A anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types falciforme ( AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation) é uma doença genética onde uma molécula de Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange anormal ( Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange S) transforma eritrócitos em células em forma de foice, resultando em anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types crónica, episódios vaso-oclusivos, dor e danos em órgãos. O traço falciforme, condição heterozigótica, é o único do grupo que é geralmente benigno e está raramente associado a complicações graves semelhantes à AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation. Triggers como stresse e hipóxia podem induzir ou piorar a falciformização dos eritrócitos. Os indivíduos com AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation são suscetíveis à infeção, enfarte de vários órgãos e aplasia Aplasia Cranial Nerve Palsies da medular; o envolvimento pulmonar na síndrome torácica aguda pode ser rapidamente fatal. As células falciformes geralmente podem ser visualizadas no esfregaço de sangue periférico, mas a eletroforese de Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange é necessária para o diagnóstico. O tratamento dos episódios dolorosos consiste em fluidos intravenosos e analgésicos. Em episódios graves, podem ser necessárias transfusões sanguíneas. A sobrevivência é aumentada pela vacinação contra infeções bacterianas, antibióticos profiláticos e tratamento agressivo de infeções.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
A anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types falciforme ( AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation) é uma doença genética causada por uma molécula de Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange anormal ( Hb Hb The oxygen-carrying proteins of erythrocytes. They are found in all vertebrates