La glomerulonefritis proliferativa difusa es una clasificación histopatológica de la glomerulonefritis caracterizada por un aumento de la proliferación celular que afecta > 50% de los LOS Neisseria glomérulos. Las células mesangiales, endoteliales y epiteliales aumentan notablemente. Las causas más comunes son la nefritis lúpica de clase IV y la nefropatía por IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions. Los LOS Neisseria individuos pueden presentar síntomas relacionados con la enfermedad renal, como fatiga, náuseas, vómitos, hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children, hipertensión y edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema. Pueden presentarse otras manifestaciones relacionadas con la enfermedad subyacente. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante pruebas de laboratorio, imagenología renal y biopsia renal. Los LOS Neisseria hallazgos microscópicos muestran hipercelularidad de las células mesangiales y endoteliales, con engrosamiento del asa ASA Anterior Cord Syndrome capilar. Está indicada una terapia agresiva precoz y se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la etiología específica.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La glomerulonefritis proliferativa difusa, una clasificación histopatológica de la glomerulonefritis comúnmente asociada con enfermedades autoinmunes, se caracteriza por un aumento de la proliferación celular que afecta > 50% de los LOS Neisseria glomérulos.
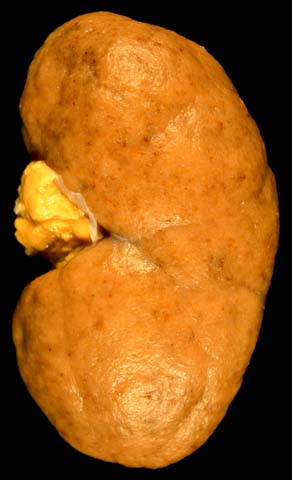
Apariencia “picada por pulgas” de la superficie cortical de un riñón en la glomerulonefritis proliferativa difusa.
Imagen: “Diffuse Proliferative Lupus Nephritis class IV” por Ed Uthman. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLas presentaciones varían considerablemente, y la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria síntomas se deben a la disminución de la tasa de filtración glomerular causada por la glomerulonefritis proliferativa difusa.

Hematuria:
La orina es oscura o de color té.
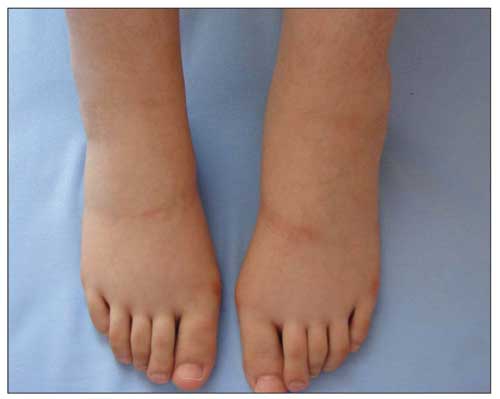
Edema de las extremidades inferiores
Imagen: “Lower extremity oedema 4 days after the initiation of insulin therapy” por Baş VN. Licencia: CC BY 2.5Debido a que la glomerulonefritis proliferativa difusa es causada por otra afección, los LOS Neisseria síntomas de la causa subyacente a menudo están presentes, como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
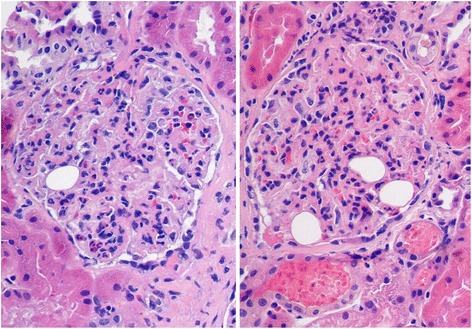
Histología de la glomerulonefritis proliferativa difusa con infiltración leucocítica
Imagen: “Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis with leukocytic infiltration” por Cannata-Ortiz P. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Para reducir la progresión de la enfermedad renal, el manejo variará según la afección subyacente. Las opciones son las siguientes: