La identificación y clasificación de las lesiones cutáneas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un paciente son pasos importantes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico de cualquier trastorno de la piel. Las lesiones primarias representan la presentación inicial del proceso de la enfermedad. Las lesiones secundarias se desarrollan a partir de lesiones primarias irritadas o manipuladas y/o progresión de la enfermedad. Junto con la evaluación de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes, se requiere un examen físico completo de la piel, los LOS Neisseria anexos y las membranas mucosas para diferenciar entre las distintas condiciones. Las características clave observadas durante el examen físico incluyen el tipo, la morfología, el tamaño, el color, la forma, la disposición y la distribución de las lesiones que se presentan. A veces, los LOS Neisseria procedimientos diagnósticos pueden ser necesarios.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
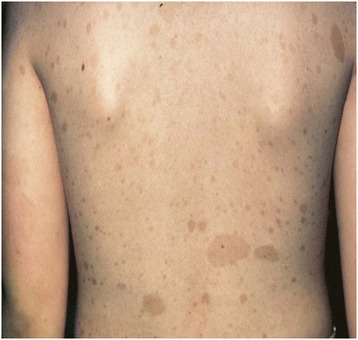
Máculas café con leche hiperpigmentadas en un paciente con neurofibromatosis tipo 1
Imagen: “Breast Cancer associated with neurofibromatosis type 1: A case series and review of the literature” por Khalil J, Afif M, Elkacemi H, Benoulaid M, Kebdani T, Benjaafar N. Licencia: CC BY 4.0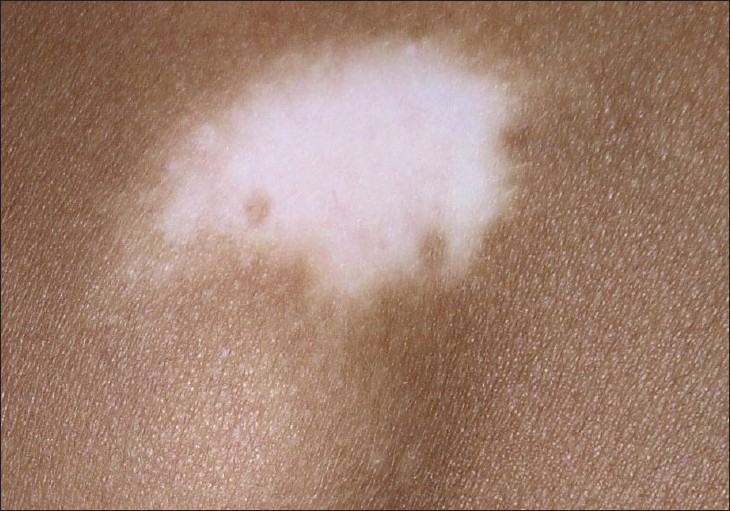
Un parche de vitíligo en un paciente con piel oscura
Imagen: “Vitiligo and the melanocyte reservoir” por Falabella, R. CC BY 2.0
Hiperpigmentación en la mejilla de un paciente con melasma
