La púrpura de Henoch-Schönlein, también conocida como vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus por inmunoglobulina A ( IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions), es una vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus autoinmune de pequeños vasos que suele presentarse como una tétrada de dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, artralgia, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma y erupción purpúrica. La fisiopatología implica el depósito de complejos inmunes de IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum múltiples vasos tras un desencadenante (infección/ambiental), y los LOS Neisseria síntomas dependen de los LOS Neisseria tejidos implicados. El diagnóstico se establece clínicamente, pero puede apoyarse de estudios de laboratorio y biopsia de piel o riñón. El tratamiento es principalmente de soporte, pero puede incluir esteroides e inmunosupresores en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos más graves. El pronóstico suele ser excelente, pero algunos pacientes pueden desarrollar una insuficiencia renal terminal.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La púrpura de Henoch-Schönlein es una vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus de pequeños vasos mediada por la inmunoglobulina A.
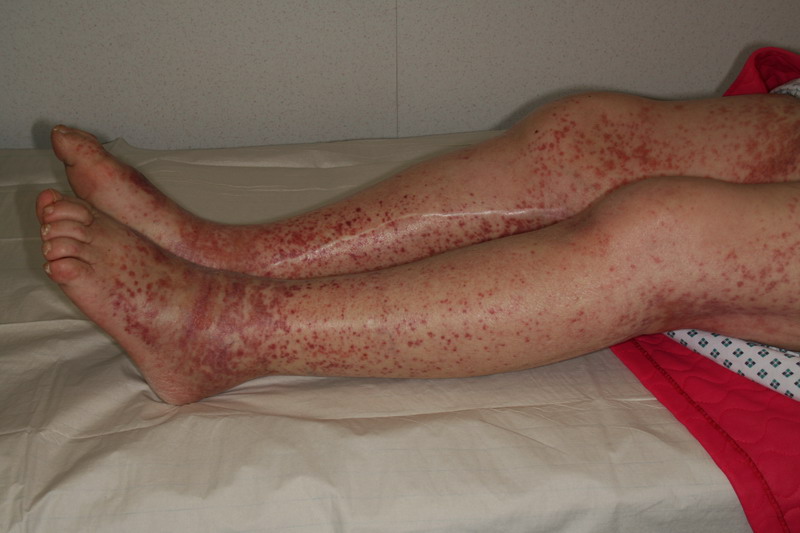
Erupción purpúrica característica de la púrpura de Henoch-Schönlein
Imagen: “Purpura Schönlein-Henoch” por Mnokel. Licencia: Dominio Público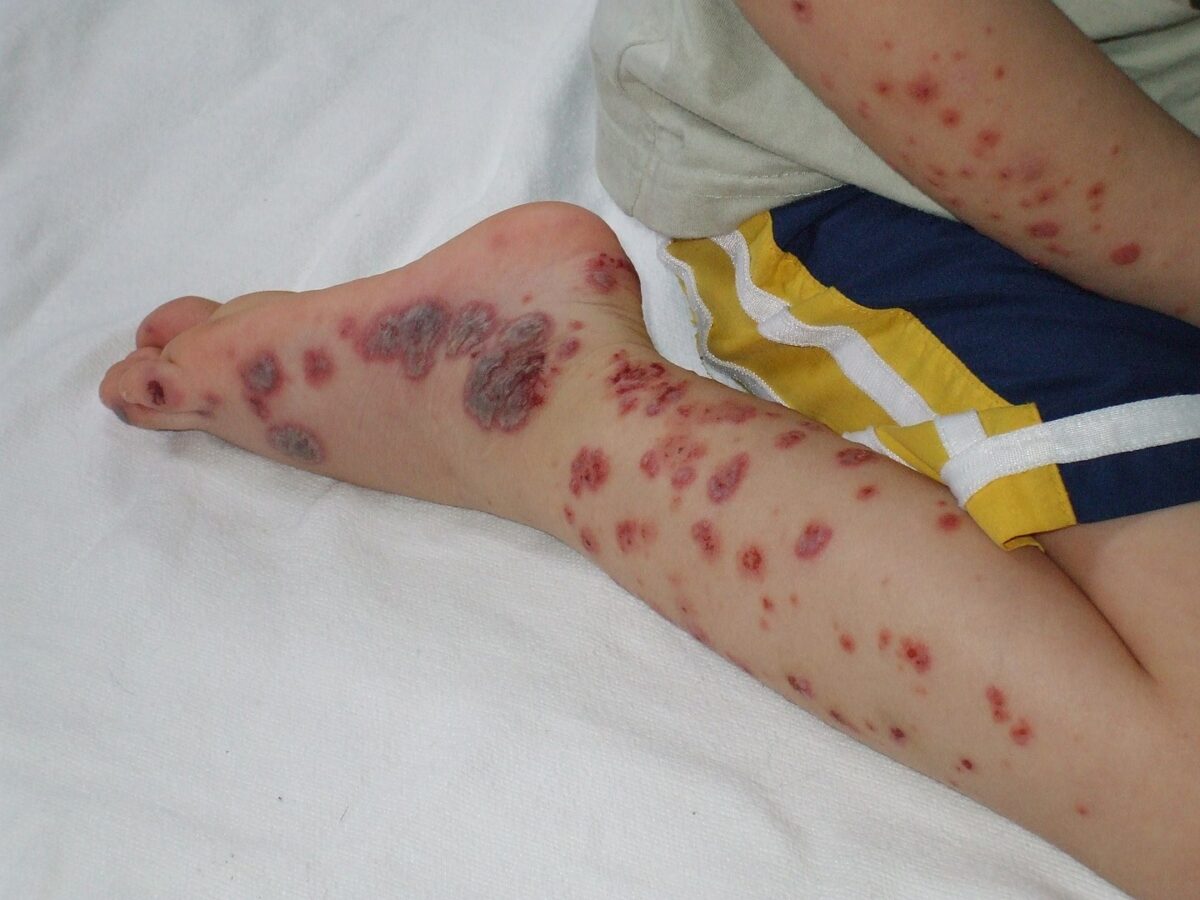
Púrpura evidente en las extremidades distales de un paciente pediátrico con púrpura de Henoch-Schönlein
