Nursing Knowledge
HIV stands for Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
AIDS stands for Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome.
HIV is a virus that attacks the body’s immune system. It can spread through certain body fluids and makes the infected person more vulnerable to infections and diseases. HIV infection is a chronic illness requiring lifelong treatment.
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection characterized by the immune system being unable to fight off opportunistic infections, leading to symptoms and illnesses occurring. Without treatment, the average life expectancy for a client with AIDS is 3 years.
In the US, most HIV infections do not progress to AIDS due to adequate treatment with antiretroviral therapy.
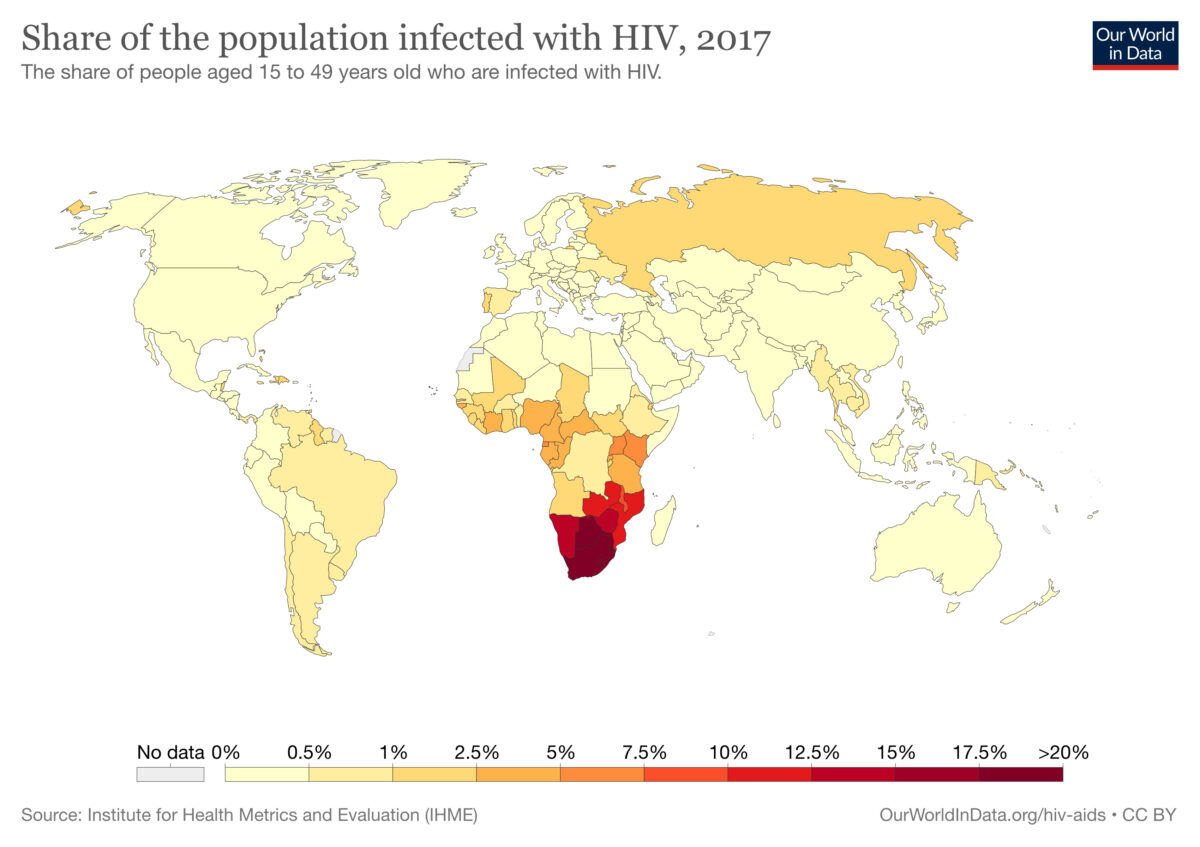
2017 world map of HIV infections (in people aged 15 to 49 years of age):
The colors indicate the percent of population with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in each country. The information regarding the corresponding percent of population (designated color) is below the world map.
Diagnostic criteria for AIDS are:
CD4 T cell count < 200 (normal range: 500–1500)
OR
Presence of one or more opportunistic infections, regardless of CD4 T cell count
HIV and AIDS can present with a variety of symptoms, often dependent on the stage of the disease. Acute HIV infection can present with flu-like symptoms. The latency stage typically is asymptomatic (can last years or decades). With the progression to AIDS, symptoms can include rapid weight loss, recurring fever, prolonged swelling of lymph nodes, fatigue, sores in mouth or genitals, night sweats, diarrhea, pneumonia, blotches on the skin, or neurological problems.
The most common routes of transmission for HIV are through unprotected sexual intercourse and sharing needles during drug use. Low rates of transmission are through blood products, maternal–fetal transmission, and occupational needle sticks.
HIV can not be transmitted through:
Remember: U = U (undetectable = untransmittable)
Clients who achieve, and maintain, undetectable HIV viral loads through treatment are unable to transmit HIV to others.
Measures to prevent HIV transmission and AIDS:
RELATED TOPIC:
Free Download
Master the topic with a unique study combination of a concise summary paired with video lectures.
Your free account gives you access to:
or