El cáncer de mama es una enfermedad caracterizada por la transformación maligna de las células epiteliales de la mama. El cáncer de mama es la forma más común de cáncer y la 2da causa más común de muerte relacionada con el cáncer entre las mujeres. Los LOS Neisseria factores genéticos, la edad y la influencia hormonal y ambiental contribuyen a la progresión de la enfermedad. El tipo histológico más común es el carcinoma ductal infiltrante, que es > 75% de todos los LOS Neisseria cánceres de mama. Se recomienda la mamografía de tamizaje para la detección temprana de la enfermedad. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante biopsia con aguja gruesa, y los LOS Neisseria factores biológicos se determinan mediante pruebas inmunohistoquímicas. La cirugía, el tratamiento sistémico (quimioterapia, terapia biológica, terapia endocrina) y la radioterapia son parte del tratamiento de la enfermedad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estadios tempranos y localmente avanzados. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cáncer de mama metastásico, el tratamiento sistémico se utiliza con medidas paliativas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Factores no modificables que aumentan el riesgo:
Factores de riesgo modificables:
Mnemotecnia:
“BReast- CA CA Condylomata acuminata are a clinical manifestation of genital HPV infection. Condylomata acuminata are described as raised, pearly, flesh-colored, papular, cauliflower-like lesions seen in the anogenital region that may cause itching, pain, or bleeding. Condylomata Acuminata (Genital Warts)ncer 1 y 2” = Los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure mutados son los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure BRCA1 y BRCA2 (cáncer de mama 1 y 2, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés).
No invasivo:
Invasivo:
Otras formas clínicas:
Basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la expresión de:
Tipos moleculares:
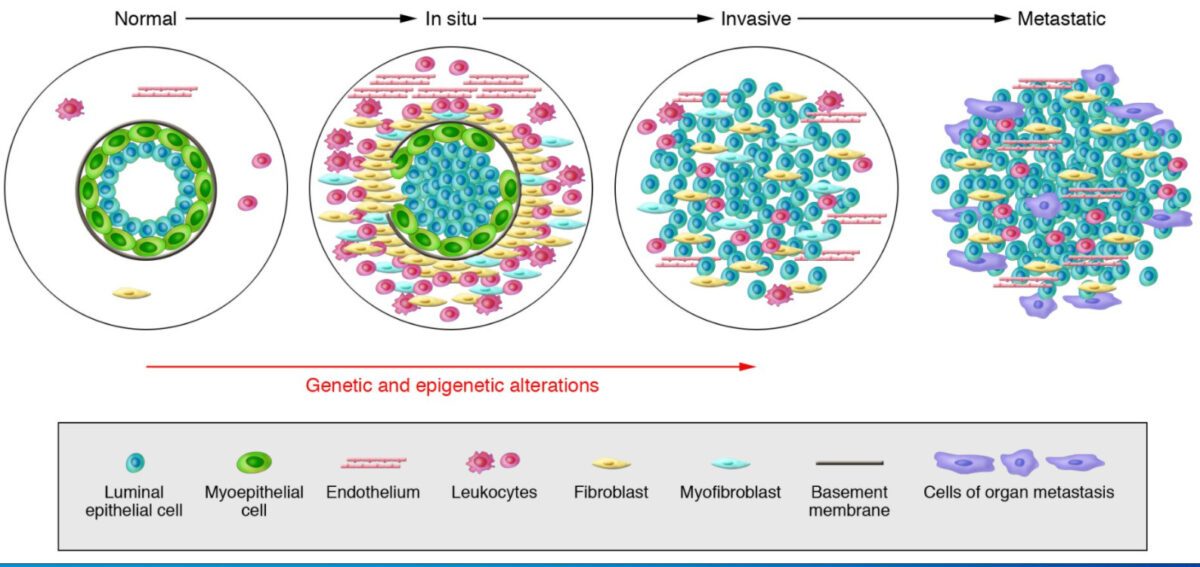
Modelo de progresión del tumor de mama
De izquierda a derecha: los conductos mamarios normales están compuestos por la membrana basal y una capa de células epiteliales y mioepiteliales luminales. El estroma incluye varios leucocitos, fibroblastos, miofibroblastos y células endoteliales. En carcinomas in situ: las células mioepiteliales se alteran epigenética y fenotípicamente y su número disminuye, posiblemente debido a la degradación de la membrana basal. Los fibroblastos del estroma, los miofibroblastos, los linfocitos y las células endoteliales aumentan. En los carcinomas invasivos, hay una pérdida de células mioepiteliales y de la membrana basal, en la que las células tumorales pueden invadir los tejidos circundantes. Las células tumorales migran a órganos distantes, lo que eventualmente conduce a metástasis.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum áreas con tamizaje de cáncer de mama establecido: la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de cáncer se diagnostican al AL Amyloidosis tener una mamografía anormal.
