Las infecciones del tracto urinario (ITU) representan un amplio espectro de enfermedades, desde la cistitis simple autolimitada hasta la pielonefritis grave que puede provocar sepsis Sepsis Systemic inflammatory response syndrome with a proven or suspected infectious etiology. When sepsis is associated with organ dysfunction distant from the site of infection, it is called severe sepsis. When sepsis is accompanied by hypotension despite adequate fluid infusion, it is called septic shock. Sepsis and Septic Shock y la muerte. Las infecciones del tracto urinario son causadas más comúnmente por Escherichia coli Escherichia coli The gram-negative bacterium Escherichia coli is a key component of the human gut microbiota. Most strains of E. coli are avirulent, but occasionally they escape the GI tract, infecting the urinary tract and other sites. Less common strains of E. coli are able to cause disease within the GI tract, most commonly presenting as abdominal pain and diarrhea. Escherichia coli, pero también pueden ser causadas por otras bacterias y hongos. Dependiendo de la localización de la infección, los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden presentar disuria, urgencia urinaria, aumento de la frecuencia urinaria, dolor Dolor Inflammation suprapúbico y fiebre. El análisis de orina y el cultivo de orina, junto con la presentación clínica, ayudan a diagnosticar las ITU. Las opciones de tratamiento incluyen antibióticos orales o intravenosos como trimetoprim-sulfametoxazol, nitrofurantoína y ceftriaxona. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ciertos casos, es posible que se necesiten más estudios para determinar las condiciones subyacentes que predisponen a una persona a las ITU.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La infección del tracto urinario (ITU) es un proceso patogénico que se desarrolla cuando un microorganismo (generalmente una bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology) ingresa al AL Amyloidosis cuerpo a través de la uretra y viaja a la vejiga y/o los LOS Neisseria riñones.
Prevalencia:
Las bacterias que no son E. coli están asociadas con factores de riesgo de resistencia a los LOS Neisseria medicamentos o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum escenarios clínicos específicos.
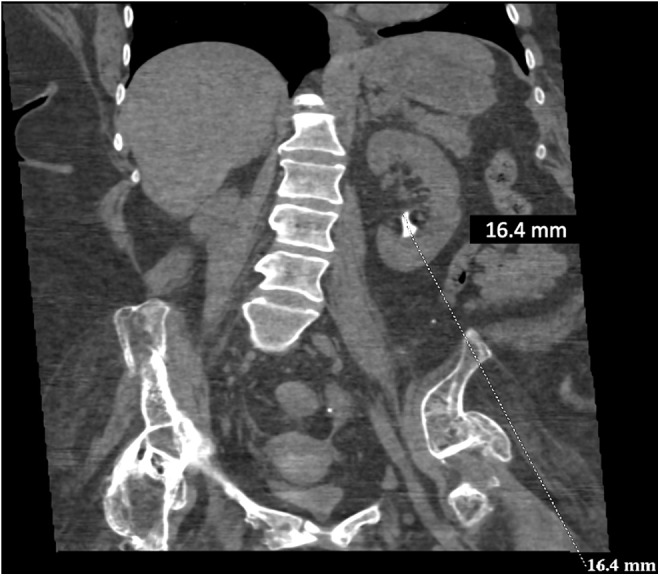
Una TC que muestra un cálculo renal izquierdo
Imagen: “Surgical Clips Migration up to Renal Collecting System from Ileal Conduit Postcystectomy” por Journal of Endourology Case Reports. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Ultrasonido que muestra un absceso renal que aparece como un área hipoecogénica de 1,19 × 0,96 cm dentro de la corteza del riñón izquierdo
Imagen: “Transient Monoclonal Gammopathy Induced by Disseminated Staphylococcus aureus Infection” por Stoimenis D, Spyridonidou C, Papaioannou N. Licencia: CC BY 3.0| Tipo de ITU | Antibióticos |
|---|---|
| ITU sin complicaciones (cistitis simple) |
|
| ITU con complicaciones (incluyendo pielonefritis) |
|
Las siguientes poblaciones de pacientes pueden requerir un estándar de atención diferente, ya que no se incluyen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las categorías habituales de infecciones urinarias: