La malaria Malaria Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease affecting humans and other animals. Most commonly transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito infected with microorganisms of the Plasmodium genus. Patients present with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and diaphoresis. Plasmodium/Malaria, una enfermedad parasitaria transmitida por vectores causada por Plasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs spp., se transmite a través de la inyección de esporozoitos o formas inmaduras del parásito en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el torrente sanguíneo de una persona. Luego, los LOS Neisseria esporozoítos infectan los LOS Neisseria hepatocitos y se diferencian en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum esquizontes, que posteriormente se rompen y los LOS Neisseria merozoítos invaden los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos. Como tal TAL Renal Sodium and Water Regulation, la farmacoterapia para la malaria Malaria Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease affecting humans and other animals. Most commonly transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito infected with microorganisms of the Plasmodium genus. Patients present with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and diaphoresis. Plasmodium/Malaria se dirige a las formas de esquizontes exoeritrocíticos y eritrocíticos. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum conjunto, estos medicamentos se clasifican como esquizonticidas.
Last updated: Mar 28, 2025
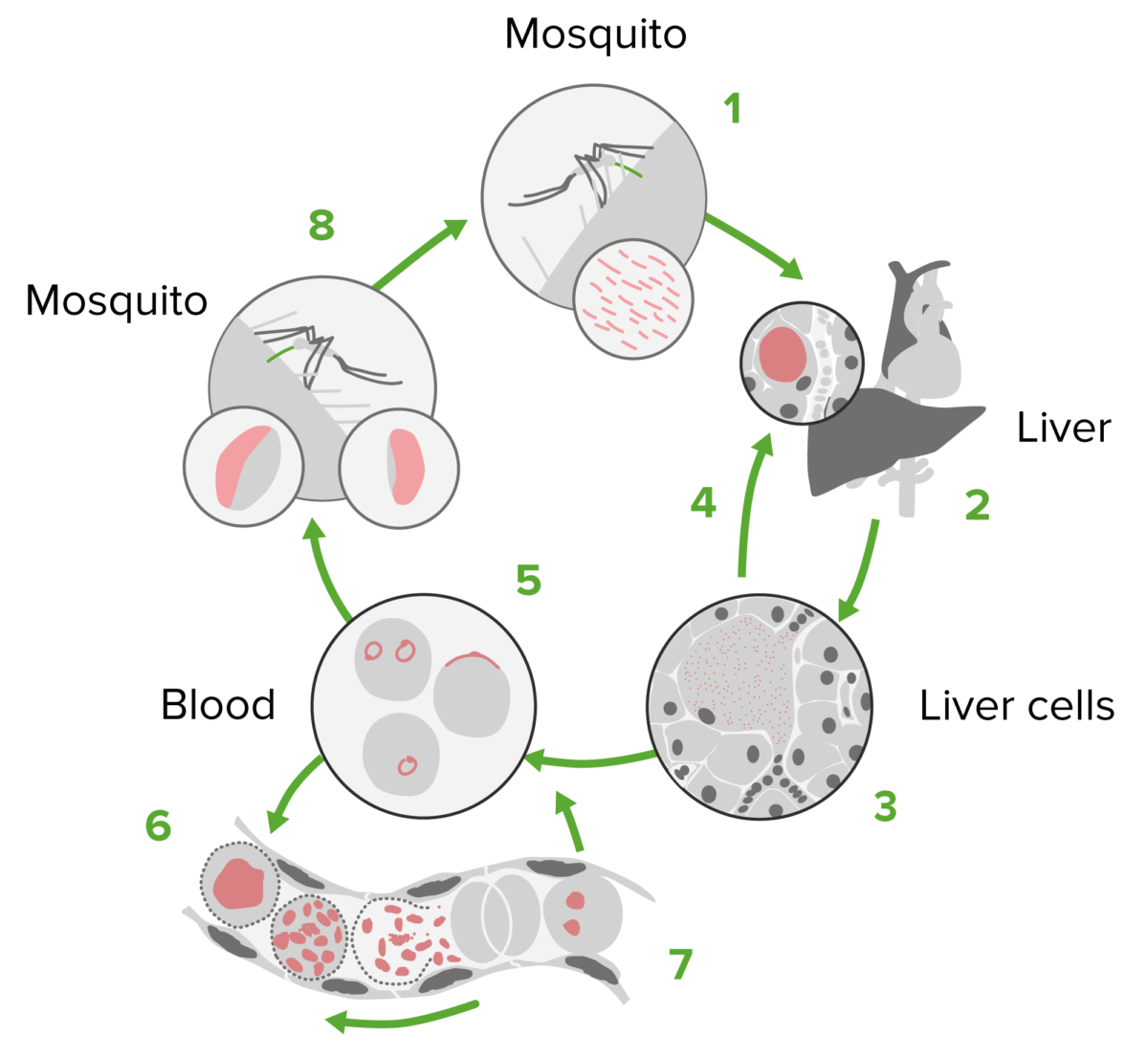
Ciclo de vida del plasmodio
Imagen por Lecturio.El tratamiento de la malaria Malaria Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease affecting humans and other animals. Most commonly transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito infected with microorganisms of the Plasmodium genus. Patients present with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and diaphoresis. Plasmodium/Malaria está dirigido a diferentes estadios del ciclo de vida del Plasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs:
El tratamiento consta de 3 pasos:
Profilaxis y prevención de la malaria Malaria Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease affecting humans and other animals. Most commonly transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito infected with microorganisms of the Plasmodium genus. Patients present with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and diaphoresis. Plasmodium/Malaria
Gametocida + esquizonticida:
| Medicamento | Efectos secundarios |
|---|---|
| Arteméter-lumefantrina (Coartem®) | Cefalea, mareo, anorexia Anorexia The lack or loss of appetite accompanied by an aversion to food and the inability to eat. It is the defining characteristic of the disorder anorexia nervosa. Anorexia Nervosa, náuseas/vómitos, debilidad, artralgia, mialgia |
| Artesunato | Cefalea, mareo, anorexia Anorexia The lack or loss of appetite accompanied by an aversion to food and the inability to eat. It is the defining characteristic of the disorder anorexia nervosa. Anorexia Nervosa, náuseas/vómitos |
