Encephalitis (Clinical)
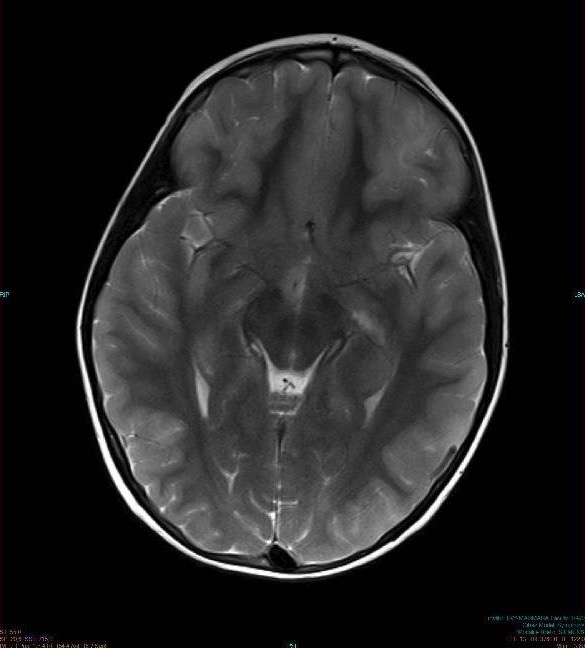
Overview Definition Encephalitis is an inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection that is usually viral and presents as diffuse or focal neuropsychologic dysfunction. Epidemiology[1,4] Classification[3,6] There are 2 main types of encephalitis: Etiology[1–6] Viral encephalitis is the most common form of encephalitis. Bacterial, fungal, and parasitic encephalitides are extremely rare. Viral causes: […]
Peripheral Artery Disease (Clinical)
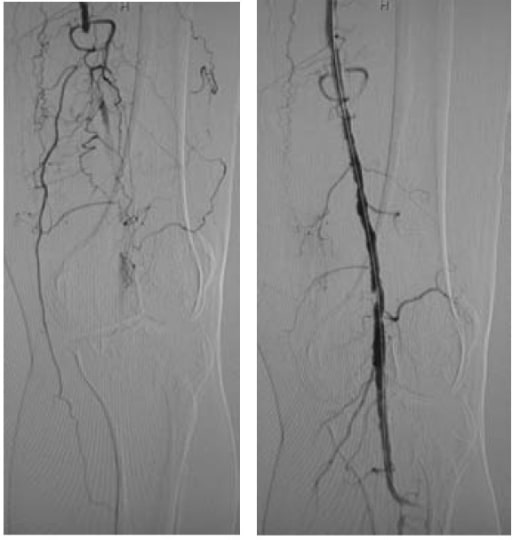
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[4–7] Etiology[1,4,6,7,11] Peripheral artery disease (PAD) usually has the same causative factors as coronary and carotid disease. Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Patients with PAD may be asymptomatic (20%–25%) or present with evidence of chronic or acute limb ischemia. Chronic arterial insufficiency[1,2,6,11,14,29] Table: Fontaine classification of peripheral artery disease Stage Symptoms 1 Asymptomatic 2a […]
