La deficiencia selectiva de inmunoglobulina A ( IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions) es el tipo más común de inmunodeficiencia primaria. Se trata de una hipogammaglobulinemia caracterizada por la falta o la reducción de los LOS Neisseria niveles de IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions. Este anticuerpo reside principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las membranas mucosas de la boca, las vías respiratorias y el tracto digestivo. Se desconoce la causa exacta. La enfermedad suele ser asintomática, aunque algunos pacientes pueden presentar infecciones respiratorias y gastrointestinales recurrentes, así como trastornos autoinmunes y malignos. El diagnóstico se realiza con la medición de niveles excepcionalmente bajos de IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el suero en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presencia de niveles normales de IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis e IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
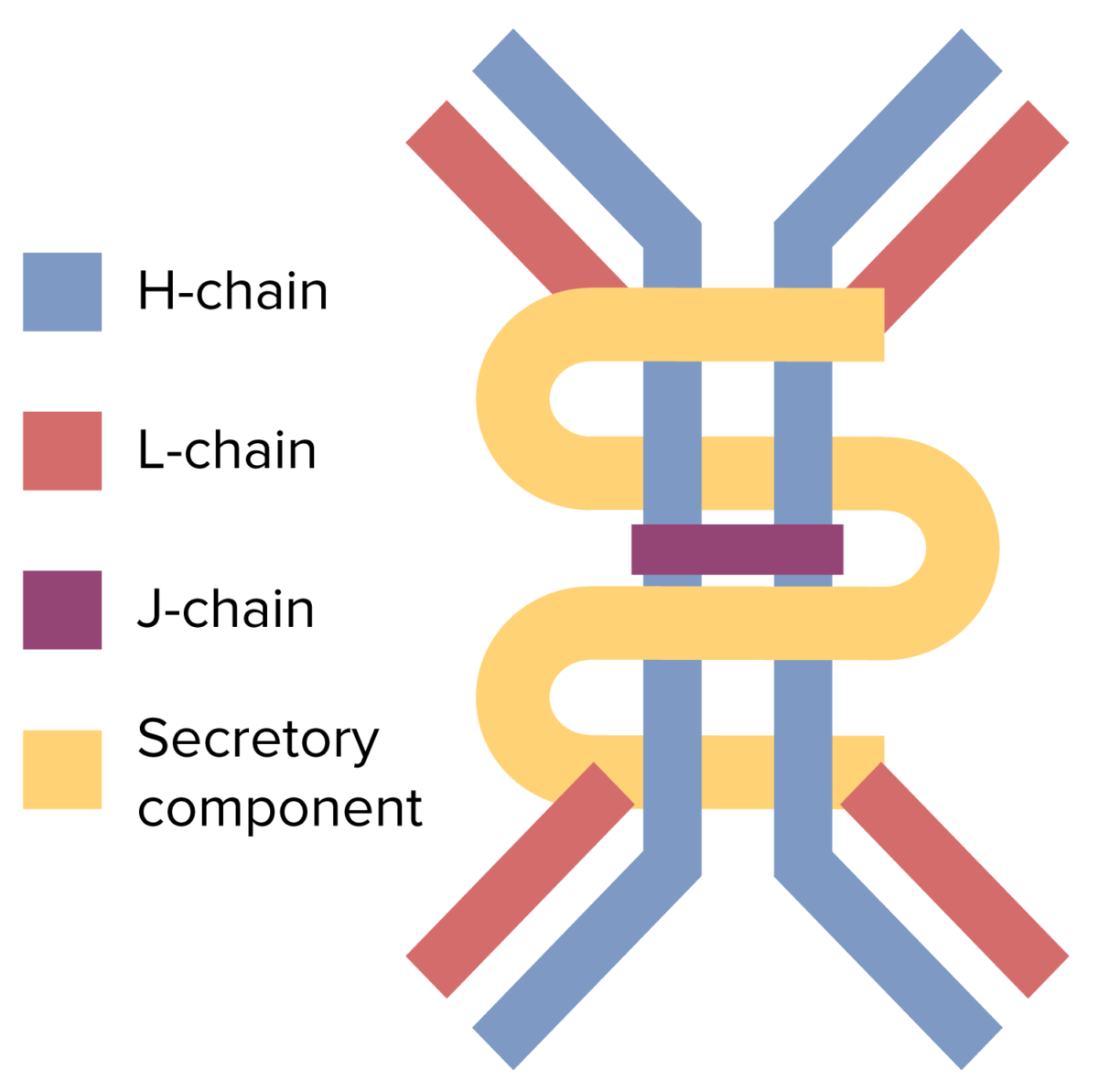
La estructura dimérica del anticuerpo IgA
Imagen por Lecturio.Aproximadamente el 90% de los LOS Neisseria casos son asintomáticos.
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes sintomáticos pueden presentar una mezcla de los LOS Neisseria siguientes síntomas:
Diagnóstico
Tratamiento
Las siguientes afecciones son otras inmunodeficiencias congénitas de células B que sirven como diagnóstico diferencial para la deficiencia selectiva de IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions.