La miastenia gravis es un trastorno neuromuscular autoinmune caracterizado por debilidad y fatigabilidad de los LOS Neisseria músculos esqueléticos, causada por la disfunción/destrucción de los LOS Neisseria receptores de acetilcolina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la unión neuromuscular. La miastenia gravis se presenta con fatiga, ptosis Ptosis Cranial Nerve Palsies, diplopía, disfagia, dificultades respiratorias y debilidad progresiva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las extremidades, lo que provoca dificultad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el movimiento. El diagnóstico se establece con base en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación clínica, detección de anticuerpos y estudios electrofisiológicos. El tratamiento tiene como objetivo aumentar la actividad de la acetilcolina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la unión neuromuscular y la supresión de anticuerpos. Esta enfermedad puede asociarse con timomas e hiperplasia tímica, y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ocasiones está indicada la timectomía. La miastenia gravis puede progresar a una crisis miasténica potencialmente mortal con insuficiencia respiratoria, pero esto se puede prevenir con el tratamiento adecuado. El pronóstico generalmente es bueno con tratamiento, y algunos pacientes pueden lograr una remisión a largo plazo.
Last updated: Sep 30, 2025
Miastenia gravis es un trastorno autoinmune crónico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el que anticuerpos atacan el complejo de receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors de acetilcolina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la unión neuromuscular.
Existen 2 formas clínicas principales de miastenia gravis:
Además, existen formas más raras de miastenia gravis que afectan principalmente a la población pediátrica:
La miastenia gravis también puede ser clasificada según el perfil serológico de los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos presentes:
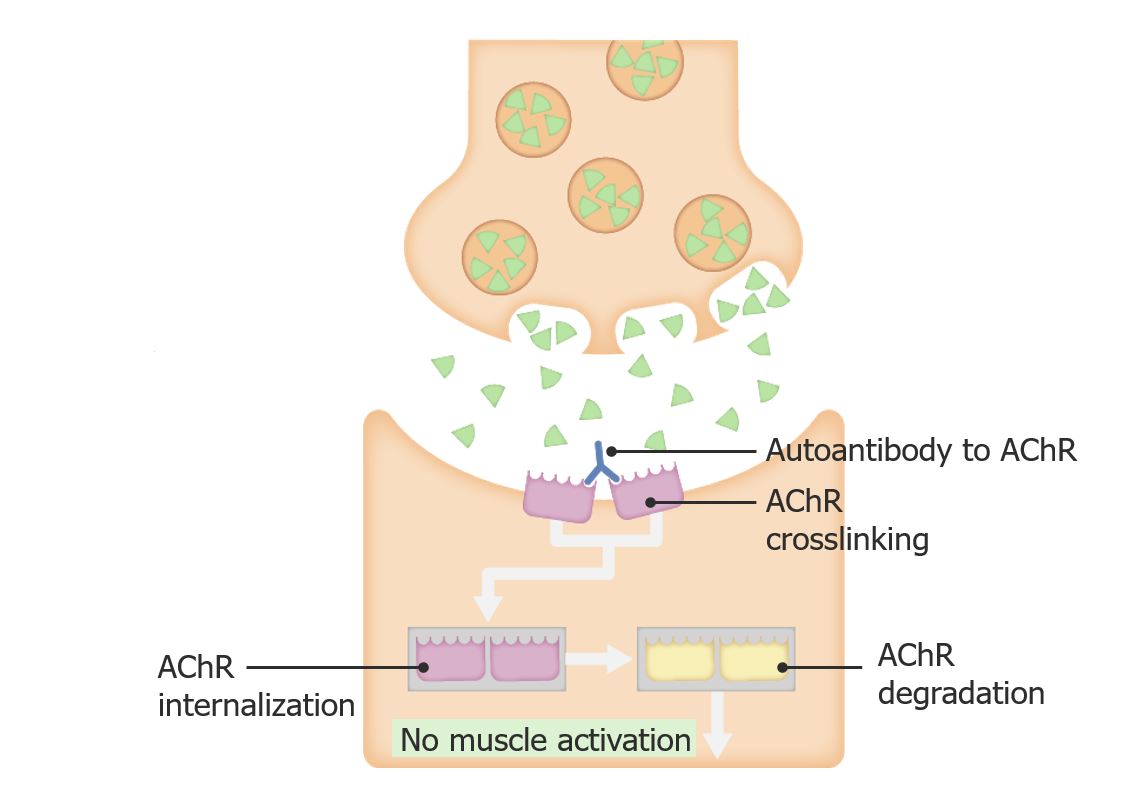
Fisiopatología de miastenia gravis
Imagen por Lecturio.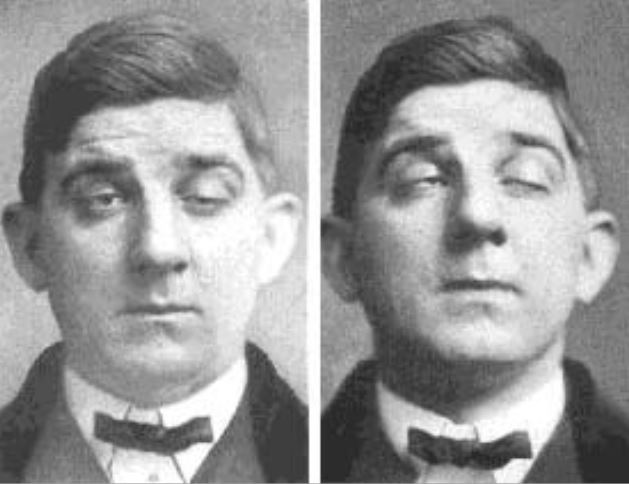
Ptosis en un paciente con miastenia gravis
Imagen: “Myasthenia Gravis” por Posey & Spiller. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoSe realiza una RM o TC de tórax para descartar la posibilidad de un timoma.
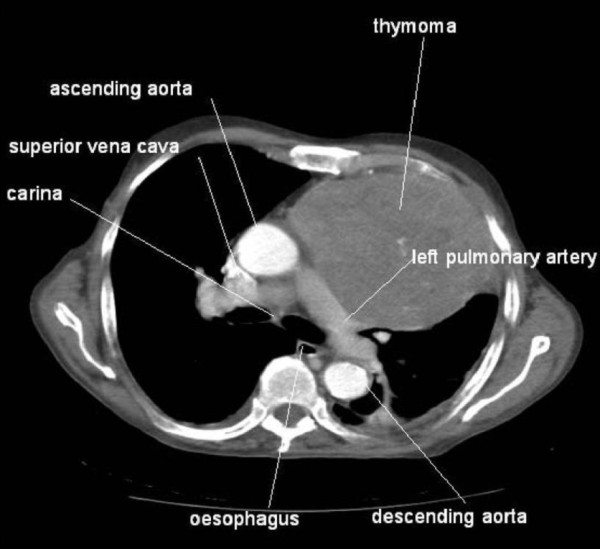
TC que muestra un gran timoma
Imagen: “Association between thymoma and persistent hypothermia: a case report” por Johns RH, Reinhardt AK. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Inhibidores de la acetilcolinesterasa:
Medicamentos inmunosupresores crónicos: