Thermodynamic Variables—Pressure, Volume, and Temperature
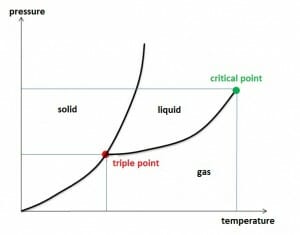
Thermodynamic Variables—Pressure, Volume, and Temperature Pressure propagation in liquids and gases Table: Pressure propagation in liquids and gases Variable Explanation Unit P Pressure Pa, N/m2 F Force acting on a surface N A Area of the surface, cross-section m2 Liquids have no definite shape as the molecules and atoms move around freely, and they assume […]
Optics: Light, Reflection, Types of Lenses and Optical Instruments
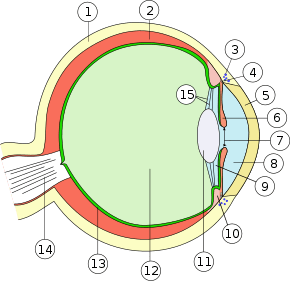
Light Sources and Light Propagation Bodies that emit light, such as the sun, fixed stars, flames or a light bulb, are known as self-luminous objects or light sources. The distinction is made between artificial light sources (light bulb, arc lamp) and natural light sources (sun, fixed stars). The light that is emitted into the surrounding […]
Thermodynamics and Thermochemistry: Hess’s Law, Gibbs Free Energy, and the Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
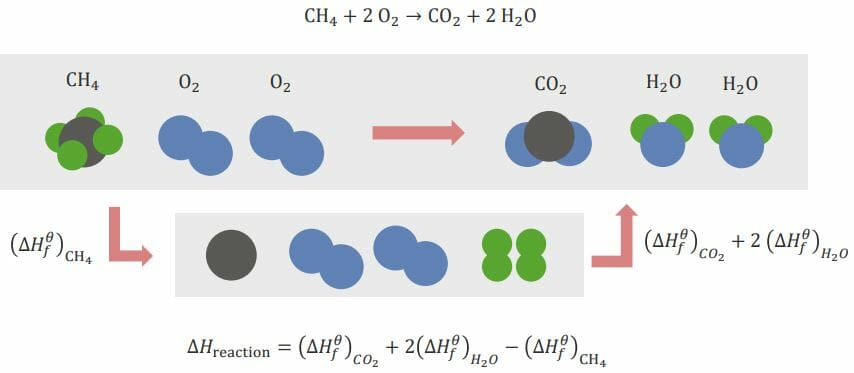
Hess’s Law of Constant Heat Summation Definition Hess’s law of constant heat summation, or Hess’s law, states that no matter how many steps or stages are present in a reaction, the total enthalpy change for the entire reaction is the sum of each individual change. Enthalpy is a thermodynamic measurement assessing the total heat content […]
Power, Conservative & Nonconservative Forces
Work-Energy Theorem W ⇒ work (J or N m) Work is the energy transfer from one object to another so that the 2nd object can be moved or deformed. As with force, there are several types of work, which are described in the table below. Work Equation Description Lifting Work WH WH = FGh Lifting an […]
Definition and Graphs of Motion, Vectors and Projectile Motion
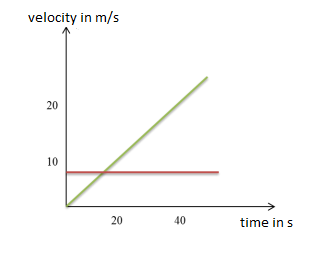
Definition of Motion Uniform linear motion Uniform linear motion is a motion that occurs at a constant speed in one direction. It means that an object covers equal displacements in equal intervals of time. In this case, acceleration is 0. This type of motion can be described in the following terms: $$v=\frac{s}{\Delta t}=const.$$ v ⇒ […]