Síntomas:
Signos:
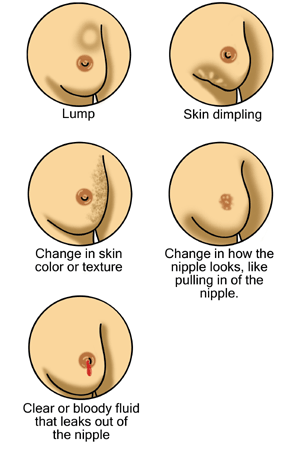
Posibles signos de cáncer de mama
De derecha a izquierda, de arriba a abajo: un bulto/masa mamaria, hoyuelos en la piel, cambio en el color/textura de la piel, cambios en el pezón, incluida la retracción (inversión del pezón hacia adentro) y secreción del pezón
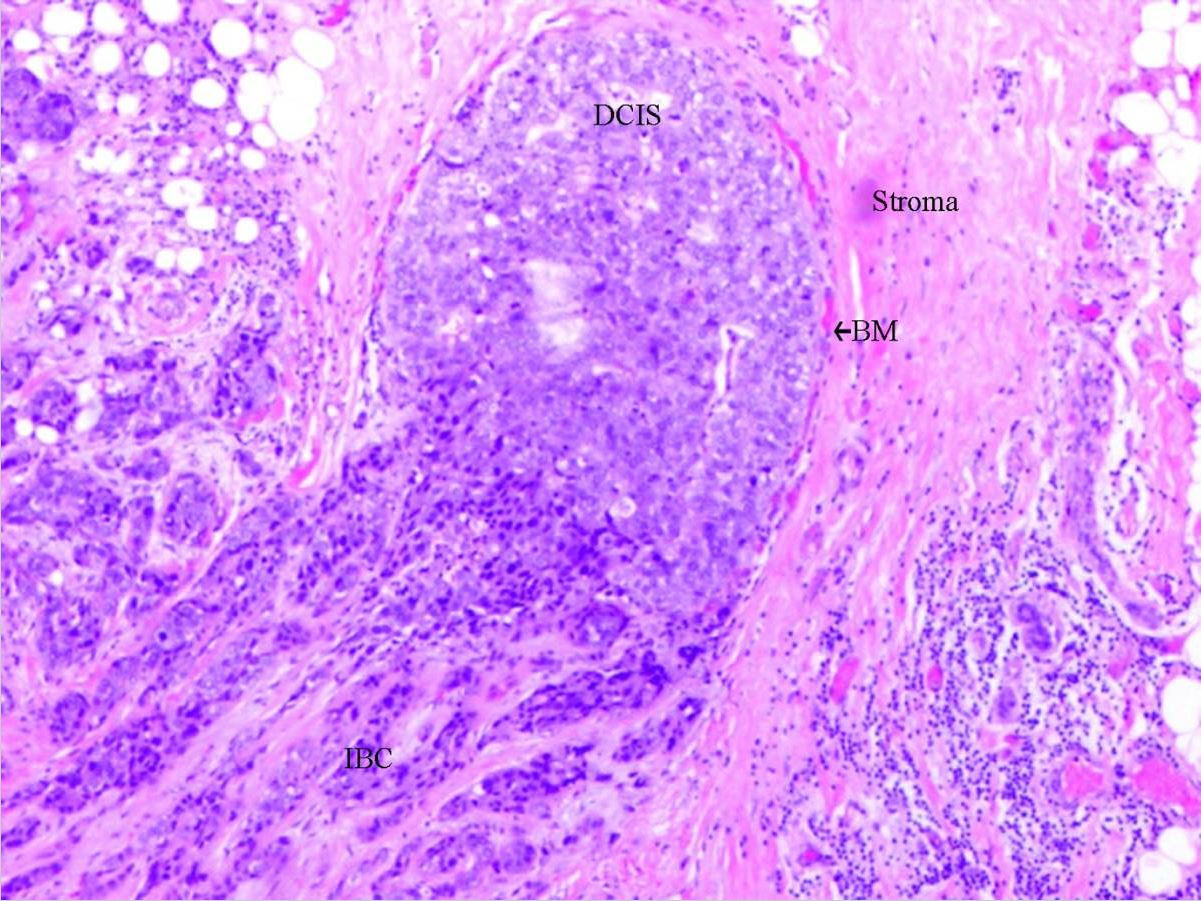
Carcinoma ductal in situ: con invasión
Abreviaturas utilizadas:
DCIS: carcinoma ductal in situ (por sus siglas en inglés)
BM: membrana basal (por sus siglas en inglés)
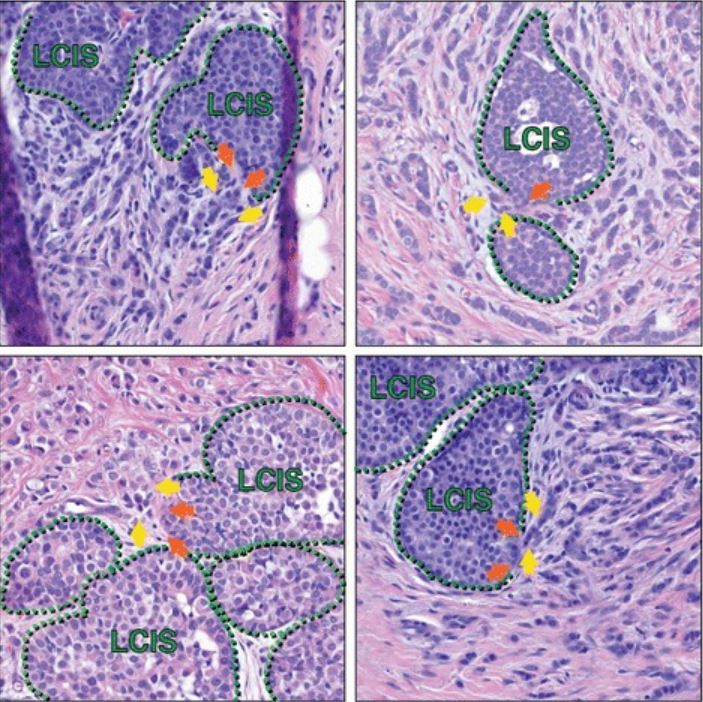
Carcinoma lobulillar in situ (LCIS, por sus siglas en inglés) en asociación con carcinoma lobulillar invasivo
Las secciones histológicas de múltiples pacientes capturan áreas de LCIS que parecen tener una interrupción focal de la capa mioepitelial adyacente a un carcinoma lobulillar invasivo, lo que sugiere una posible progresión de LCIS a carcinoma lobulillar invasivo en tales transiciones. Las líneas verdes punteadas marcan la capa mioepitelial; las flechas naranjas son posibles focos de alteración mioepitelial; las flechas amarillas resaltan las células invasivas. Además de las células marcadas con flechas amarillas, en cada imagen hay células de carcinoma lobulillar invasivo adicionales en todo el estroma, que rodean las áreas del LCIS.
| CDIS | CLIS | |
|---|---|---|
| Presentación | Unifocal Unifocal Retinoblastoma | Multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma |
| Patrones |
|
Sólido |
| Calcificación | Sí/no | Generalmente no |
| Riesgo de cáncer de mama invasivo | Más alto | Más bajo |
| Ubicación del cáncer | Mama ipsilateral | Ipsilateral o contralateral |
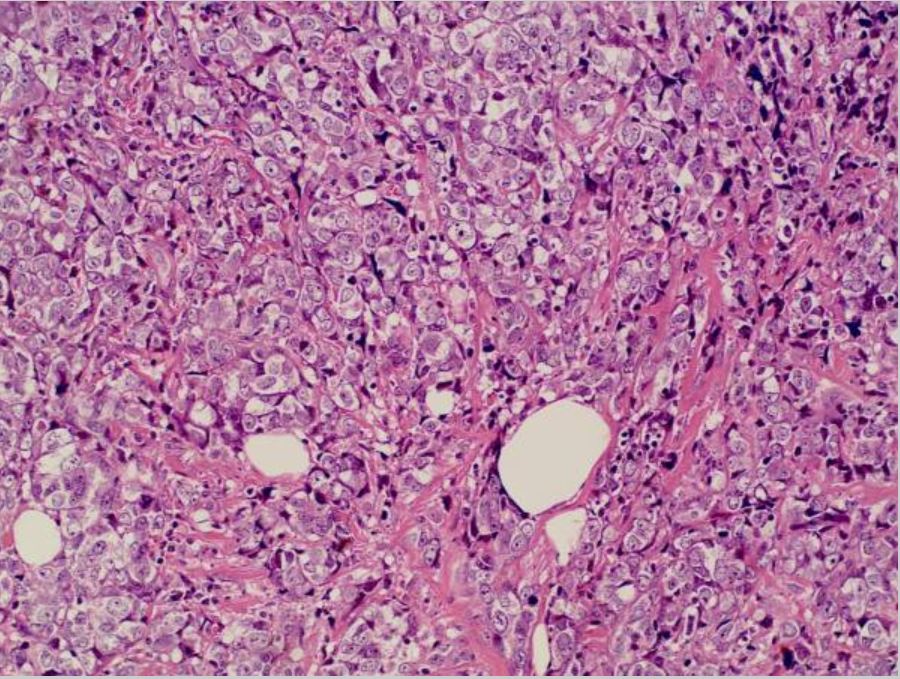
Cáncer de mama: carcinoma ductal invasivo en mama izquierda
Imagen: “Invasive ductal breast cancer metastatic to the sigmoid colon” por Zhou XC, Zhou H, Ye YH, Zhang XF, Jiang Y. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.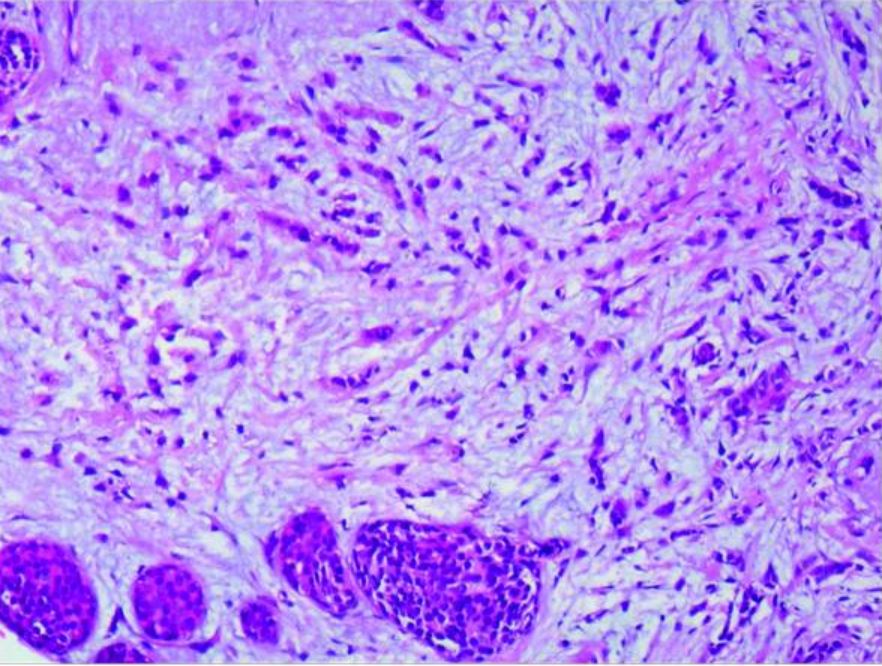
Carcinoma lobulillar: carcinoma lobulillar infiltrante de mama derecha y carcinoma lobulillar in situ (amplificado 20×10)
Imagen: “Case report of small bowel obstruction caused by small intestinal metastasis of bilateral breast cancer” por Lv L, Zhao Y, Liu H, Peng Z. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.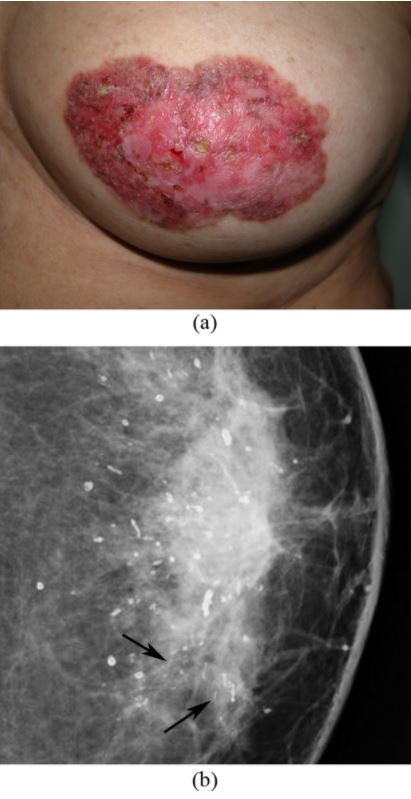
Enfermedad de Paget de la mama: cambios en la areola del pezón izquierdo