Imagen: “A study comparing chemical peeling using modified Jessner’s solution and 15% trichloroacetic acid versus 15% trichloroacetic acid in the treatment of melasma” por Safoury OS, Zaki NM, El Nabarawy EA, Farag EA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0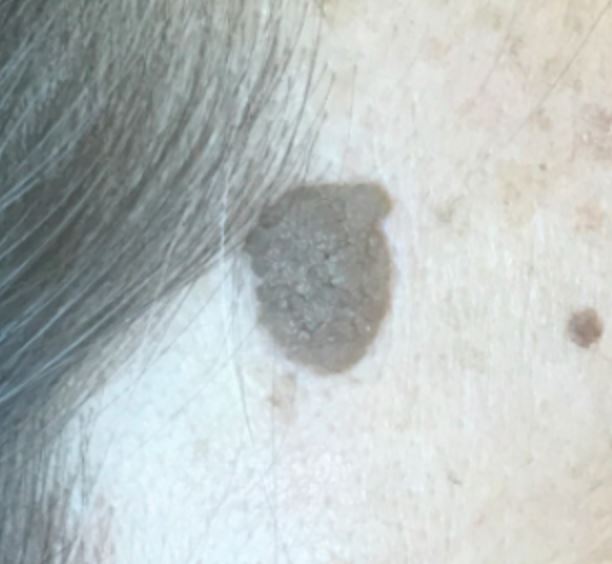
Queratosis seborreica
Imagen por Jeremy Greer, MD (Lecturio).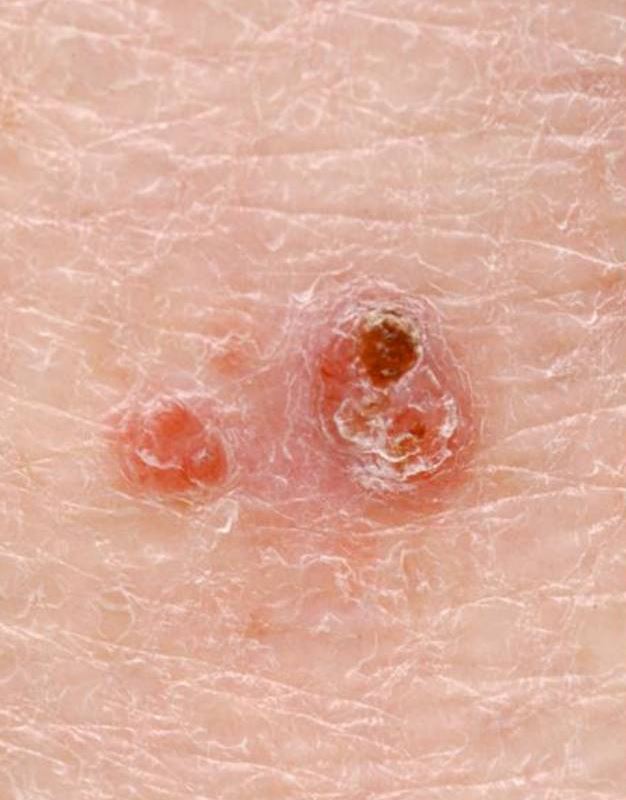
Dos pápulas que representan un carcinoma de células basales
Imagen: “Photodynamic Therapy and Non-melanoma Skin Cancer” por Cancers. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, recortada por Lecturio.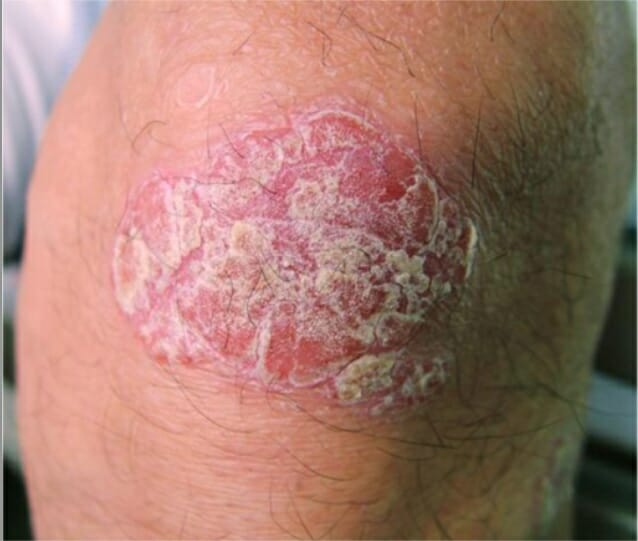
Una lesión psoriásica en la rodilla
Imagen: “Psoriatic lesion on the knee” por Department of Neurology, Wakayama Medical University, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0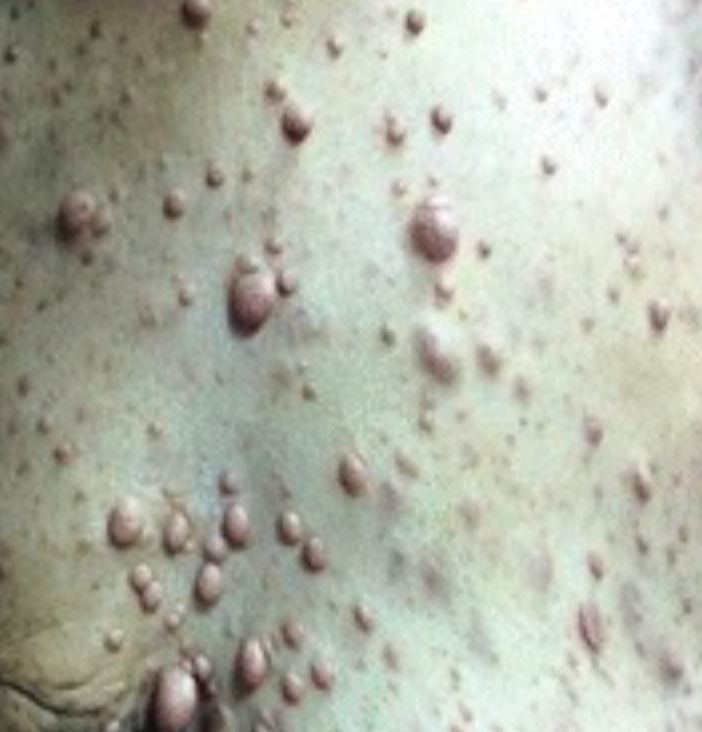