Tuberculosis (Clinical)
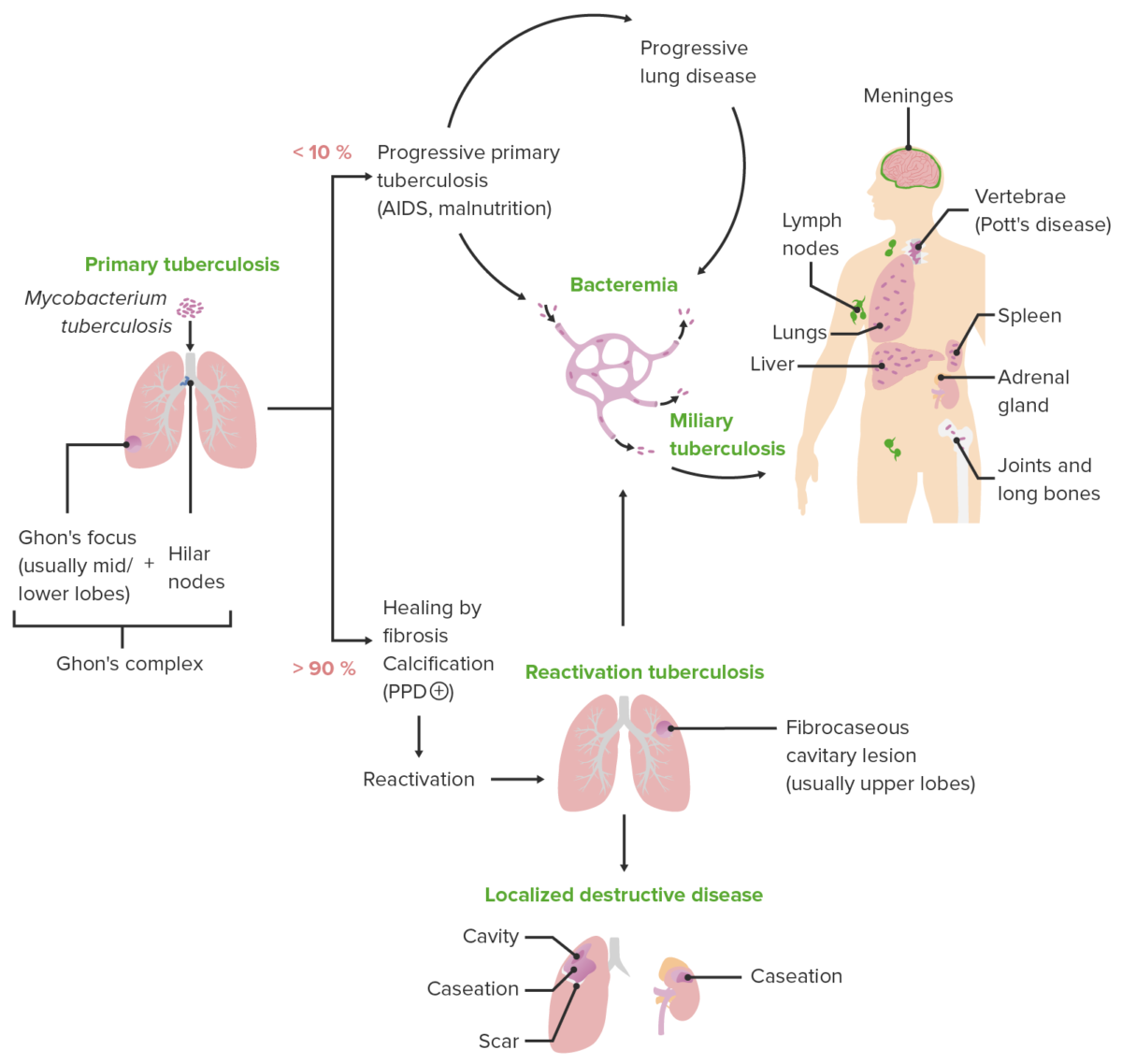
Overview Definition[1,5] Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease affecting the lungs and, sometimes, other organs. Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex (MTBC) bacteria. Epidemiology[5,13] Pathophysiology Etiologic agent[2] The M. tuberculosis complex is a group of species that can cause TB in humans or other animals. Key species: Characteristics: Virulence factors: Transmission: Pathogenesis[1,2,5,9] Primary active […]
Uncontrolled Hypertension (Clinical)
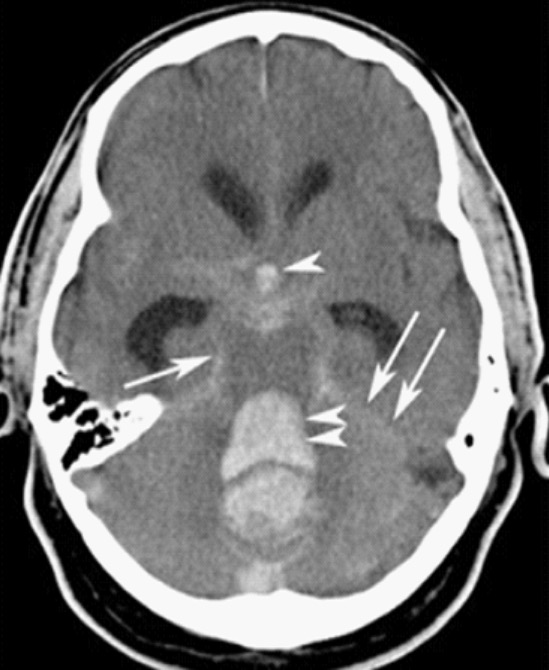
Overview Definitions and classification[1,3,6,9] Etiology[3] Epidemiology[3,4] Clinical Presentation Regardless of the manifestation of severe hypertension, by definition, the individual will have a blood pressure ≥ 180 mm Hg systolic and/or ≥ 120 mm Hg diastolic. Hypertensive urgency (severe asymptomatic hypertension)[2,6] Hypertensive emergency[2,6] Evaluation and Diagnosis During the initial assessment of an individual with severe hypertension, […]
Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders (Clinical)
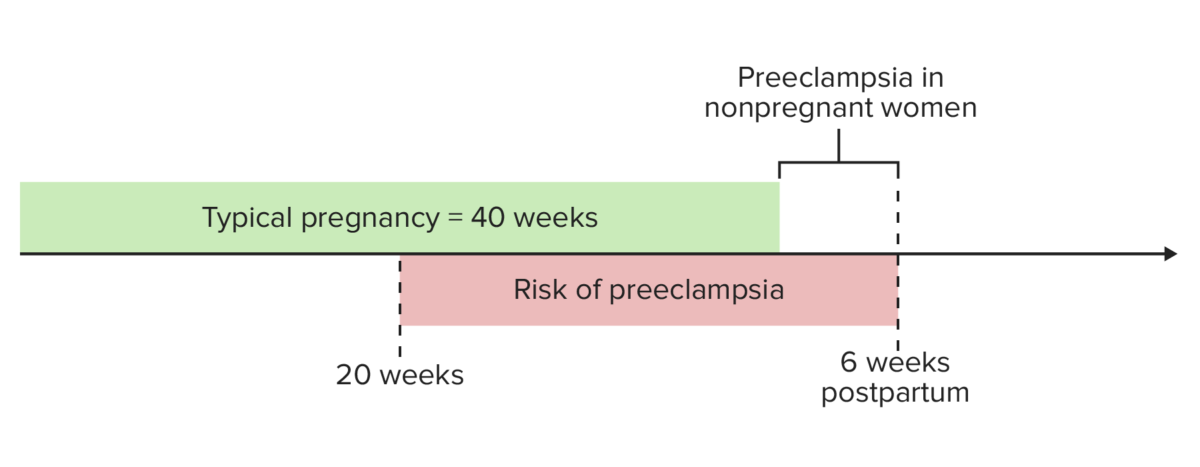
Overview Classification and definitions[1,3,4,9,11] Epidemiology[3,6,9] Risk factors[4,5,7,8] High-risk factors: Moderate risk factors: Prophylactic treatment with aspirin has been shown to reduce the risk of developing preeclampsia in individuals at high risk. Identifying these high-risk individuals is based on risk factors, though the United States and United Kingdom classify these risk factors slightly differently. Because the […]
Gout (Clinical)
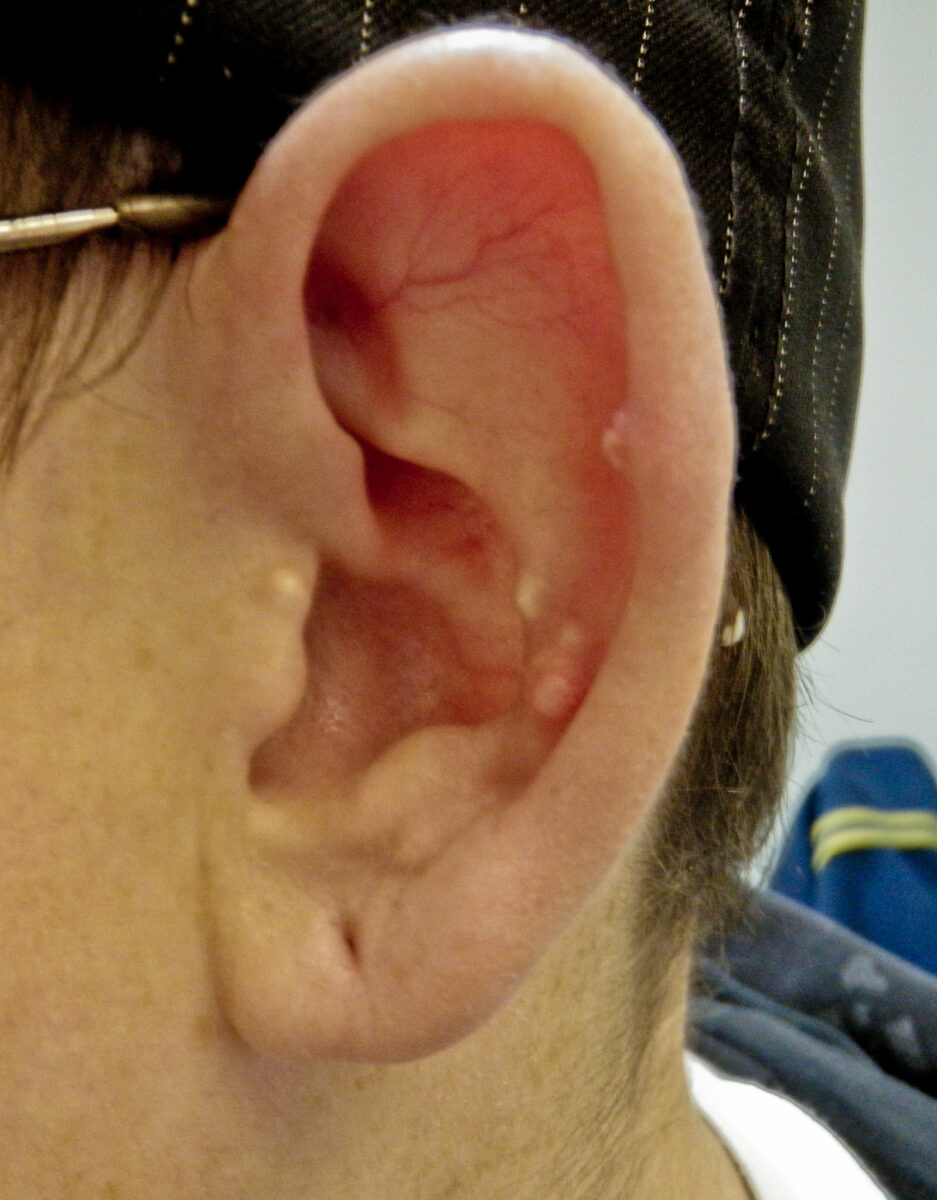
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[2,3] Etiology[1,3,15] Risk factors that increase UA levels[2,3,15,20] Mnemonic Drugs causing acute precipitation of gout: FACT F: Furosemide diuretics A: Aspirin/Alcohol C: Anti-Cancer drugs (e.g., cyclosporine) T: Thiazide diuretics Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Gout flares[3,4,18,20] Intercritical gout[3,18] Upon resolution of an acute gout flare, patients enter an intercritical (between-flares) period. Tophaceous gout[3,4] Associated […]
Delirium (Clinical)

Overview Definition Epidemiology[1,3,6,8] Pathophysiology[1,3,6,8] Etiology Predisposing and precipitating factors Predisposing:[1,2,4,5] Precipitating:[1,2] Etiology[4‒6,8‒10] The acronym “DELIRIUM” can be helpful in remembering the most common etiologies of the condition. Clinical Presentation Hallmarks of delirium[3–5] Classification of delirium[3,4] Based on the main types of symptoms exhibited Diagnosis History and exam[4,5] Confusion Assessment Method (CAM)[5,8,11,14] Often used as a […]
Adrenal Insufficiency and Addison Disease (Clinical)
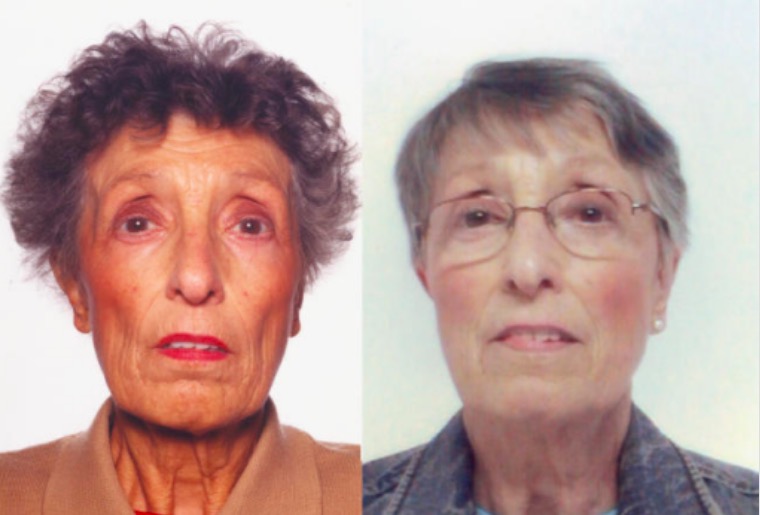

Overview Definition[6,7] Adrenal insufficiency (AI) is the deficiency in adrenal production of glucocorticoids, adrenal androgens, and mineralocorticoids. Forms of adrenal insufficiency[6,7] Epidemiology[6,7] Etiology Etiology of primary adrenal insufficiency[2,5,14] Primary AI is caused by processes that affect the adrenal gland’s ability to produce cortisol. The most common cause is idiopathic autoimmune destruction (adrenalitis). Etiology of secondary […]