(a) La fotografía de la mama izquierda muestra engrosamiento de la piel, eritema, erosión del pezón y descamación alrededor del área del pezón-areola.
(b) La mamografía muestra calcificaciones dispersas en forma de bastón y grupos de microcalcificaciones lineales, finas y pleomórficas en el cuadrante interno (flechas). La mastectomía simple reveló carcinoma ductal in situ y calcificaciones secretoras en la mama y enfermedad de Paget del pezón.
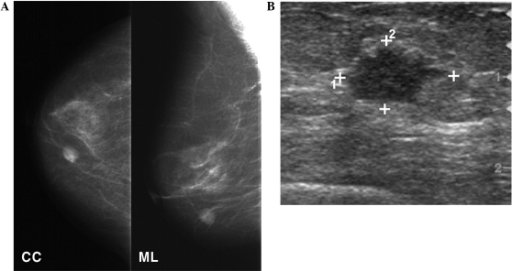
Mamografía y ultrasonido mamarios
A: La mamografía muestra una masa redonda de alta densidad en el cuadrante inferior interno de la mama derecha.
B: El ultrasonido de seguimiento muestra una masa hipoecoica de forma irregular de 1,3 cm en la mama.
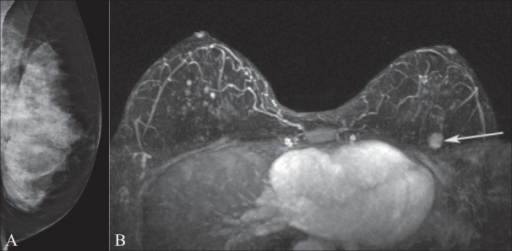
Mamografía y RM de mama
La imagen A muestra una mamografía de la mama izquierda en una portadora de la mutación del gen BRCA1. Obsérvese el tejido mamario extremadamente denso.
La imagen B de RM muestra una masa realzada (flecha) en la parte superior izquierda de la mama que estaba oculta en la mamografía.
