El linfoma de Hodgkin es una neoplasia maligna de los LOS Neisseria linfocitos B que se origina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos. Su hallazgo histológico patognomónico es una célula de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (linfocitos B multinucleados gigantes con inclusiones eosinofílicas). La enfermedad se presenta más comúnmente con linfadenopatía (el cuello es el más comúnmente afectado), sudores nocturnos, pérdida de peso, fiebre y, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ocasiones, esplenomegalia y hepatomegalia. Las pruebas de diagnóstico incluyen análisis histológicos de los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos que muestran células de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg, análisis de sangre y TC y tomografía por emisión de positrones ( PET PET An imaging technique that combines a positron-emission tomography (PET) scanner and a ct X ray scanner. This establishes a precise anatomic localization in the same session. Nuclear Imaging, por su siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). El linfoma de Hodgkin se trata con quimioterapia y radioterapia. El pronóstico ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia mejorado significativamente con el advenimiento de los LOS Neisseria regímenes quimioterapéuticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El linfoma de Hodgkin es un linfoma monoclonal de linfocitos B (neoplasia) que se origina en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria que las células malignas de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg se mezclan con una población heterogénea de células inflamatorias no neoplásicas.
Según la clasificación de la World Health Organization (WHO), los LOS Neisseria linfomas de Hodgkin tienen los LOS Neisseria siguientes tipos y subtipos según el inmunofenotipo y la morfología.
Linfoma de Hodgkin clásico (95%):
Linfoma de Hodgkin con predominio de linfocitos nodulares:
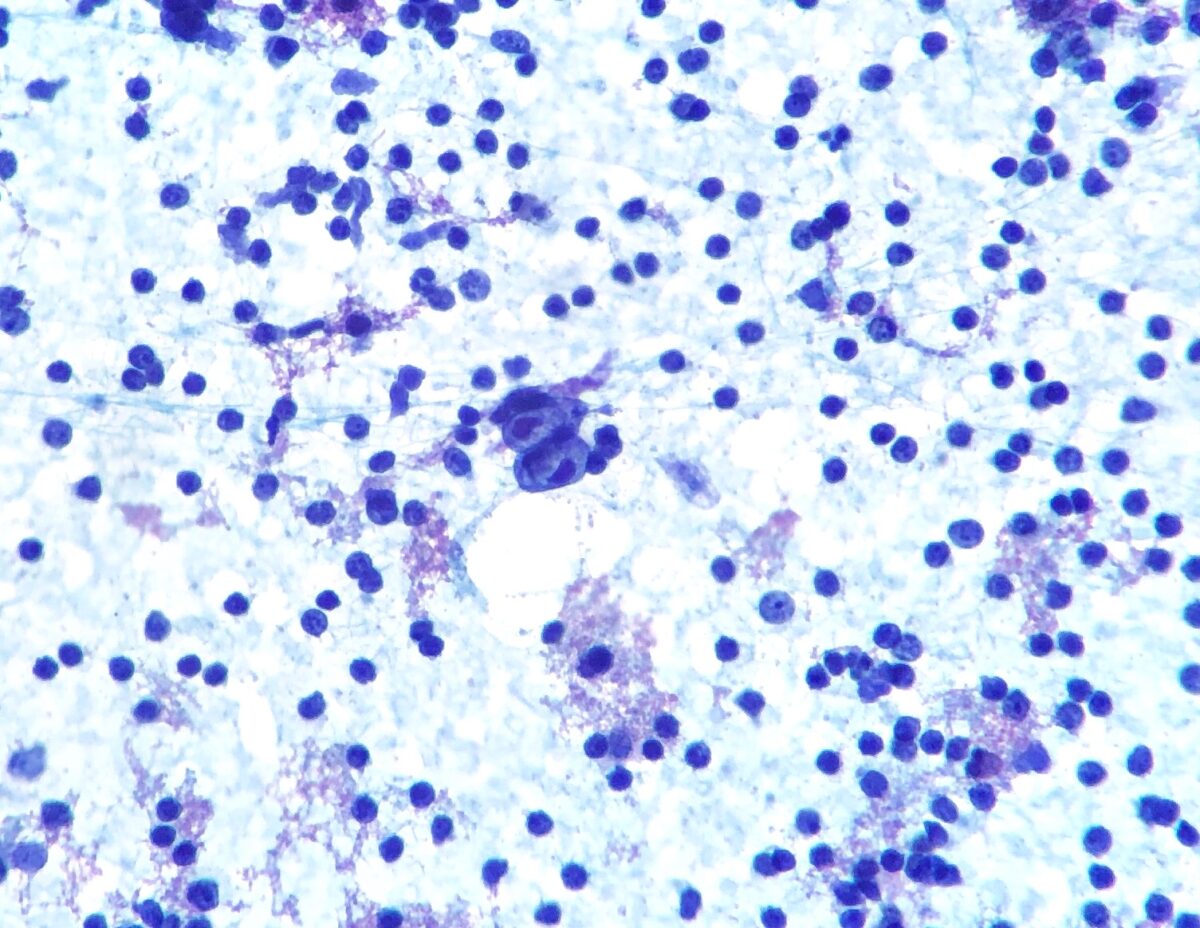
Linfoma de Hodgkin:
Aspiración con aguja fina de un ganglio linfático que muestra células de Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg (células bilobuladas en el centro)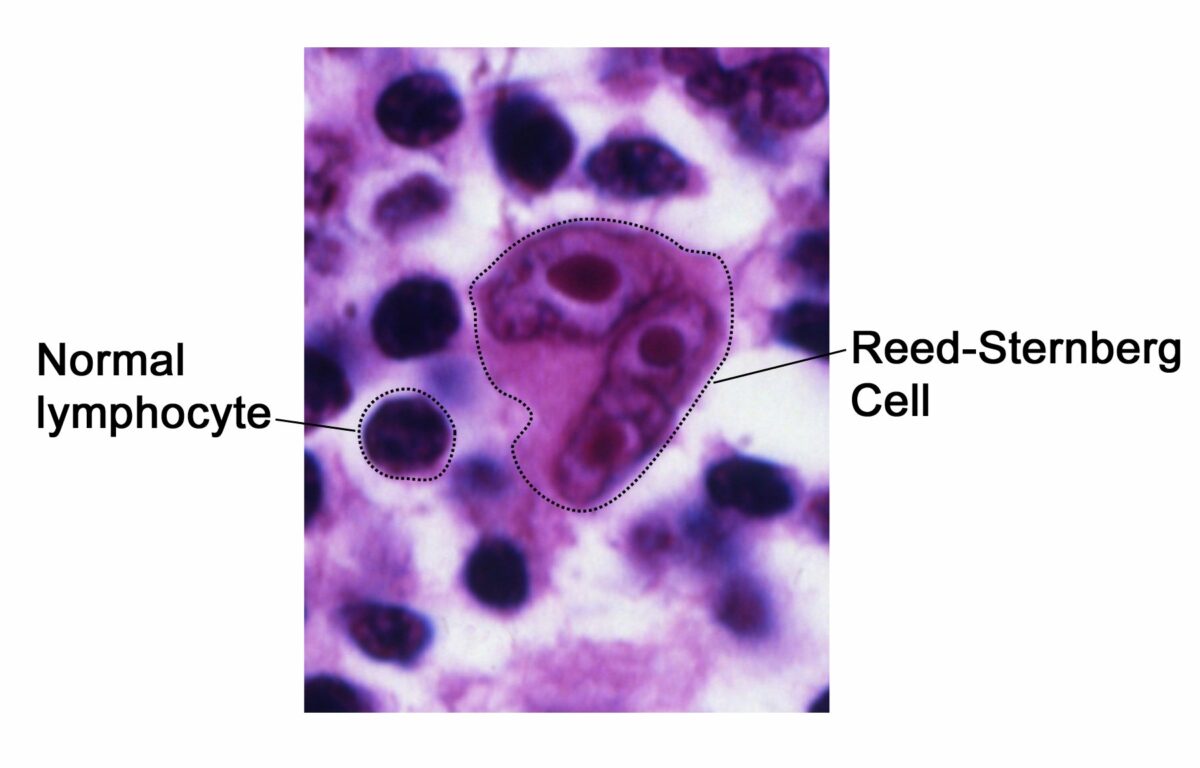
Hallazgo histológico patognomónico para el linfoma de Hodgkin:
La célula de Reed-Sternberg con “ojos de búho”
Evolución:
Presentaciones más comunes:
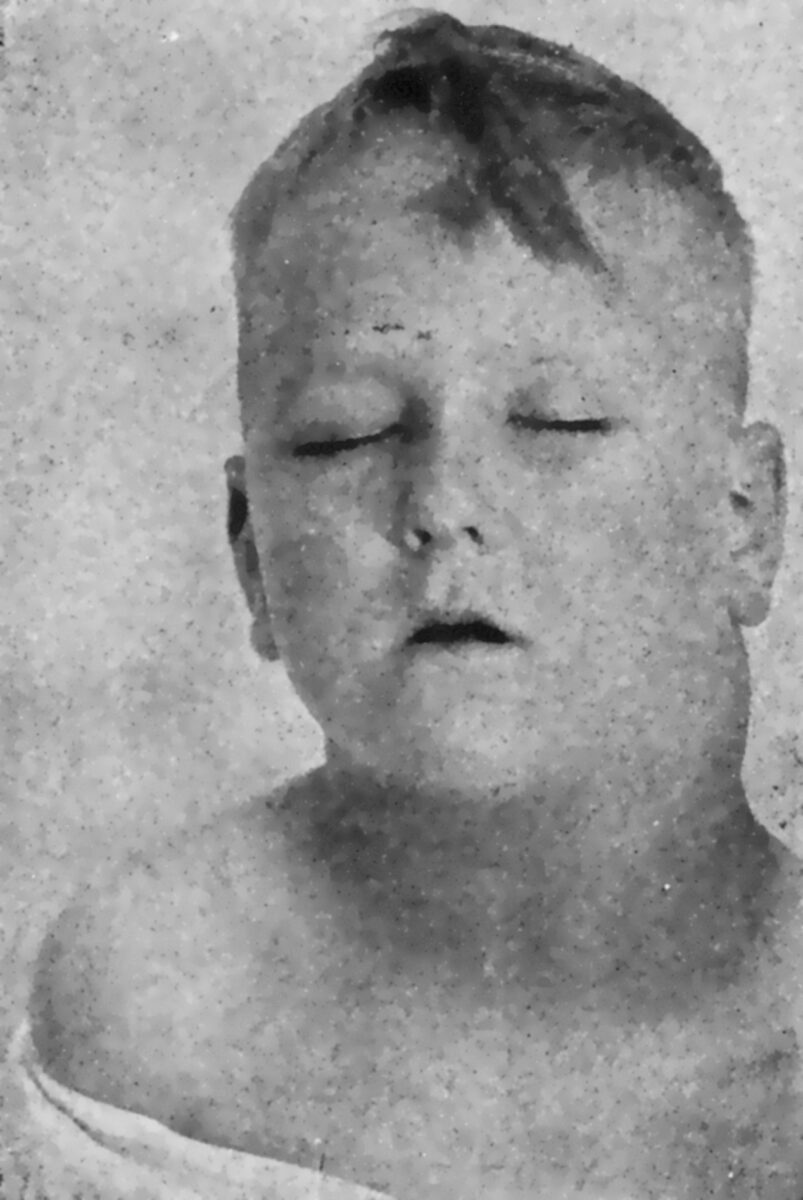
Linfoma de Hodgkin:
Adenopatías cervicales prominentes
Síntomas “B” (constitucionales) presentes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el 40% de los LOS Neisseria casos:
Otros síntomas:
Estudios de laboratorio:
Imagenología:
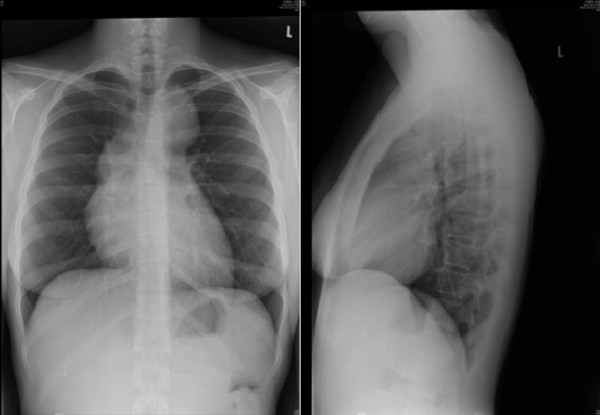
Radiografía de tórax que muestra adenopatías mediastínicas en el linfoma de Hodgkin
Imagen: “Hodgkin’s lymphoma presenting with markedly elevated IgE: a case report” por Ellis AK, Waserman S. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Biopsia:
La estadificación se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la clasificación de Ann Arbor.