| Atovacuona-proguanil (Malarone®) | Dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal, náuseas/vómitos, cefalea, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños |
| Cloroquina |
|
| Hidroxicloroquina | Molestias gastrointestinales, cefalea, erupción cutánea, cambios visuales |
| Doxiciclina | Fotosensibilidad, malestar gastrointestinal (mitigado al AL Amyloidosis tomarlo con alimentos), decoloración permanente de los LOS Neisseria dientes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum niños <8 años |
| Mefloquina |
|
| Primaquina | Molestias gastrointestinales, cefalea, metahemoglobinemia, hemólisis (debido a la deficiencia de G6PD G6PD Pentose Phosphate Pathway) |
| Quinidina |
|
| Tafenoquina |
|
| Medicamento | Clasificación | Mecanismo de acción | Indicaciones | Contraindicaciones |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arteméter-lumefantrina (Coartem®) |
|
Metabolizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vacuola alimentaria plasmodial a radicales libres tóxicos |
|
|
| Artesunato |
|
Metabolizado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la vacuola alimentaria plasmodial a radicales libres tóxicos |
|
Hipersensibilidad conocida a las artemisininas |
| Atovacuona-proguanil (Malarone®) |
|
|
|
Insuficiencia renal grave (ClCr <30 ml/minuto) |
| Cloroquina |
|
Entra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las vacuolas alimentarias del plasmodio e interrumpe la polimerización del grupo hemo | Profilaxis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum zonas con paludismo sensible a la cloroquina |
|
| Hidroxicloroquina | Esquizonticida sanguíneo | Hipersensibilidad conocida a los LOS Neisseria derivados de 4-Aminoquinolonas | ||
| Doxiciclina |
|
Inhibe la síntesis de proteínas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el apicoplasto plasmodial |
|
|
| Mefloquina |
|
Entra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las vacuolas alimentarias del plasmodio e interrumpe la polimerización del grupo hemo | Profilaxis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum zonas con malaria Malaria Malaria is an infectious parasitic disease affecting humans and other animals. Most commonly transmitted via the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito infected with microorganisms of the Plasmodium genus. Patients present with fever, chills, myalgia, headache, and diaphoresis. Plasmodium/Malaria sensible a la cloroquina o zonas resistentes a la cloroquina |
|
| Primaquina |
|
Profilaxis
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum zonas predominantes de
P. vivax
P. vivax
A protozoan parasite that causes vivax malaria. This species is found almost everywhere malaria is endemic and is the only one that has a range extending into the temperate regions.
Plasmodium/Malaria
|
|
|
| Quinidina IV |
|
Descontinuado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria Estados Unidos | ||
| Quinina |
|
|
|
|
| Tafenoquina | Interfiere con la polimerización del hemo | Profilaxis
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum todas las zonas
|
|