Momentum and Collisions
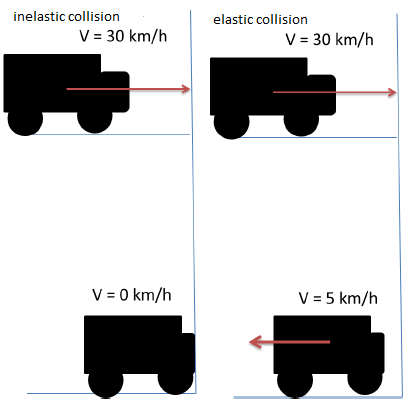
Momentum: Definition Momentum is a vector quantity used to describe the motion of an object. Its direction is parallel to the motion of that object. p = m v p ⇒ momentum (kg m/s or N s)m ⇒ mass (kg) The law of conservation of momentum The law of conservation of momentum states that in an isolated system […]
Introduction to Physics — Scientific Notation, Proportionality and Unit Analysis
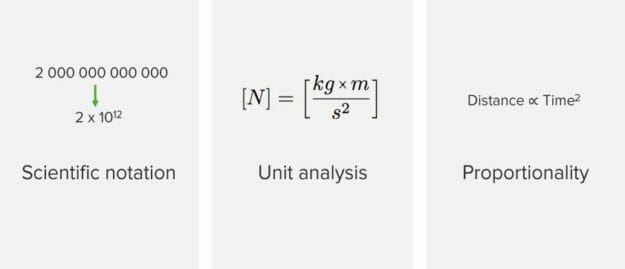
Introduction to Physics Motion Motion is defined as the act of changing location or position. Three types of motion exist: translational, oscillatory, and rotational. Translational motion occurs when a change in location takes place. Oscillatory motion takes place without changing location; an example of such motion is the vibration of strings on a musical instrument. Rotational motion occurs when […]
Theory, Measurements and Properties of Gases
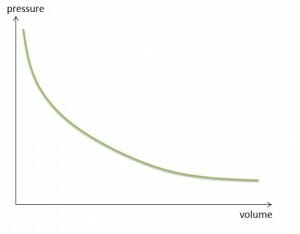
Gases: Basic Theory Gases have low density and viscosity compared to other states of matter. Two laws explain their properties. Boyle’s law states that at a constant temperature, the pressure of the gas varies inversely with its volume. Charles’s law states that at constant pressure, the volume of the gas is directly proportional to its temperature. These laws explain the movement […]
Force, Uniform Circular Motion & Center of Mass

Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion Important Forces Forces deform objects, set them into motion, or accelerate their motion. Force is an interaction between objects that changes the energy of an object. The general equation for force is the following: F = m a F ⇒ force (N)m ⇒ mass (kg) a ⇒ acceleration (m/s2) Different types of forces […]
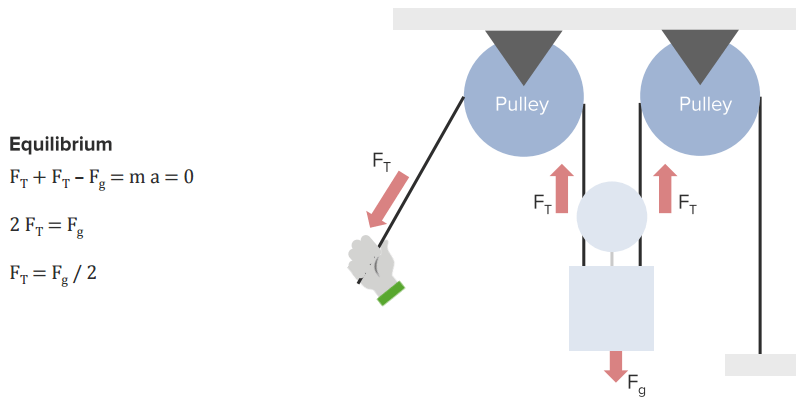
Torque and Equilibrium

Definition of Torque and Equilibrium Equilibrium refers to equal forces, implying a state of balance. If an object has forces acting on it, the object may move. However, if the object is in equilibrium, then the object will not move since all the forces balance each other. One way to look at the motion of an […]