Neurofibromas
Imagen: “Breast cancer associated with neurofibromatosis type 1: A case series and review of the literature” por Khalil J, Afif M, Elkacemi H, Benoulaid M, Kebdani T, Benjaafar N. Licencia: CC BY 4.0 , recortada por Lecturio.
Vesículas causadas por el virus del herpes simple
Imagen: “Transplant biology at a crossroads” por Sedwick C. . Licencia: CC BY 4.0 , recortada por Lecturio.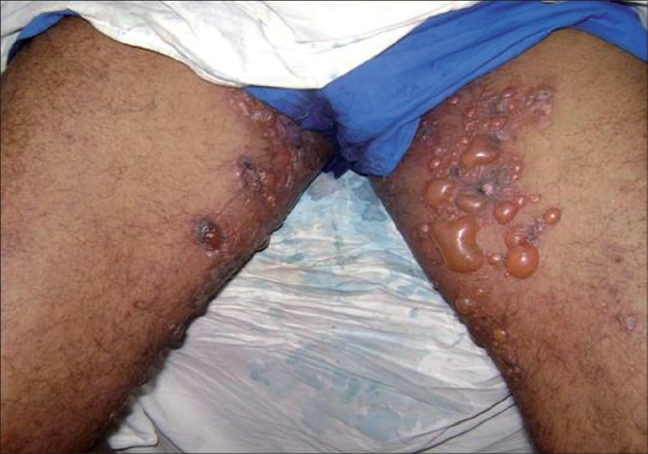
Hallazgos cutáneos en penfigoide ampolloso:
Múltiples vesículas y ampollas grandes y tensas en la ingle en piel normal a levemente eritematosa
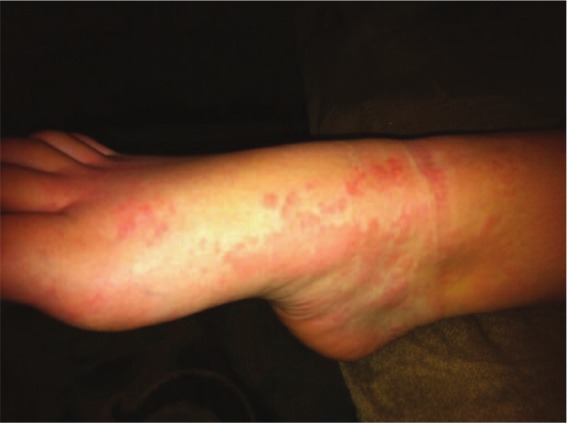
Urticaria
Imagen: “Urticarial Vasculitis in a Teenage Girl” por McGuffin A, Vaughan A, Wolford J. Licencia: CC BY 3.0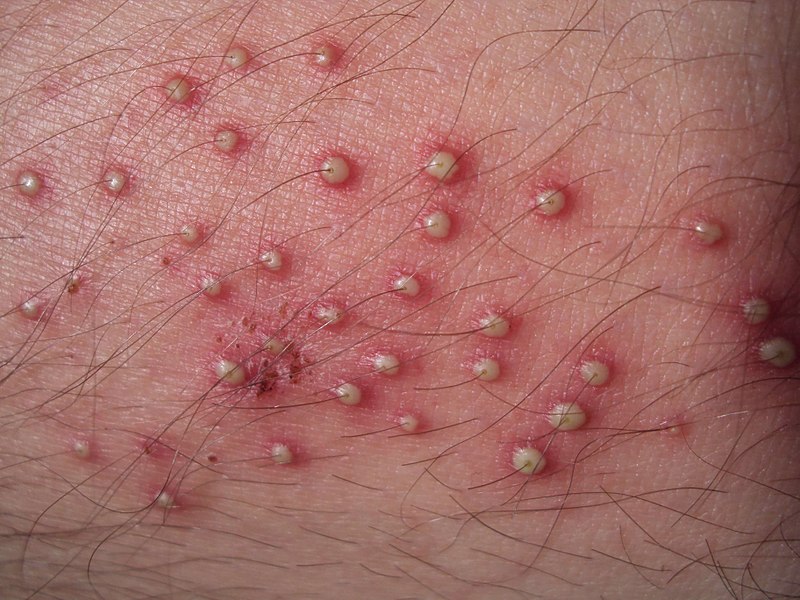
Foliculitis bacteriana en la parte inferior de la pierna que se presenta como pústulas foliculares
Imagen: “Folliculitis on lower leg” por Da pacem Domine. Licencia: Dominio Público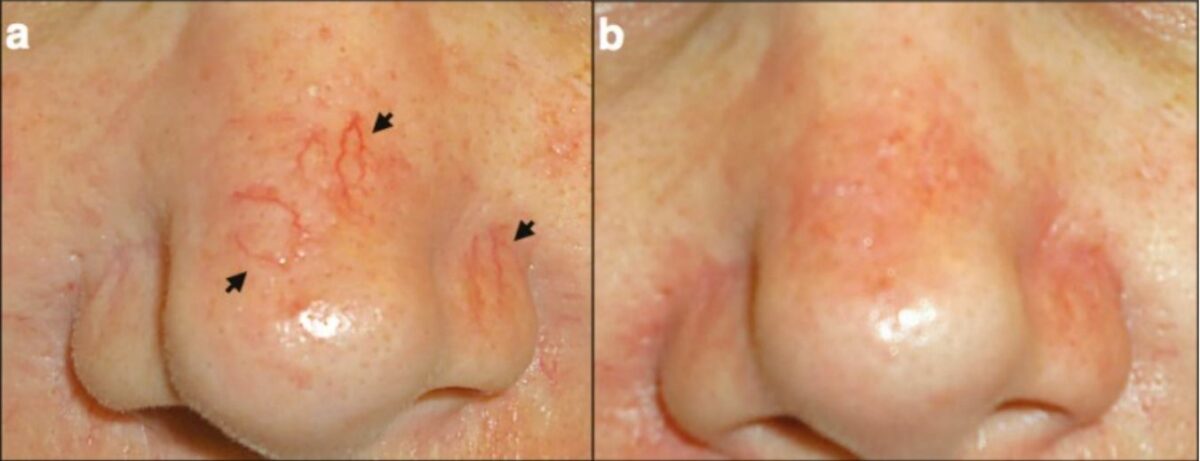
Telangiectasias nasales:
a: Telangiectasias (flechas)
b: Después del tratamiento con cauterio
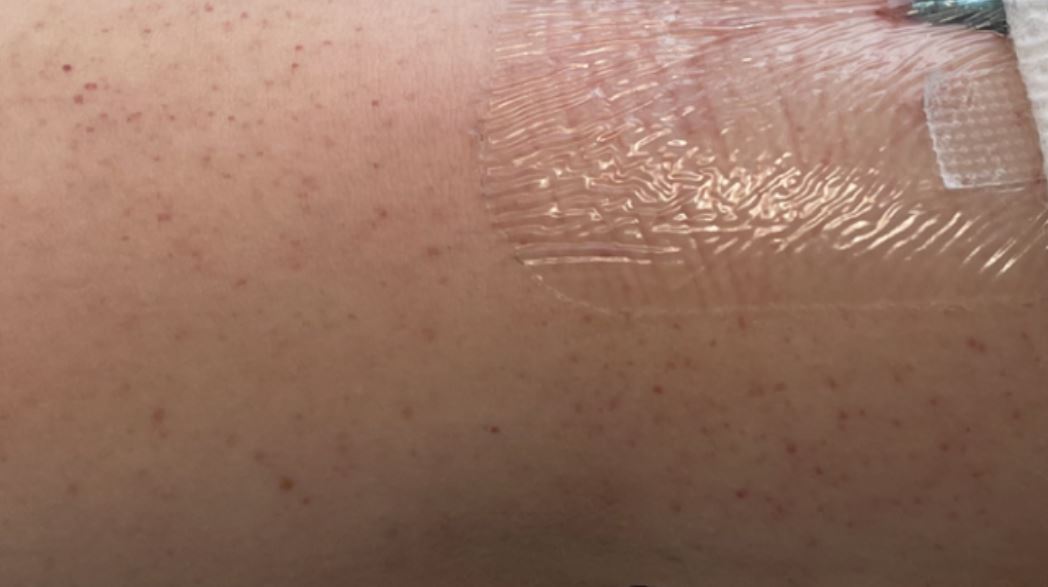
Petequias alrededor del sitio intravenoso
Imagen por Jeremy Greer, MD (Lecturio).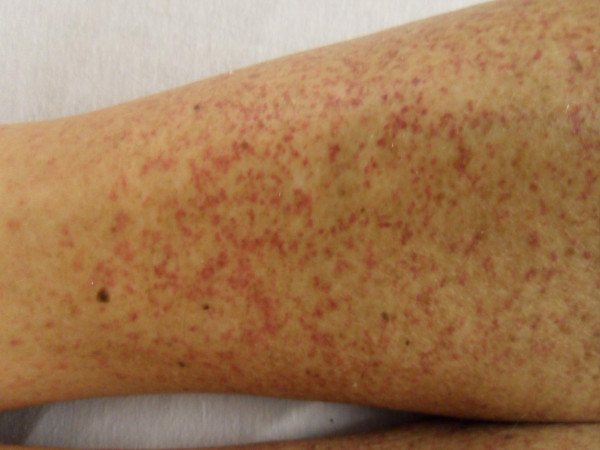
Petequias/púrpura en el miembro inferior visto en la púrpura de Henoch-Schöenlein
Imagen: “Henoch-Schönlein Purpura in an older man presenting as rectal bleeding and IgA mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis: A case report” por Cheungpasitporn W, Jirajariyavej T, Howarth CB, Rosen RM. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Se debe realizar un examen físico general así como un examen dermatológico dirigido:
