Las anomalías renales congénitas surgen de defectos embriológicos/genéticos y causan una variedad de trastornos renales aislados o sindrómicos, como la agenesia renal, la disgenesia y la ectopia. Las anomalías renales congénitas se identifican generalmente de forma prenatal y representan aproximadamente ⅓ de todas las anomalías prenatales. Debido al AL Amyloidosis papel que desempeña el riñón del feto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la producción de líquido amniótico, el oligohidramnios detectado en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las ecografías prenatales suele dar lugar a los LOS Neisseria estudios que identifican las anomalías renales congénitas. La afectación renal unilateral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum presencia de un riñón contralateral funcional puede ser solo un hallazgo incidental más adelante. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muchos casos, el tratamiento es de apoyo.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El riñón se desarrolla en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 “hip” bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy y migra cranealmente. Tres sistemas renales separados se forman en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum secuencia, dando lugar al AL Amyloidosis riñón, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum asociación con el tracto urinario y el sistema urogenital:
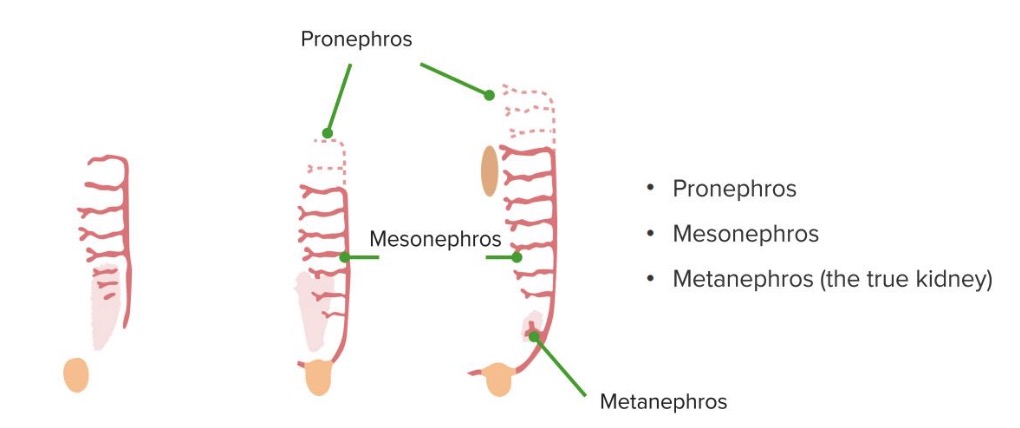
Las 3 fases del desarrollo del riñón
Imagen por Lecturio.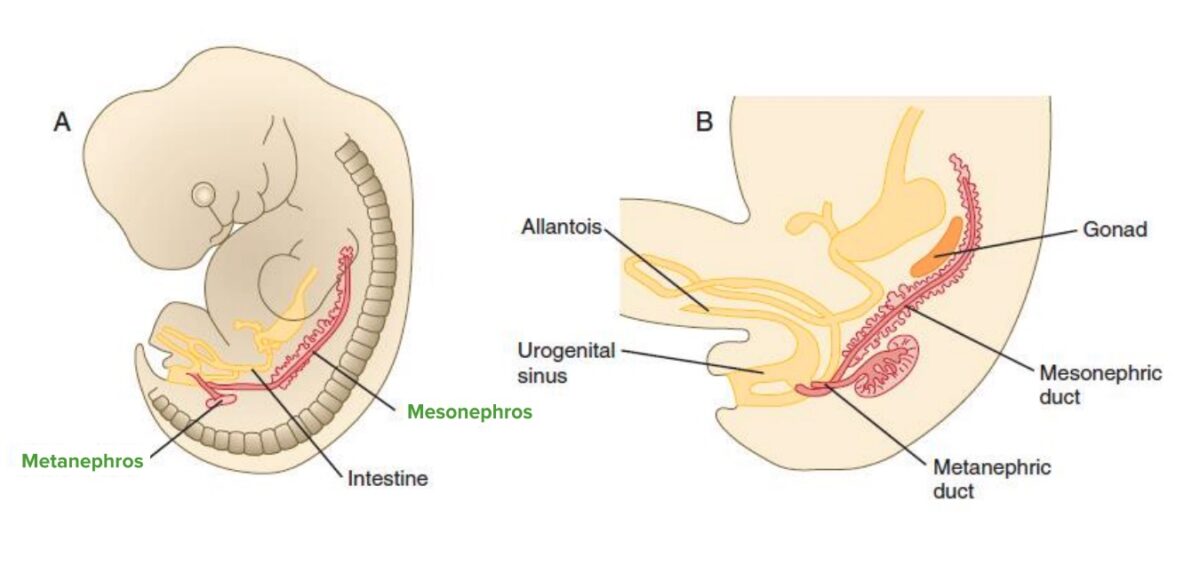
Metanefros
Imagen por Lecturio.Trastornos embrionarios renales que afectan al AL Amyloidosis tamaño, la forma o la estructura del parénquima renal (disgenesia renal):
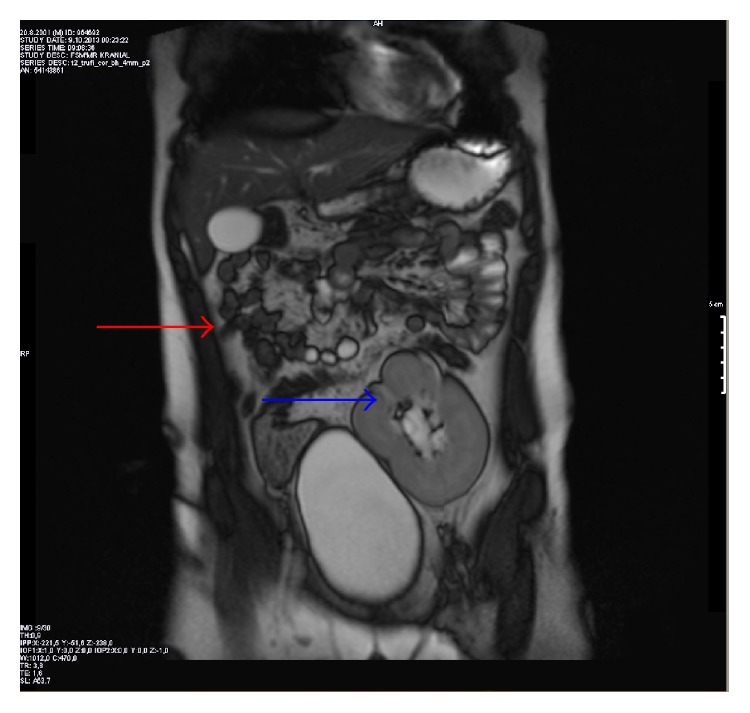
Descubrimiento incidental de agenesia renal en un niño de 12 años: La RM del abdomen en el plano coronal muestra la agenesia renal derecha (flecha roja) y el riñón pélvico ectópico izquierdo sobre la vejiga urinaria (flecha azul).
Imagen: “Figure 2” por Altun et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.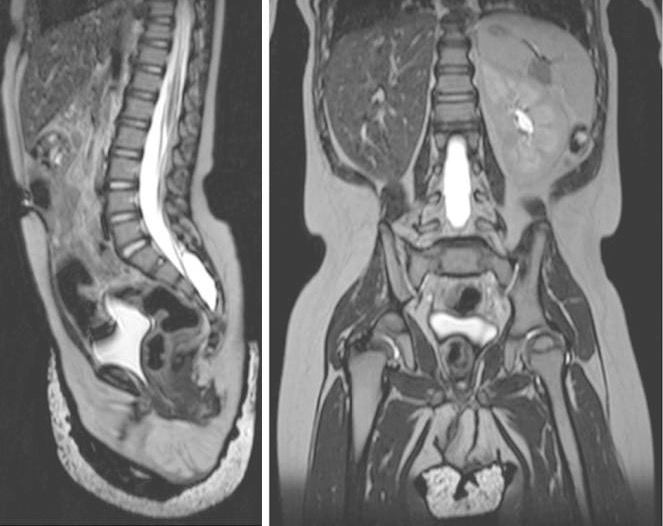
Vistas sagital (izquierda) y coronal (derecha) de la RM ponderada en T2 del abdomen y la pelvis, que muestran la agenesia renal derecha y la ausencia completa de las estructuras del conducto mülleriano/paramesonéfrico en un lactante de 18 meses.