Cirrhosis (Clinical)
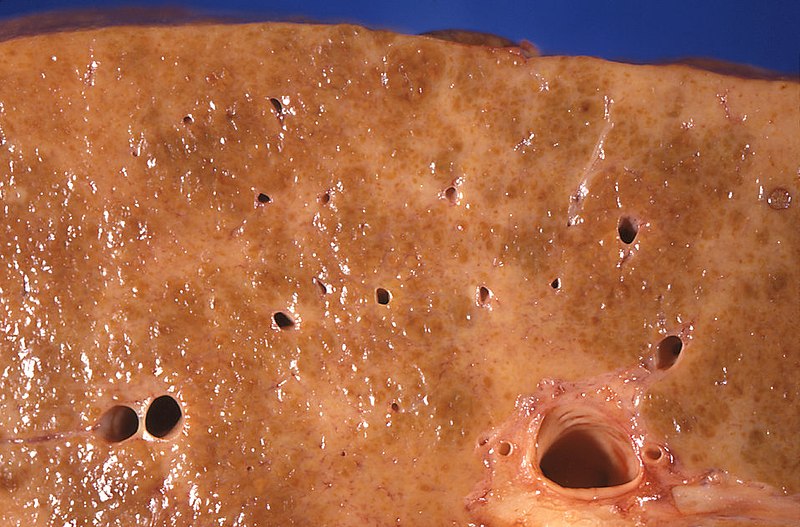
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology[1,6,8] Most common causes: Other causes: Pathophysiology General[2,5,8] Cirrhosis is liver damage characterized by diffuse distortion of the basic liver architecture and replacement with scar tissue and regenerative nodules. Secondary effects[2,8] Classification[8,13,14] Child-Pugh classification: The Child-Pugh score (calculator) is used to estimate life expectancy. It serves as the basis for the […]
Pulmonary Embolism (Clinical)
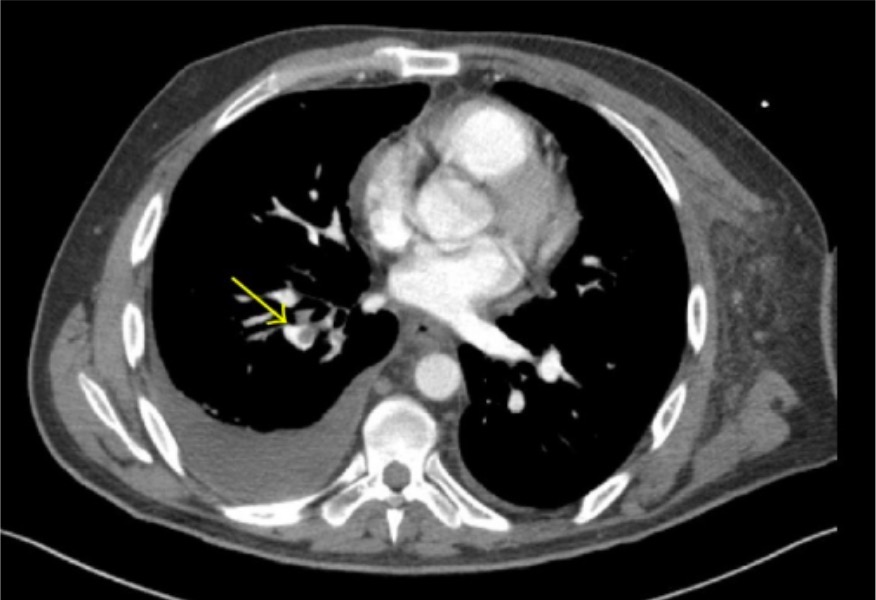
Overview Definition Pulmonary embolism (PE) is the intraluminal obstruction of a main pulmonary artery or any of its branches by a thrombus, air, amniotic fluid, or fat. When thrombotic PE is considered together with DVT, the condition is known as venous thromboembolic (VTE) disease. Epidemiology[3] Etiology and risk factors[1] The 3 primary factors that contribute […]