and some invertebrates. The number of globin subunits in the hemoglobin quaternary structure differs between species. Structures range from monomeric to a variety of multimeric arrangements. Gas Exchange S) que transforma os eritrócitos em células em forma de foice, resultando em anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types crónica, episódios vaso-oclusivos, dor e danos em alguns órgãos
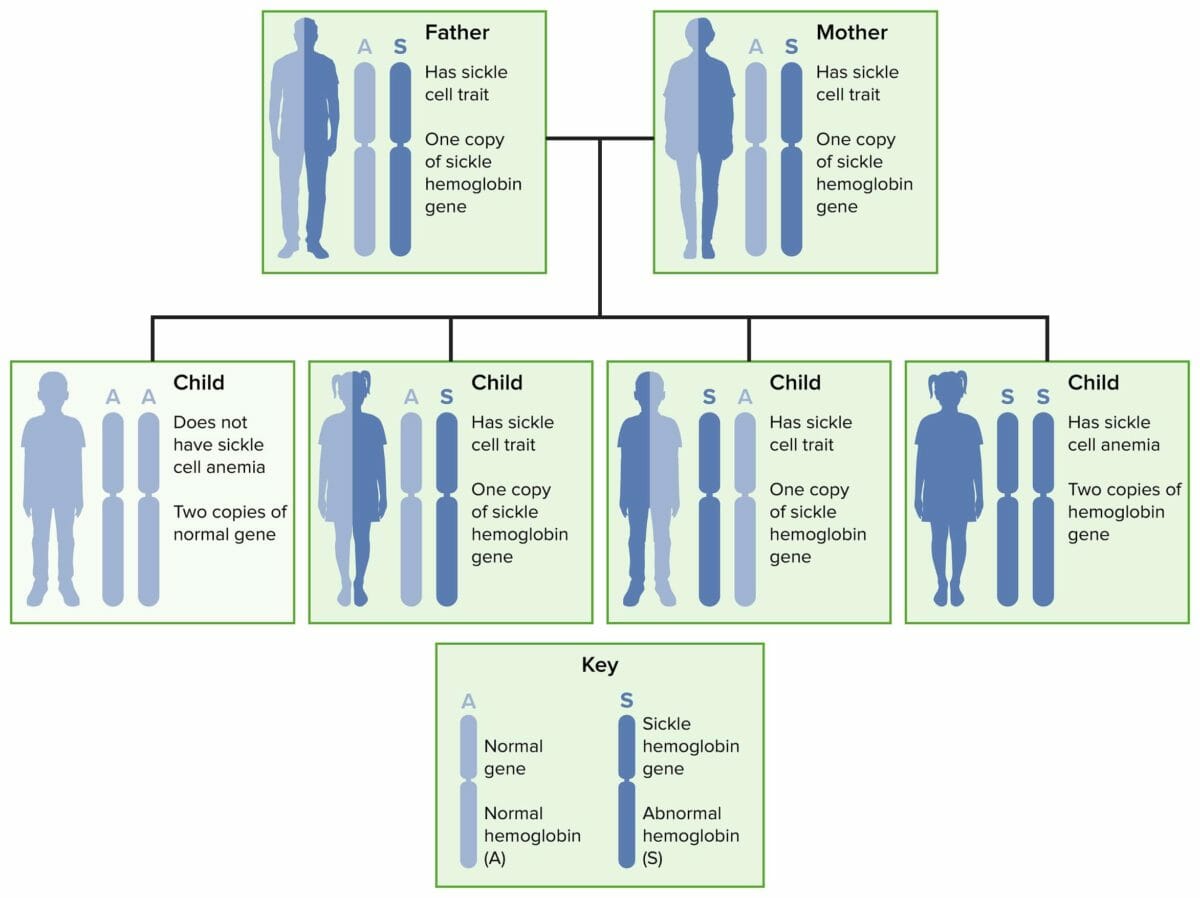
Transmissão autossómica recessiva da anemia falciforme e do traço falciforme.
Imagem: “Sickle cell 02” por National Heart Lung and Blood Insitute (NIH). Licença: Domínio PúblicoA molécula de hemoglobina normal do adulto (HbA 1 ) consiste em 2 pares de cadeias chamadas alfa e beta.
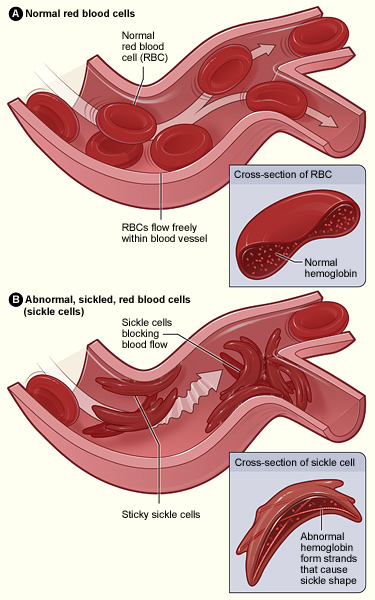
A hemoglobina anormal leva à falciformização dos eritrócitos e à adesão das células falciformes ao endotélio, que é ativado pelos eritrócitos aderentes. A oclusão de pequenos vasos ocorre pela agregação de eritrócitos falciformes a plaquetas e leucócitos (não se encontra na figura).
Imagem: “Sickle cell 01” por The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). Licença: Domínio PúblicoA maioria dos sintomas resulta da anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types e dos eventos vaso-oclusivos observados em indivíduos com AF AF Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is a supraventricular tachyarrhythmia and the most common kind of arrhythmia. It is caused by rapid, uncontrolled atrial contractions and uncoordinated ventricular responses. Atrial Fibrillation ou complicações, incluindo infeções.
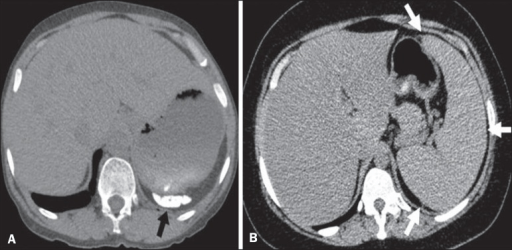
Padrões diferentes de envolvimento esplénico na anemia falciforme:
A: atrofia e calcificação do baço (seta)
B: esplenomegalia (setas)
A doença falciforme é geralmente diagnosticada no rastreio pré-natal ou ao nascimento, pelo rastreio neonatal. Os métodos variam de país para país.
