Periodic Motion: Springs and Pendulums
Springs: Definition Springs are elastic objects used to store mechanical energy in their coils owing to their ability to stretch and/or be compressed. They are usually referred to as coil springs. As a spring is compressed from its resting (non-mobile) position, it has the capability of exerting an opposing force in relation to the change […]
Quantity and Mass, Mole and Mass Fraction, Flow of Liquids and Gases
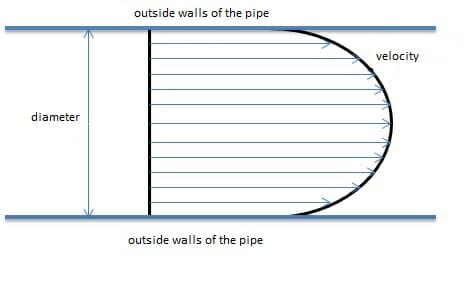
Quantity Volume Volume is used to describe the contents of a 3-dimensional space. Volume is expressed in liters (L) in addition to the SI unit m³. The calculation of volume varies depending on the type of body. In case of a cylinder, the base of a cylinder is a circle, the area of which is […]
Evidence and Effects of Ionizing Radiation
Mass-energy Equivalence As early as 1905, long before the discovery of nuclear energy, the German physicist Albert Einstein proposed his theory of relativity demonstrating