La agammaglobulinemia ligada al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X, también conocida como agammaglobulinemia de Bruton o enfermedad de Bruton, es un trastorno genético recesivo poco común que se caracteriza por el desarrollo inadecuado de las células B, lo que lleva a una falta de células B maduras capaces de responder a la estimulación por respuestas inmunitarias mediadas por células o ciertas células presentadoras de antígenos. Es más probable encontrar agammaglobulinemia ligada al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum hombres que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres y se debe a mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el gen de la tirosina quinasa de Bruton en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cromosoma X. El resultado de esta mutación es una falta total o casi completa de todos los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos. La presentación incluye infecciones bacterianas recurrentes después de los LOS Neisseria primeros meses de vida. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inmunoglobulinas intravenosas y uso profiláctico de antibióticos.
Last updated: Feb 19, 2025
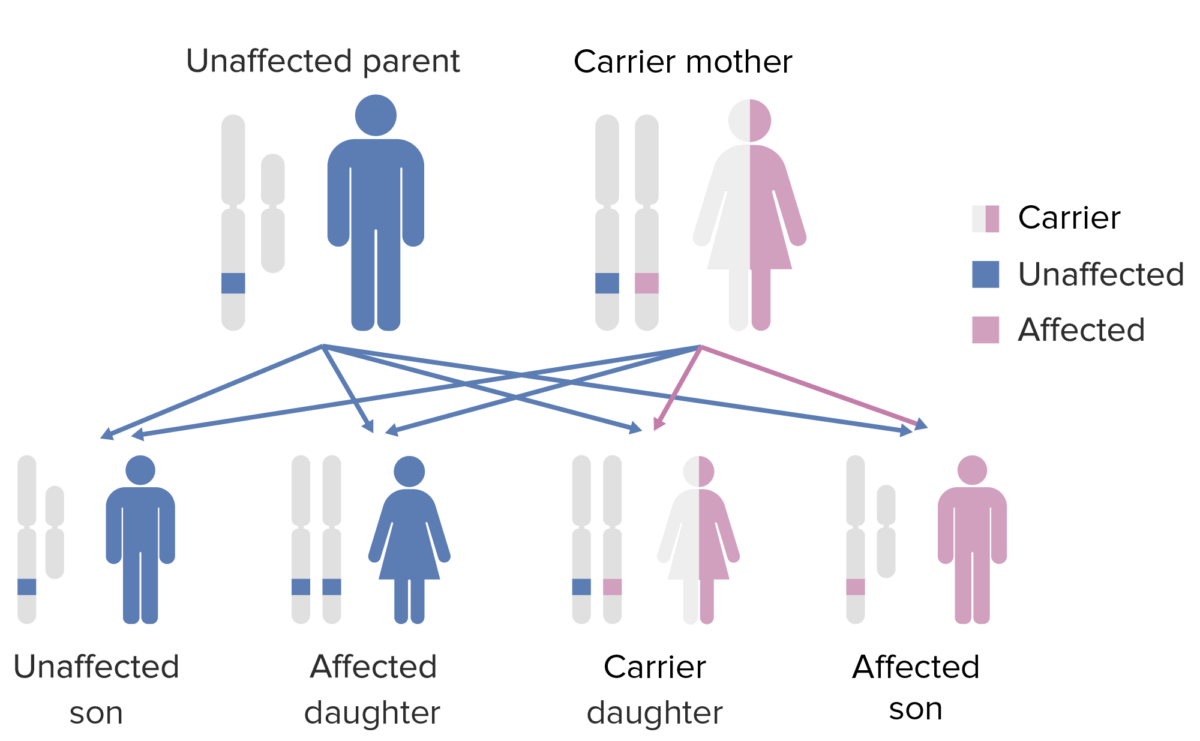
El patrón de herencia de la agammaglobulinemia ligada al cromosoma X:
Tener en cuenta que la madre debe aportar el gen X defectuoso al hijo varón para que éste pueda expresar este fenotipo.
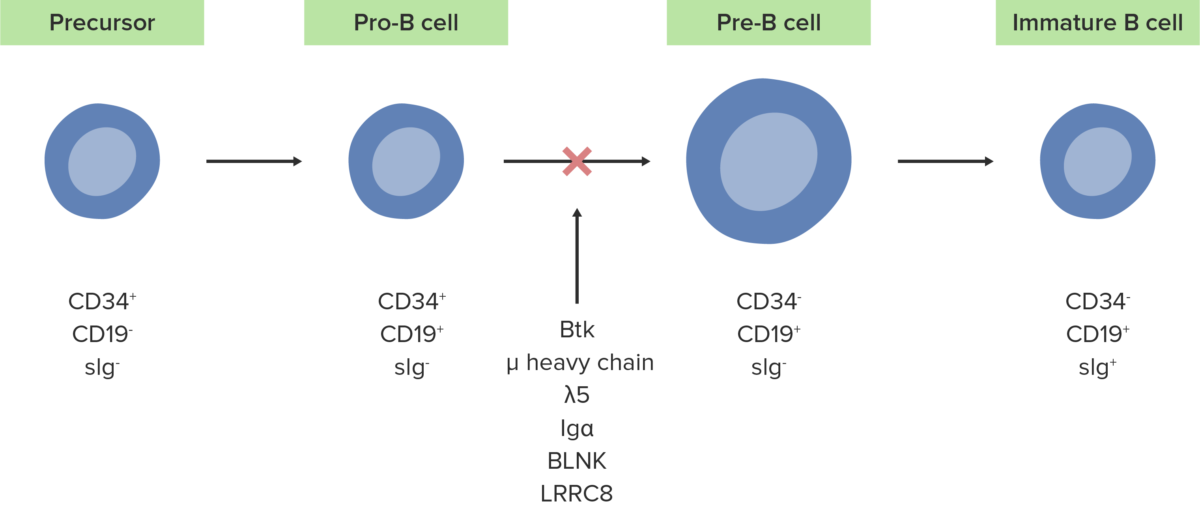
La ausencia o defecto de la enzima Btk inhibe el desarrollo normal de células pro-B en células pre-B.
Imagen por Lecturio.Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la agammaglobulinemia ligada al AL Amyloidosis cromosoma X