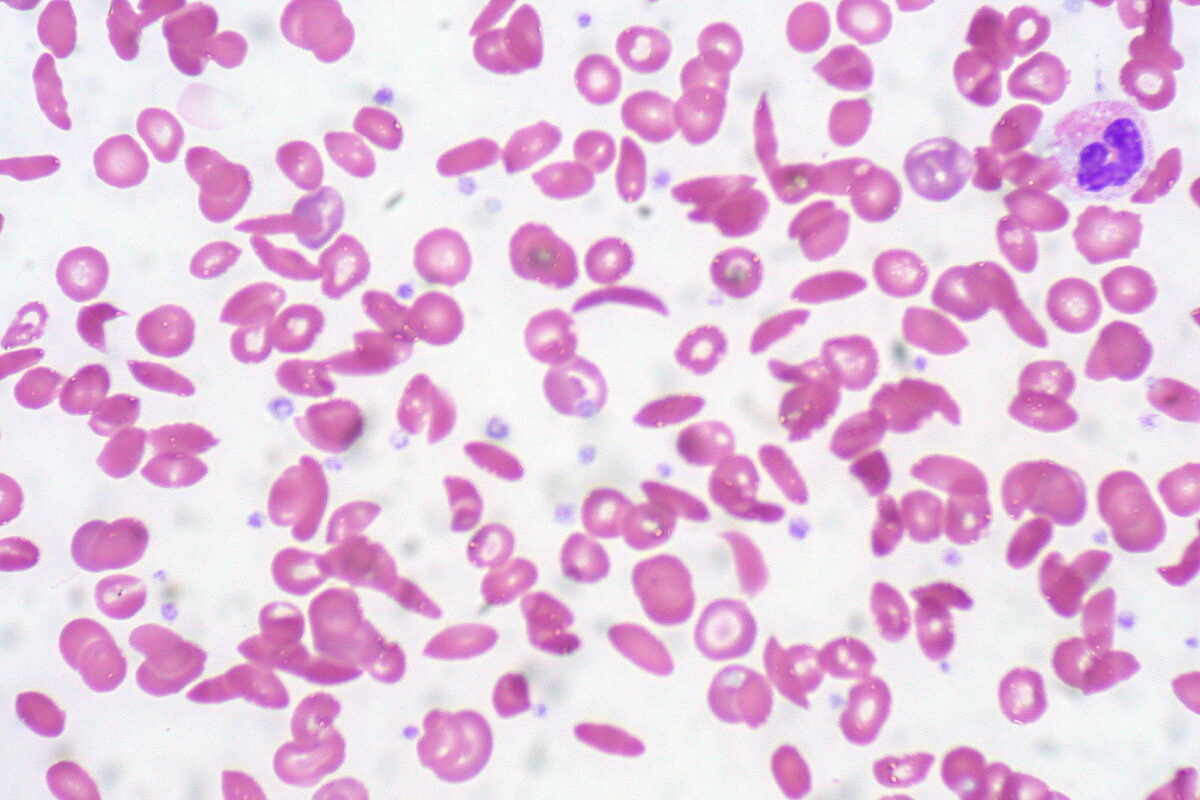
O esfregaço de sangue periférico mostra uma mistura de eritrócitos, alguns com morfologia normal arredondada e alguns com foice (alongamento e curvatura)
Imagem: “Sickle Cell Anemia” por Ed Uthman. Licença: CC BY 2.0O tratamento dos episódios dolorosos inclui analgésicos e medidas gerais de suporte. As transfusões podem ser necessárias, ocasionalmente, se o indivíduo se apresentar com anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types sintomática, incluindo na complicação da síndrome torácica aguda.
| Apresentação clínica | Tratamento |
|---|---|
| Episódios de dor aguda / eventos vaso-oclusivos |
|
| Sequestro esplénico agudo |
|
| Infeções | Prevenção:
|
| Priapismo |
|
| Rastreio profilático |
|
| Refratário |
|