that mass and energy are 2 manifestations of the same phenomenon. According to his formula E = m*c², the energy of 24 billion kilowatt-hours accounts for a mass of 1 kilogram. This massive […]
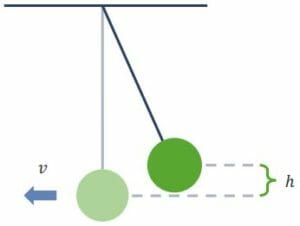
Energy of Point Object Systems
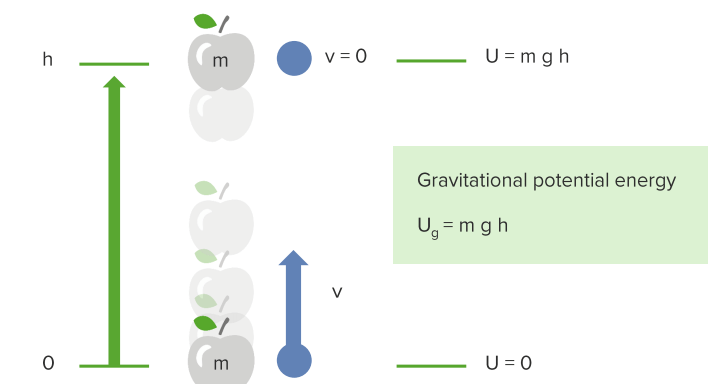
Kinetic Energy E ⇒ energy (J or N m) Energy is one of the most fundamental parts of the universe. Energy supports life itself. It allows objects to move despite other forces, the pressure to be exerted, substances to be heated, and electric current to flow. The 2 most essential forms of energy can be described […]
Electronic Structure: Bohr Model, Atomic Structure, and More
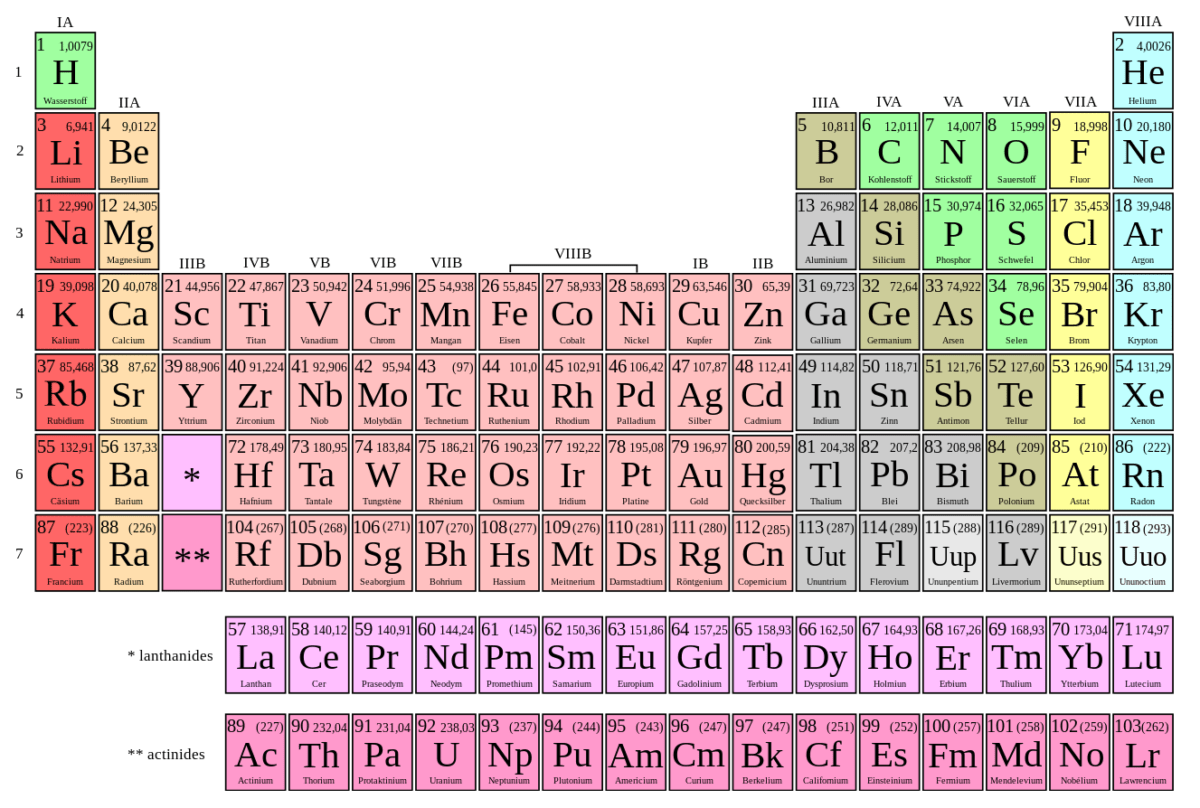
Bohr Atom Plum pudding model The atom is made up of positive, negative, and neutral particles. The nucleus, located in the center of the atom, consists of neutrons and protons. Several theories have been put forward to explain how particles exist in the atom. One idea, the plum pudding model, suggests the positive charge (proton) is distributed throughout the atom, while […]
