La babesiosis es una infección causada por un protozoo que pertenece al género Babesia. La Babesia más común que se observa en Estados Unidos es B. microti, que se transmite por la garrapata Ixodes. Los protozoos crecen y se replican dentro de los eritrocitos del húesped. La lisis de los eritrocitos y la respuesta inmunitaria del organismo dan lugar a síntomas clínicos. Los pacientes generalmente presentan una enfermedad similar a la gripe e ictericia. En casos severos, puede ocurrir daño a los órganos. El diagnóstico se confirma por la presencia visual de parásitos dentro de los eritrocitos, que a menudo se observa en una configuración de "Cruz de Malta". Las pruebas serológicas y la reacción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cadena de la polimerasa ( PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) también se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico. La azitromicina y la atovacuona se utilizan a menudo en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento. La coinfección con Borrelia Borrelia Borrelia are gram-negative microaerophilic spirochetes. Owing to their small size, they are not easily seen on Gram stain but can be visualized using dark-field microscopy, Giemsa, or Wright stain. Spirochetes are motile and move in a characteristic spinning fashion due to axial filaments in the periplasmic space. Borrelia y Anaplasma es común.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Para la babesiosis Babesiosis Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body’s immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis:
Para la enfermedad grave:
Fuera de un huésped humano:
Dentro de un huésped humano:
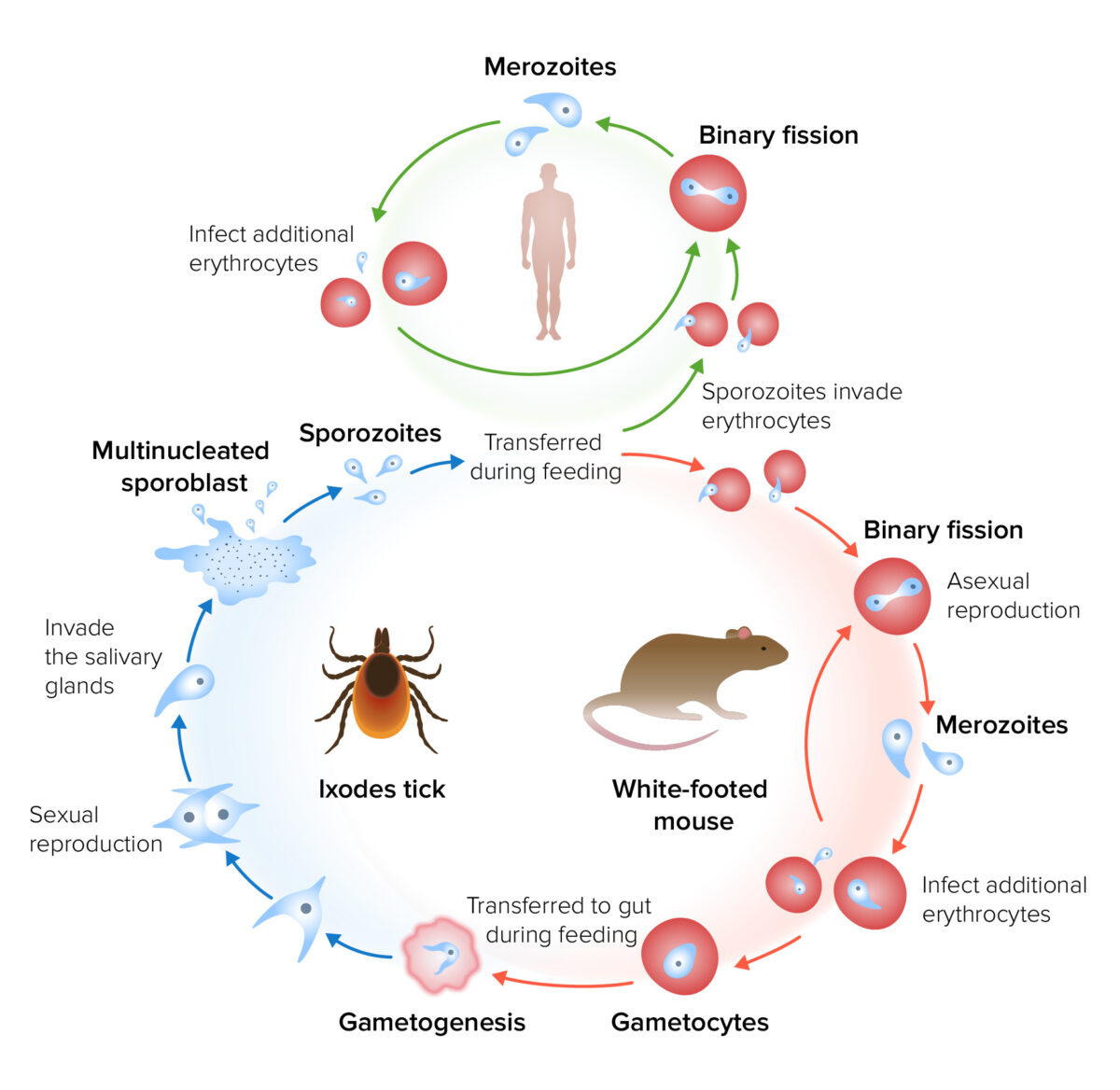
Ciclo de vida y transmisión de Babesia
Imagen por Lecturio.El período de incubación de la babesiosis Babesiosis Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body’s immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis es de 1–4 semanas.