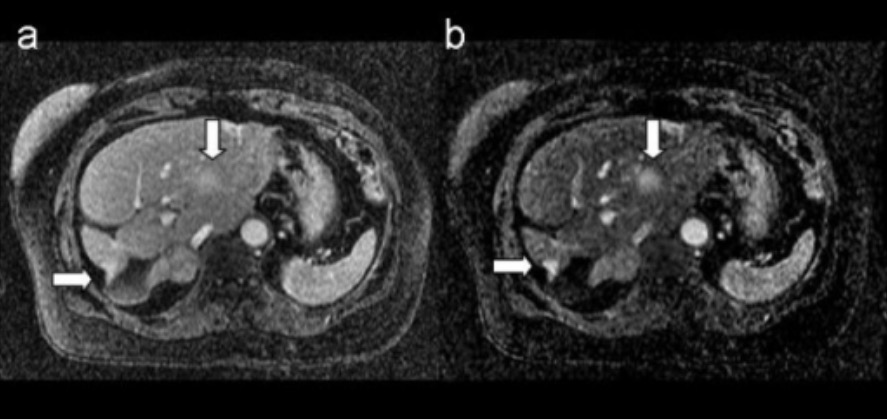
RM de metástasis mamaria: las imágenes muestran lesiones mamarias metastásicas en el hígado
A. Imagen 3D postcontraste ponderada en T1
B. Imagen de sustracción 3D correspondiente
Las flechas indican las lesiones metastásicas.
| Estadio tumoral | Descripción |
|---|---|
| Tx | El tumor Tumor Inflammation primario no se puede evaluar |
| T0 | Sin evidencia de tumor Tumor Inflammation primario |
| Tis |
|
| T1 | Tumor Tumor Inflammation ≤ 20 mm MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su mayor dimensión |
| T2 | Tumor Tumor Inflammation > 20 mm MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma pero ≤ 50 mm MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su mayor dimensión |
| T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | Tumor Tumor Inflammation de > 50 mm MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum su mayor dimensión |
| T4 T4 The major hormone derived from the thyroid gland. Thyroxine is synthesized via the iodination of tyrosines (monoiodotyrosine) and the coupling of iodotyrosines (diiodotyrosine) in the thyroglobulin. Thyroxine is released from thyroglobulin by proteolysis and secreted into the blood. Thyroxine is peripherally deiodinated to form triiodothyronine which exerts a broad spectrum of stimulatory effects on cell metabolism. Thyroid Hormones | Tumor Tumor Inflammation de cualquier tamaño, con extensión directa a la pared torácica y/o piel (ulceración o nódulos macroscópicos) |
| Estadio ganglionar | Descripción |
|---|---|
| cNX | Los LOS Neisseria ganglios linfáticos regionales no se pueden evaluar. |
| cN0 | Sin metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ganglios linfáticos regionales |
| cN1 | Metástasis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum ganglios linfáticos axilares móviles ipsilaterales de nivel I, II |
| cN2 |
|
| cN3 |
|
| Metástasis | Descripción |
|---|---|
| M0 | Sin evidencia de metástasis a distancia (clínica o radiográfica) |
| M1 | Metástasis detectables |
| Estadio | Subestadios | Tumor Tumor Inflammation | Ganglio | Metástasis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Tis | N0 | M0 | |
| I |
|
T0–T1 | N1 | M0 |
| II |
|
T0– T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | N0–N1 | M0 |
| III |
|
T0– T3 T3 A T3 thyroid hormone normally synthesized and secreted by the thyroid gland in much smaller quantities than thyroxine (T4). Most T3 is derived from peripheral monodeiodination of T4 at the 5′ position of the outer ring of the iodothyronine nucleus. The hormone finally delivered and used by the tissues is mainly t3. Thyroid Hormones | N1–N2 | M0 |
| IV | Cualquier T | Cualquier N | M1 |
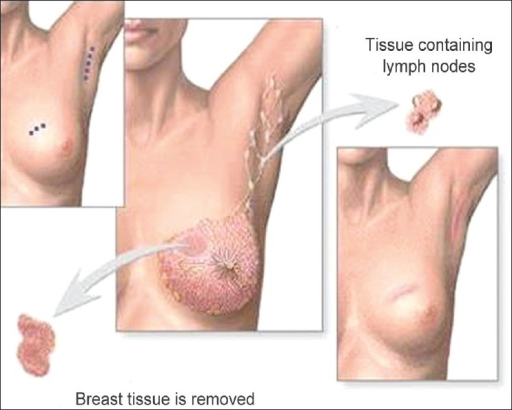
Cirugía conservadora de la mama (tumorectomía): escisión del tumor hasta los márgenes negativos y evaluación de los ganglios linfáticos axilares
Imagen: “Phantom breast syndrome” por Indian Journal of Palliative Care. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.