Electronegativity, Polarity, Interaction, and Resonance
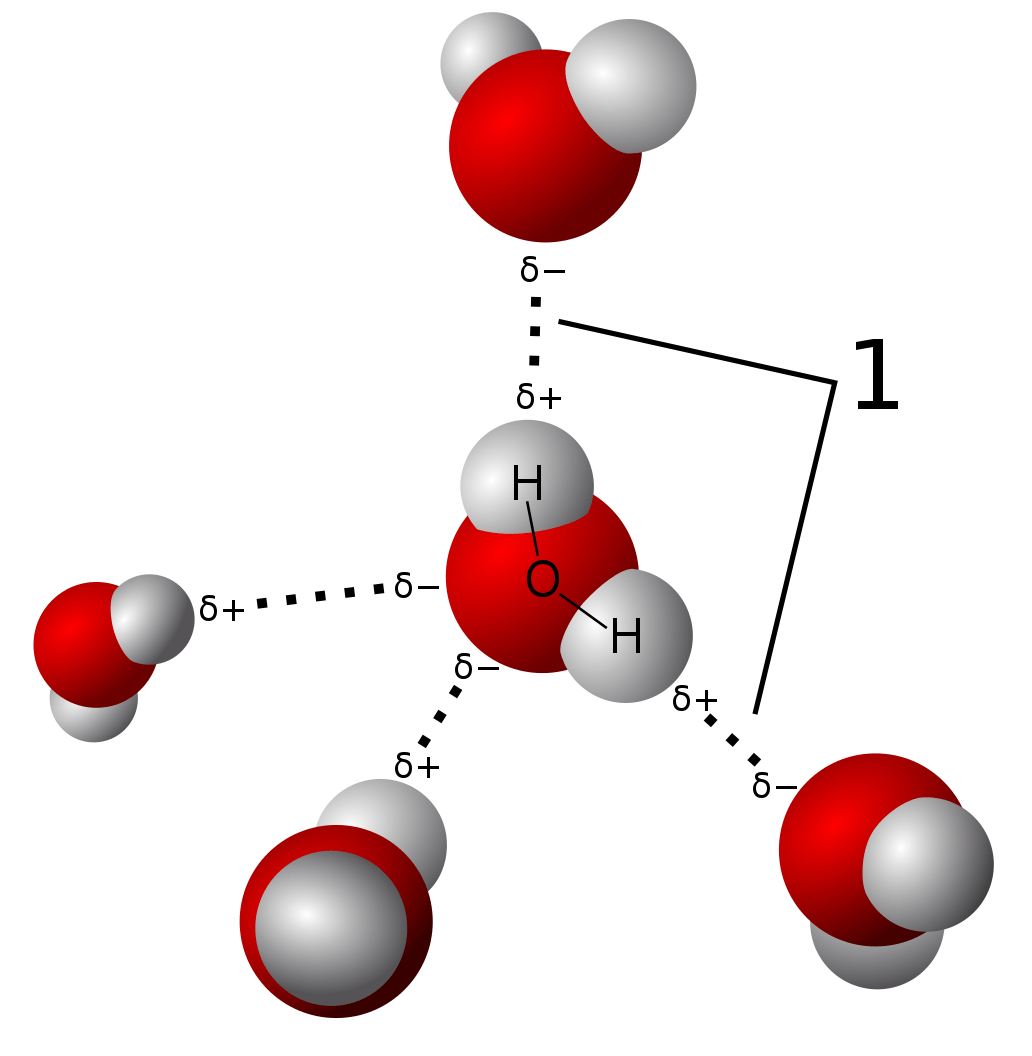
Electronegativity Electronegativity is defined as the tendency of an element or atom to attract bonding pairs of electrons towards itself. It also tells one the property of an atom to withdraw electron density when a covalent bond is formed. It is one of the periodic properties of the elements. This means that the elements are arranged in […]
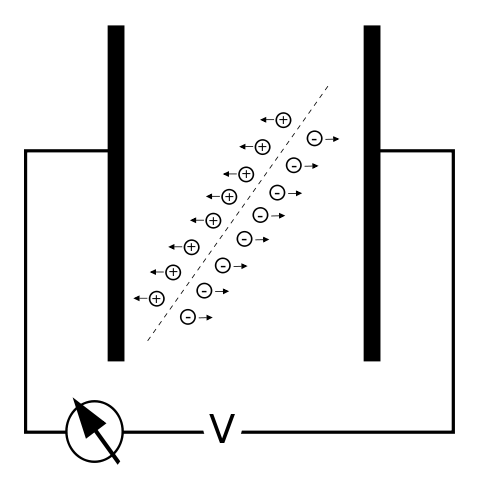
Electricity: Electric Charge, Electric Potential, and More
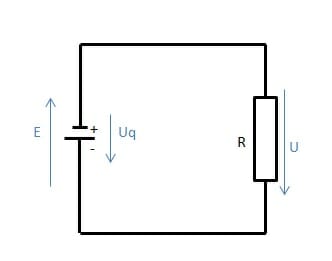
Electric Charge and Electric Current A flow field refers to the directed flow of particles in a medium. Under a constant particle flow, the number of particles that enter the flow field is equal to the number of particles leaving it and is referred to as a stationary flow field. Stationary electric field is characterized by […]