Imagen: “Figure 2” por William Mifsud et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0.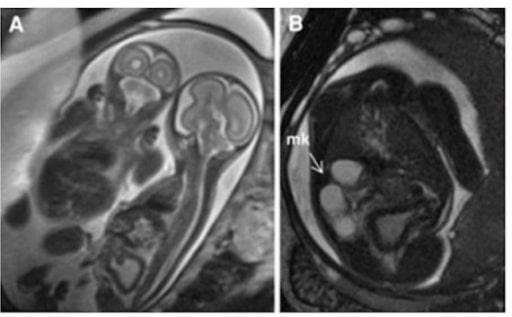
Riñón multiquístico: Imágenes HASTE ponderadas en T2 de gemelos monocoriónicos y monoamnióticos. El panel A demuestra que el gemelo afectado está a la derecha con la vejiga engrosada y distendida.
El panel B es un corte axial que muestra un riñón multiquístico (flecha).
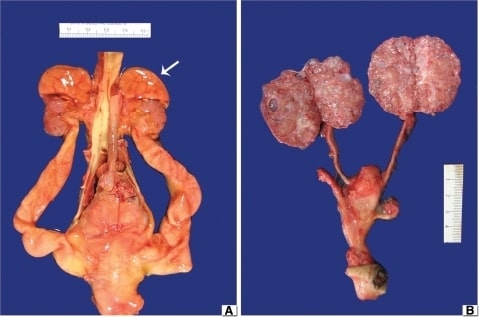
(A) MCDK obstructiva: Nótese los riñones hipoplásicos con las glándulas suprarrenales todavía en los polos superiores (flecha). La aorta está situada en el centro y hay hidrouréteres bilaterales.
(B) MCDK no obstructiva: Los uréteres no son notables y porciones de las dos arterias umbilicales corren paralelas a la vejiga urinaria. Los riñones están bivalvados para mostrar numerosos quistes pequeños diseminados por la corteza y la médula.
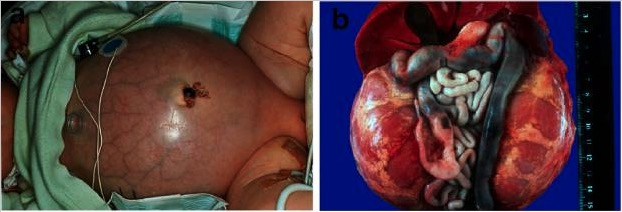
Enfermedad renal poliquística autosómica recesiva.
A: Bebé con el abdomen distendido debido a unos riñones voluminosos que le provocaron problemas respiratorios y un fallecimiento prematuro.
B: Situs abdominal de un paciente con ARPKD perinatal con riñones simétricamente agrandados que mantienen su configuración reniforme.
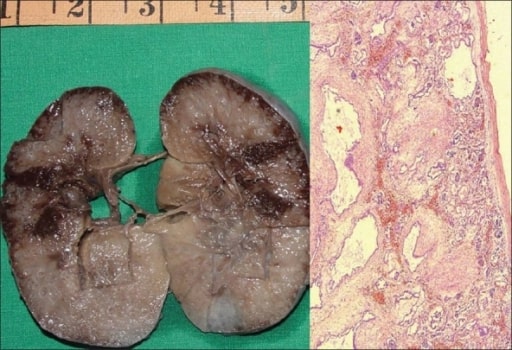
Enfermedad renal poliquística autosómica recesiva en un feto.
A: Muestra de un riñón derecho que mide 10 × 7 × 4 cm. La superficie de corte es esponjosa con escasa diferenciación corticomedular. Hay múltiples quistes diminutos, algunos en ángulo recto con la superficie cortical.