Imagen: “Purpura2” por Okwikikim. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria análisis de laboratorio se utilizan para descartar diagnósticos diferenciales y evaluar complicaciones.
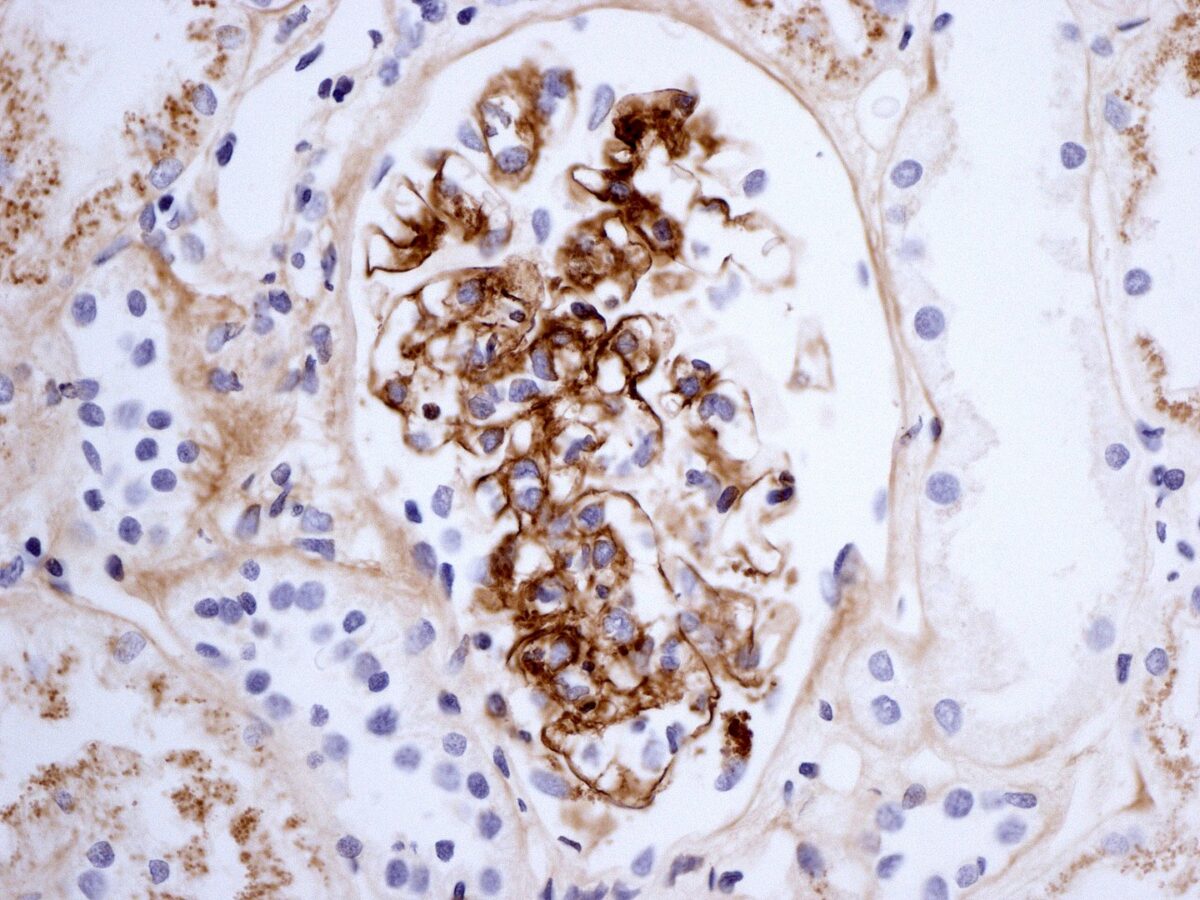
Biopsia renal en la púrpura de Schönlein-Henoch que muestra inmunotinción para IgA
Imagen: “Henoch-Schönlein nephritis IgA immunostaining” por Lazarus Karamadoukis, Linmarie Ludeman, and Anthony J Williams. Licencia: CC BY 2.0La imagenología se utiliza para las presentaciones complicadas.
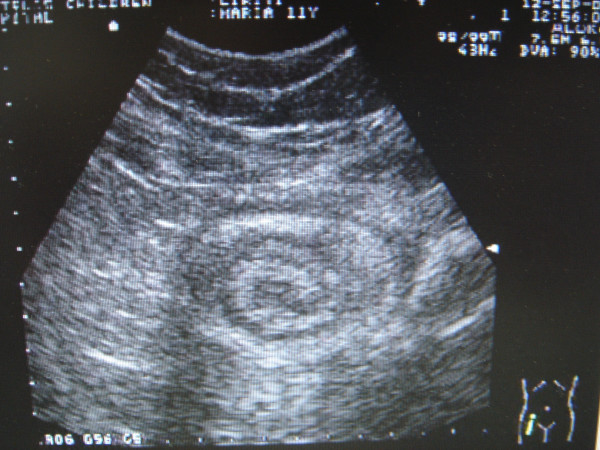
Signo de la diana típico de la intususcepción en el ultrasonido abdominal
Imagen: “Pelvic plastron secondary to acute appendicitis in a child presented as appendiceal intussusception. A case report” por Christianakis E, Sakelaropoulos A, Papantzimas C, Pitiakoudis M, Filippou G, Filippou D, Rizos S, Paschalidis N. License: CC BY 2.0