Características de la piel y afecciones y/o lesiones de la piel comúnmente asociadas a tener en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cuenta:
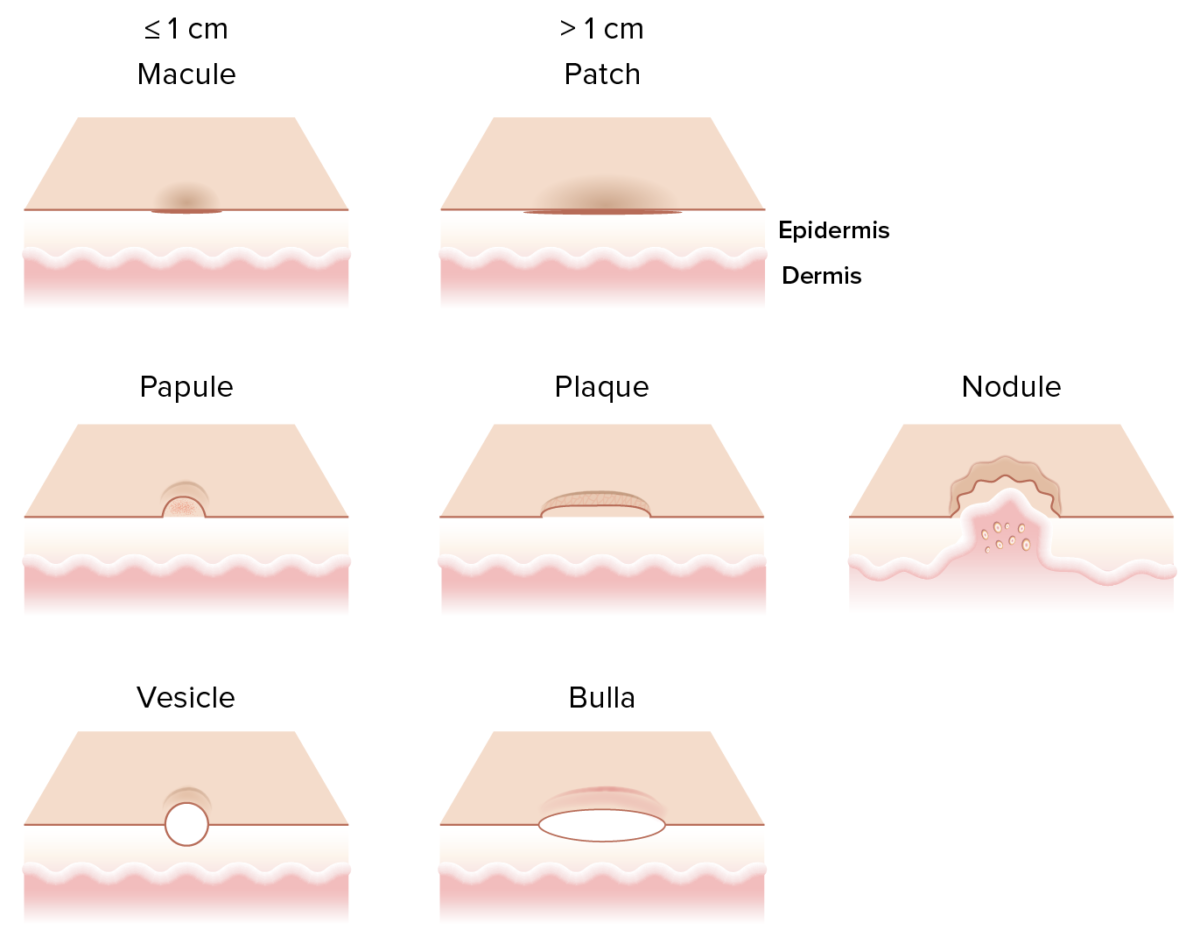
Diferentes lesiones cutáneas primarias:
Una mácula es una lesión cutánea plana y no palpable ≤ 1 cm.
Una pápula es una lesión cutánea elevada y palpable ≤ 1 cm. Un nódulo es una lesión cutánea de 1-5 cm elevada, grande y firme que generalmente se extiende hacia la dermis y el tejido celular subcutáneo Una placa es una lesión cutánea elevada que mide > 1 cm que sufre cambios mientras surge de la epidermis. Una vesícula es una lesión cutánea pequeña de ≤1 cm que contiene líquido mientras que la bulla es una lesión >1 cm con contenido transparente.