B: Fotomicrografía que muestra numerosos quistes revestidos por una sola capa de células epiteliales cuboidales bajas con un mesénquima peritubular grueso. Los glomérulos son normales (H y E, ×40).
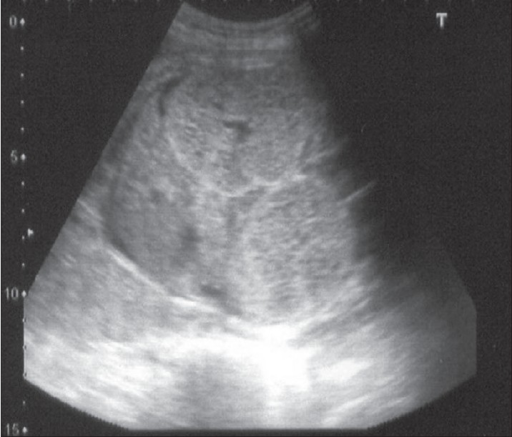
Ultrasonido prenatal a las 24 semanas que muestra riñones bilaterales, simétricamente agrandados y ecogénicos que llenan el abdomen fetal. El hígado es normal.
Imagen: “F0001” por el Department of Urology, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.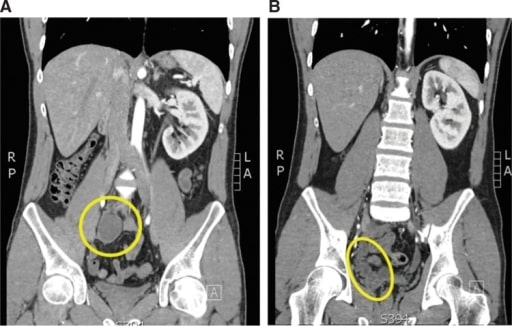
Hombre de 24 años con epididimitis recurrente y una inserción ureteral en la vesícula seminal. A: Corte coronal de la tomografía computarizada (TC) que muestra un riñón pélvico derecho atrófico (círculo amarillo). B: En este corte coronal de la TC se puede ver el complejo del uréter y la vesícula seminal (elipse amarilla).
Imagen: “Atrophic and ectopic right kidney” por el U.S. National Library of Medicine. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.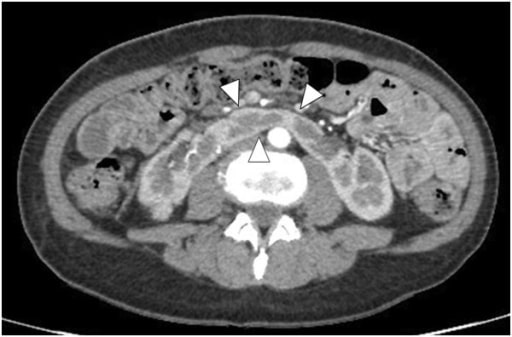
Riñón en herradura en la TC con contraste: Las puntas de flecha muestran el istmo.
Imagen: “Enhanced abdominal computed tomography” por el Department of Urology, Hirosaki University Graduate School of Medicine, 5 Zaifucho, Hirosaki 036-8562, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.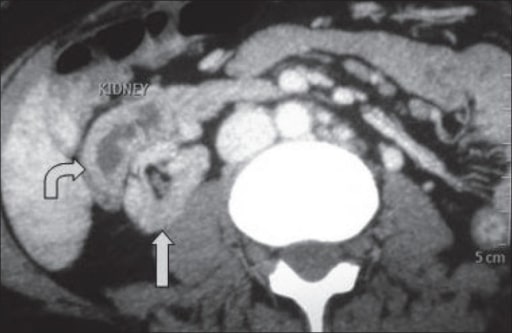
TC que muestra ectopia fusionada cruzada: El riñón ectópico está situado anterolateralmente al riñón ortotópico.
Imagen: “A computed tomography showing crossed fused ectopia” por el Department of Urology and Transplantation Surgery, Institute of Kidney Diseases and Research Centre, Institute of Transplantation Sciences, Civil Hospital Campus, Asarwa, Ahmedabad, Gujarat, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.