Nursing Knowledge
Geriatric nursing focuses on the care of elderly patients, addressing their complex healthcare needs such as chronic conditions, cognitive impairments, mobility issues, and polypharmacy.
As a nursing specialty, the field opens up job options in long-term care facilities, outpatient clinics, and home healthcare.
Aging is the normal process of cellular, metabolic, and functional changes occurring in the body over time. These changes can predispose older individuals to disease. Genetic factors, lifestyle, and environment contribute to wide variation in the health and functional status of the geriatric population.
It is important to distinguish normal age-related changes from signs of disease.
Educate your clients about health promotion strategies that help mitigate age-related changes and diseases:
In general, take extra care when communicating with geriatric clients to:
The most common reason for hospitalization of elderly clients is heart failure, followed by chronic conditions like respiratory issues or infections.
Multiple comorbidities are common and make the treatment of elderly nursing clients more complex.
Normal age-related changes are natural physiological changes that occur as people age. They do not need medical intervention, but may be alleviated or reduced in impact with lifestyle measures and precautions.
Age-related diseases are medical conditions that become more common with age, but do not naturally and inevitably occur with aging. They need medical intervention.
Elderly patients often fear losing their independence. Being bedridden or needing long-term care are worrying possibilities for many aging clients. Related to this, general worries about deteriorating health and mobility play into fears of getting treatment at hospitals. Concerns about hospital-acquired infections, fear of dying while not at home, or worries related to being isolated and alone while getting treated in a hospital and feeling disoriented by the unfamiliar setting, are also common fears.
Theories as to why elderly patients are prone to developing delirium or acute confusion with UTIs include:
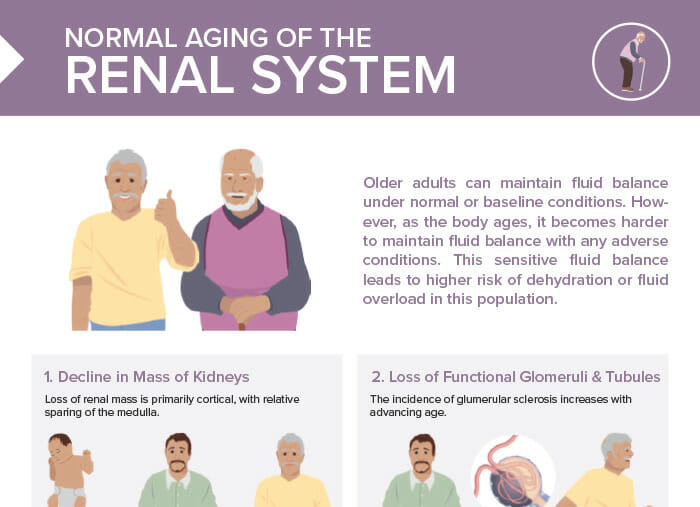
Older adults can maintain fluid balance under normal or baseline conditions. However, as the body ages, it becomes harder to maintain fluid balance with any adverse conditions. This sensitive fluid balance leads to higher risk of dehydration or fluid overload in this population.
Loss of renal mass is primarily cortical, with relative sparing of the medulla.
The incidence of glomerular sclerosis increases with advancing age.
RBF is well maintained at about 600 mL/min.
3 expected changes the kidneys go through during the natural aging process.
RELATED TOPIC:
Free Download
Master the topic with a unique study combination of a concise summary paired with video lectures.
Your free account gives you access to:
or