Enfermedad leve a moderada:
Enfermedad severa:
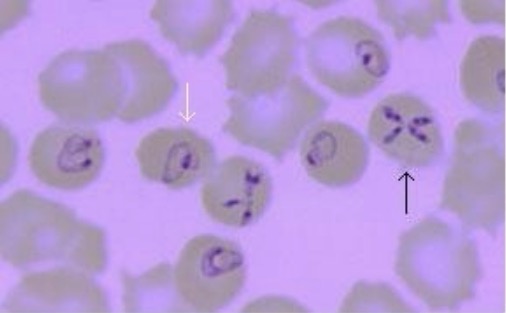
Frotis de sangre periférica que demuestra infección por Babesia:
La flecha blanca indica estructuras pleomórficas en forma de anillo que a menudo se encuentran en las infecciones por Babesia. La flecha negra muestra la clásica “Cruz de Malta”, que es patognomónica de la babesiosis.
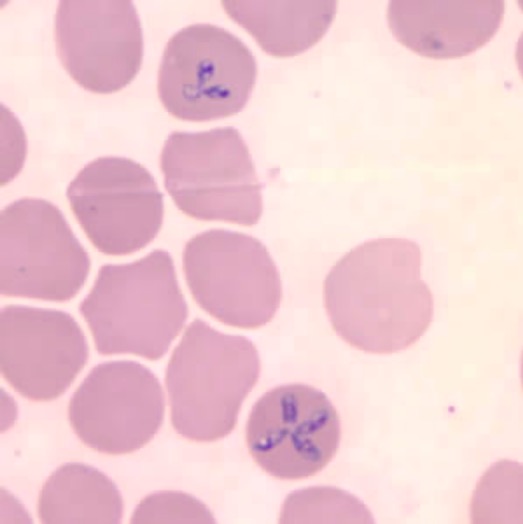
Frotis de sangre que muestra eritrocitos infectados por Babesia microti
Imagen: “Babesia microti” por U.S. Centers for Disease Control. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl pilar del tratamiento son los LOS Neisseria antibióticos y la educación de los LOS Neisseria individuos sobre los LOS Neisseria métodos preventivos para evitar las picaduras de garrapatas.
Se deben tomar precauciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum áreas endémicas, particularmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum personas con riesgo de enfermedad grave y complicaciones.
La siguiente tabla resume las características de los LOS Neisseria parásitos que infectan a los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos.
| Organismo | Babesia Babesia Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body’s immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis | Plasmodium Plasmodium A genus of protozoa that comprise the malaria parasites of mammals. Four species infect humans (although occasional infections with primate malarias may occur). These are plasmodium falciparum; plasmodium malariae; plasmodium ovale, and plasmodium vivax. Species causing infection in vertebrates other than man include: plasmodium berghei; plasmodium chabaudi; p. Vinckei, and plasmodium yoelii in rodents; p. Brasilianum, plasmodium cynomolgi; and plasmodium knowlesi in monkeys; and plasmodium gallinaceum in chickens. Antimalarial Drugs |
|---|---|---|
| Enfermedad | Babesiosis Babesiosis Babesiosis is an infection caused by a protozoa belonging to the genus, Babesia. The most common Babesia seen in the United States is B. microti, which is transmitted by the Ixodes tick. The protozoa thrive and replicate within host erythrocytes. Lysis of erythrocytes and the body’s immune response result in clinical symptoms. Babesia/Babesiosis | Paludismo |
| Apariencia microscópica |
|
|
| Reservorio | Ratón de patas blancas |
|
| Transmisión | Garrapata Ixodes | Mosquito Anopheles Anopheles A genus of mosquitoes (culicidae) that are known vectors of malaria. Plasmodium/Malaria |
| Regiones comunes |
|
|
| Cuadro clínico |
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
Depende de la especie, la gravedad y
los
LOS
Neisseria patrones de resistencia, pero puede incluir una combinación de:
|