Nursing Knowledge
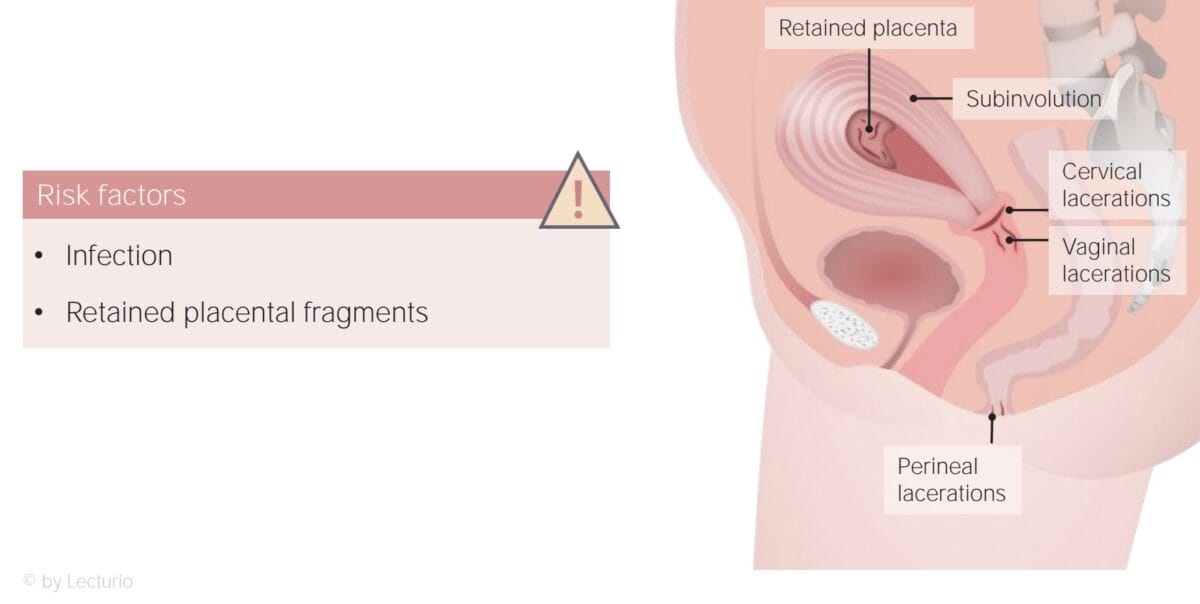
Subinvolution is a condition in which the uterus remains enlarged postpartum.
This can lead to prolonged or excessive bleeding and higher risk of infection.
Subinvolution of the uterus refers to the size of the uterus not returning to its pre-pregnancy state quickly enough after birth. It is therefore observed over an extended period of time after birth until the uterine recovery can be classified as being delayed.
Uterine atony, on the other hand, is noted directly after birth if the uterus fails to contract effectively postpartum and bleeding is occurring. It is the most common cause of postpartum hemorrhage.
Clinical features of subinvolution are heavy, prolonged bleeding, a boggy uterus, and the irregular descent of the uterus.
Subinvolution can be diagnosed by physical assessment of the height of the uterus.
On the day of delivery, the fundus should be at the umbilicus. Each postpartum day after, the umbilicus should be approximately 1 fingerbreadth lower.
Additional signs could show up, such as:
Retained placental fragments are one of the most common causes of subinvolution of the uterus. Other causes include postpartum infections (chorioamnionitis, endometritis), excessive stretching of the uterus during pregnancy, previous surgeries, and uterine submucosal fibroids.
Assessing clients after birth, preventive measures and nursing care for uterine subinvolution include:
In dilation and curettage, the cervix is dilated to allow access for surgical instruments into the uterus and the uterine lining is scraped off with a curette. The goal is to remove any remaining fetal tissue or polyps to prevent infection. The procedure is usually done under general or local anesthesia and may lead to cramping and bleeding for a few days after.
Six weeks is a good rule of thumb for how long the uterus takes after birth to return to its pre-pregnancy size. Of course, this can vary individually, but generally, by two weeks postpartum the uterus is no longer palpable abdominally.
Fundal massage stimulates the uterus to contract more effectively after birth. This is necessary to prevent excessive bleeding/hemorrhage. The massage also is a way for nurses to assess the tone of the uterus, to monitor for uterine atony and take countermeasures early enough.
How long clients experience cramping after delivery can vary individually, but can typically be expected for a few days to a week with decreasing intensity over time. Cramping may be more noticeable during breastfeeding, since the release of oxytocin promotes uterine contractions.
RELATED TOPIC:
Free Download
Master the topic with a unique study combination of a concise summary paired with video lectures.
Your free account gives you access to:
or