis efecto de la malformación capilar-venosa dentro del cerebro, la piel y el ojo. No todos los LOS Neisseria síntomas tienen que estar presentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un individuo para que se le diagnostique síndrome de Sturge-Weber y algunos síntomas pueden desarrollarse más adelante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vida.
Mancha en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum vino de oporto:
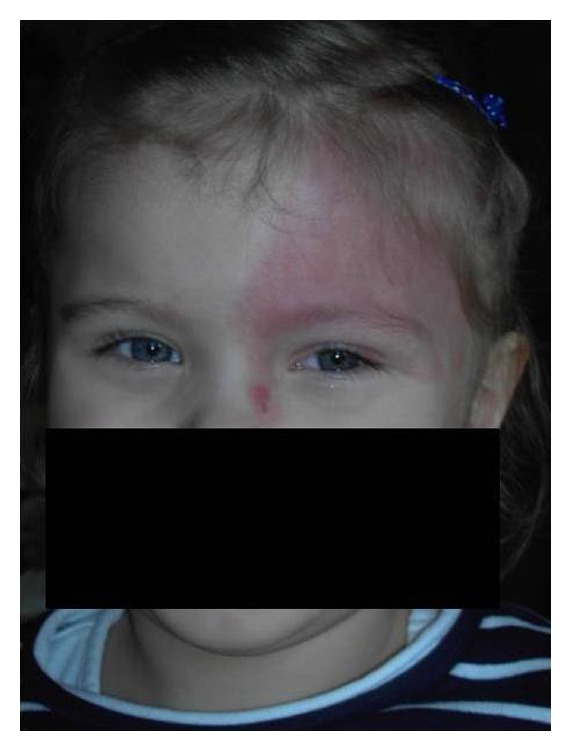
Mancha en vino de oporto:
Nevo flamígero difuso que afecta el párpado superior izquierdo y la frente
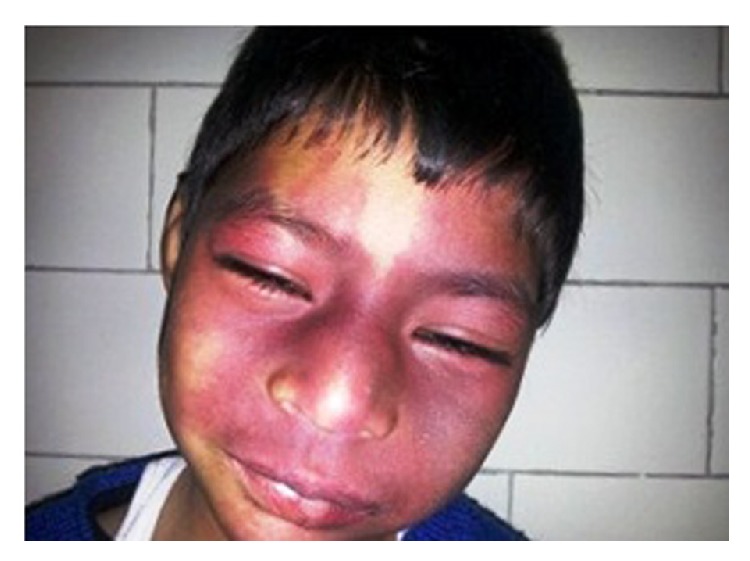
Mancha en vino de oporto:
Nevo flamígero bilateral sobre la cara
Una manera fácil de recordar es usando la mnemotecnia “STURGE” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
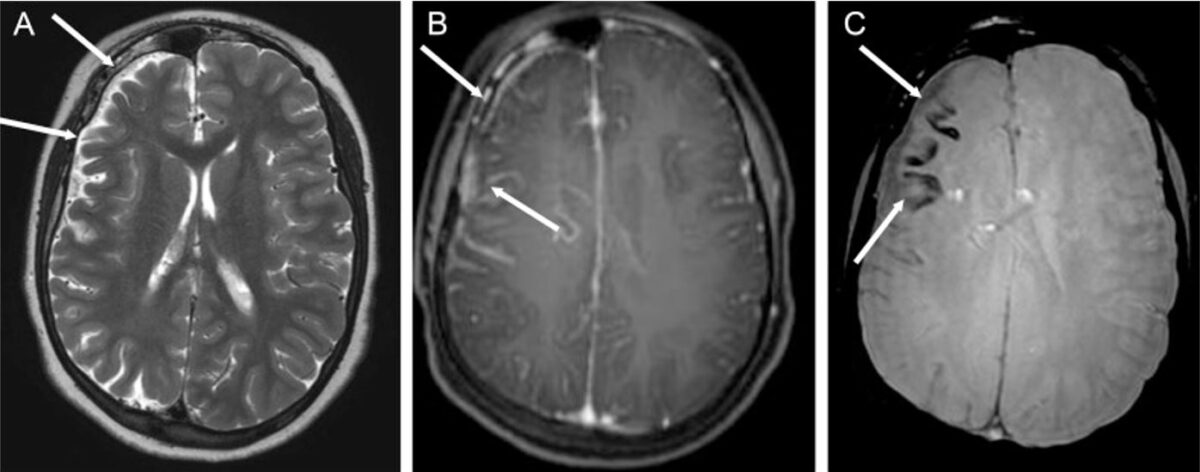
Epilepsia asociada al síndrome de Sturge-Weber (SWS): Síndrome de Sturge-Weber en un niño de 14 años con múltiples focos epilépticos en el hemisferio cerebral derecho y epilepsia parcial crónica
A: imagen axial ponderada en T2 que muestra hemiatrofia cerebral derecha (flechas blancas)
B: secuencia axial ponderada en T1 después de la inyección de gadolinio, que demuestra realce leptomeníngeo de la región frontoparietal (flechas blancas)
C: las flechas blancas apuntan a la calcificación cortical en el lóbulo frontal, que aparece como vacíos de señal de las imágenes ponderadas sometidas.