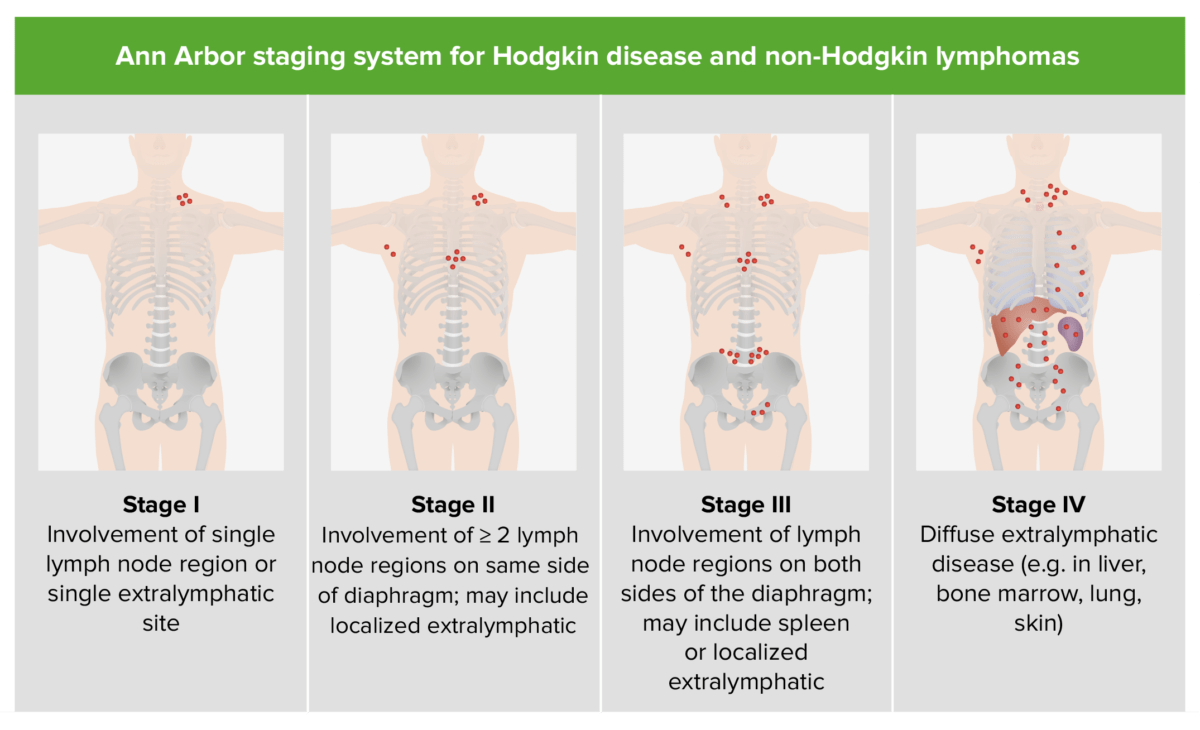
Estadificación de la enfermedad de Hodgkin y del linfoma no Hodgkin
Imagen por Lecturio.